This annual report details the operations and achievements of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions for the year 2024-25. It covers the mandates and activities of its various departments, including the Department of Personnel and Training, Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, and Department of Pensions and Pensioners’ Welfare. The report highlights major initiatives, personnel policies, cadre management, training programs, e-HRMS, vigilance, international cooperation, public grievances, administrative reforms, and the progressive use of Hindi in official work, alongside financial management and audit observations.
SOURCE PDF LINK :
Click to access AR2024-25English.pdf
Click to view full document content

ANNUAL REPORT 2024-25
MINISTRY OF PERSONNEL, PUBLIC GRIEVANCES AND PENSIONS GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
.
ANNUAL REPORT
$2024-25$

Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions
Government of India
.
CONTENTS
| List of chapters | Page No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Vision and Mission | iii | |
| Executive Summary | iv | |
| DEPARTMENT OF PERSONNEL AND TRAINING | ||
| 1. | Overview | 1 |
| 2. | Major Initiatives/Achievements/Events during the year | 5 |
| 3. | Personnel Policies | 18 |
| 4. | Reservation in the Central Government Services | 34 |
| 5. | Cadre Management | 39 |
| a) Indian Administrative Service (IAS) | 39 | |
| b) Central Secretariat Service (CSS) | 46 | |
| c) Central Secretariat Stenographers’ Service (CSSS) | 48 | |
| d) Central Secretariat Clerical Service (CSCS) | 48 | |
| e) State Reorganization | 53 | |
| f) Retraining and Redeployment and Departmental council(R&R and DC) | 54 | |
| 6 . | Senior Appointments under Government of India | 57 |
| 7. | Training Policy and Programmes | 62 |
| 8 . | Training Institutions | 82 |
| 9 . | e-HRMS | 96 |
| 10. | Administrative Vigilance Division | 99 |
| 11. | International Cooperation | 107 |
| 12. | Central Bureau of Investigation | 110 |
| 13. | Joint Consultative Machinery | 119 |
| 14. | Administrative Tribunals | 121 |
| 15. | Staff Welfare | 125 |
| 16. | Right to Information | 134 |
| 17. | Grievance Redressal Mechanism \& Citizens’ Charter | 139 |
| 18. | Progressive Use of Hindi in Official Works | 141 |
| 19. | Financial Management | 146 |
| ANNEXURES – Department of Personnel and Training | ||
| Annexure-I – Organizational Chart of Department of Personnel and Training | 151 | |
| Annexure-II – Incumbency Position of Group ‘A’ Officers in D/o Personnel and Training | 152 | |
| Annexure- III- List of Courses offered by ISTM | 155 | |
| Annexure-IV- Name, date of setting, no. of courts and location of various benches of Central Administrative Tribunal | 159 | |
| Annexure-V – Statement showing the position of institution, disposal and pendency of cases in the Central Administrative Tribunal since inception upto December, 2024 | 160 | |
| Annexure – VI – Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace | 161 |
| 20. | DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS AND PUBLIC GRIEVANCES | 163 |
|---|---|---|
| 21. | Administrative Reforms | 174 |
| 22. | Public Grievances | 184 |
| 23. | Organisation and Methods Division | 191 |
| 24. | E-Governance | 195 |
| 25. | International Exchange & Cooperation (IE\&C) | 200 |
| 26. | Documentation and Dissemination Division (D\&D) | 208 |
| 27. | Official language Division | 211 |
| 28. | DEPARTMENT OF PENSIONS AND PENSIONERS’ WELFARE | 214 |
| ANNEXURES – Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances | ||
| Annexure-VII – Organisational Chart of DARPG | 249 | |
| Annexure-VIII – Incumbency position of Under Secretary level officers and above in DARPG | 250 | |
| Annexure-IX – Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace | 252 | |
| Annexure-X – Observance of Constitution Day 2024 | 253 | |
| Annexure-XI- Observance of Vigilance Awareness Week 2024 | 254 | |
| Annexure XII- Celebration of International Women’s Day 2024 | 255 | |
| Annexure XIII – Welfare of SC, ST, OBC and Person with Disability (PWD) | 256 | |
| ANNEXURES – Department of Pensions and Pensioners’ Welfare | ||
| Annexure – XIV – Organisational Chart of DPPW | 257 | |
| Annexure – XV – Incumbency position of Officers in D/o Pension \& Pensioner’s Welfare as on 31/03/2025 | 258 |
Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions
Department of Personnel & Training
Vision
To create an enabling environment for the development and management of Human Resources of the Government for efficient, effective, accountable, responsive and transparent and ethical governance.
Mission
Development and management of government personnel by attracting the best talent, providing excellent career advancement opportunities, encouraging competence and innovation, adopting a dynamic framework of personnel policies and procedures, ensuring capacity building at all levels, inculcating and supporting a culture of transparency, accountability and zero tolerance to corruption in public affairs, and institutionalizing a system of continuous and constructive engagement with stakeholders to make the public services in India more efficient, effective, accountable and responsive.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions is the nodal Ministry responsible for personnel matters, especially in respect of issues concerning recruitment, training, career development, staff welfare, and the post-retirement dispensation. The Ministry also works towards the promotion of responsive, people-oriented, and modern administration.
The Ministry comprises three Departments:
(i) Department of Personnel and Training (DoP&T)
(ii) Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG)
(iii) Department of Pensions and Pensioners’ Welfare (DPPW)
DEPARTMENT OF PERSONNEL AND TRAINING (DOPT)
The Department is headed by the Secretary, Department of Personnel and Training. An organizational chart of the Department is at Annexure-I and incumbency position of Group ‘A’ level officers is at Annexure-II. Various wings of DoP\&T are as under:
Establishment Officer’s (EO) Wing
Services \& Vigilance (S\&V) Wing
Personnel Policy Wing
AT, IR, Welfare \& Administration
Training Wing
Central Secretariat
The Establishment Officer’s Wing deals with the matter relating to senior appointments under the Government of India requiring approval of the ACC.
The Services \& Vigilance Wing handles matters relating to Administration of Rules on all the service matters in respect of All India Services and acts as the nodal agency in the arena of vigilance and anticorruption.
The Personnel Policy Wing is responsible for framing and revising rules and regulations regarding service conditions of the employees and personnel policies of the Central Government employees other than All India Service Officers. This wing handles the work related to Service conditions of Central Government, Reservation Policy of the Government, Joint Consultative Machinery (JCM) and Cadre Review. This wing also looks after the work related to the allocation of State cadre employees consequent upon the reorganization of the States and Redeployment and Retraining of surplus Staff of various Central Government Organisations.
The IR, AT, Welfare \& Admin Wing is responsible for governing and implementation of the RTI Act. It handles the administrative matters relating to the Administrative Tribunals and Central Information Commission. This wing also handles the work related to internal Administration \& Coordination of DoPT and welfare activities for benefit of the employees of the Government.
The Training Wing acts as the nodal agency for capacity building of Government functionaries and is primarily responsible for formulating policies regarding training.
The Central Secretariat Wing deals with the matters related to Cadre Management of the Central Secretariat Service, Central Secretariat Stenographers’ Service and the Central Secretariat Clerical Service.
The Department of Personnel and Training also handles the administrative work relating to the following Institutions: –
- Union Public Service Commission
- Central Vigilance Commission
- Lokpal
- Central Administrative Tribunals
- Central Information Commission
- Central Bureau of Investigation
- Staff Selection Commission
- Public Enterprises Selection Board
- Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration
- Institute of Secretariat Training and Management
- Capacity Building Commission
- National Recruitment Agency
- Karmayogi Bharat – Special Purpose Vehicle
DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS & PUBLIC GRIEVANCES
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is the nodal agency of the Government of India for administrative reforms as well as redressal of public grievances relating to the States in general and those pertaining to the Central Government agencies in particular. The Department endeavours to document and disseminate successful governance practices by way of audio-visual media and publications. The Department also undertakes activities in the field of international exchange and cooperation to promote public service reforms. There are 7 Divisions in the Department namely Administrative Reforms, Organization \& Methods, e-Governance, Documentation \& Dissemination, International Cooperation, Administration \& Coordination and Public Grievances.
DEPARTMENT OF PENSIONS AND PENSIONERS’ WELFARE
The Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare was set up in 1985 as part of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions to formulate policy and coordination of matters relating to retirement benefits of Central Government employees (except Defence, Railway and Post \& Telecommunication).
.
CHAPTER-1
OVERVIEW
1.0 The Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions acts as the formulator of policies pertaining to recruitment, regulation of service conditions, and deputation of personnel besides advising all organizations of the Central Government on issues pertaining to personnel management.
Major Initiatives/Achievements/Events during the year (Chapter 2)
1.1 Major Initiatives/Achievements during the period of April 2024 – March 2025 have been brought out in Chapter 2.
Personnel Policies (Chapter 3)
1.2 The Department is responsible for framing rules and regulations governing service conditions including recruitment rules, promotions and seniority, Flexible Complementing Scheme, Leave Travel Concession, Deputation and Leave of employees. Personnel are recruited for the Central Government by the Union Public Service Commission through competitive examinations conducted by them for appointments to higher civil services and through the Staff Selection Commission for non-gazetted staff in Group ‘B’ & ‘C’ categories.
Reservation in the Central Government Services (Chapter 4)
1.3 In order to achieve the objective of upliftment and welfare of the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes and Persons with Disabilities and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS); the Department frames policies to provide reservation to these groups in various Central Government services and for monitoring its implementation.
Cadre Management (Chapter 5)
1.4 This Department is responsible for the management of the cadres of All India Services (AIS) (IAS, IPS, and IFoS) and all three Secretariat Services namely Central Secretariat Services (CSS), Central Secretariat Stenographers’ Services (CSSS) and Central Secretariat Clerical Services (CSCS). In addition, this Department frames and revises Rules and Regulations regarding conditions of the All India Services, such as Indian Police Service (IPS) and Indian Forest Service (IFoS), in consultation with the Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change respectively. This Department is also responsible for the cadre review of 67 existing Central Group ‘A’ Services/ Cadres periodically.
Senior Appointments under Government of India (Chapter 6)
1.5 The Department deals with appointments at senior level and personnel policies of the Government of India. All proposals for senior appointments under the Government of India, which require the approval of the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC), are processed by the Department. These include board-level appointments to Central Public Sector Undertakings and appointments under the Central Staffing Scheme for posts of Joint Secretary, Director, and Deputy Secretary in Ministries /Departments. In addition, all appointments by promotion, which require the approval of the ACC, are also processed by the Department.
Training Policy and Programmes (Chapter 7)
1.6.1 The Department is the nodal Department to impart training to the government functionaries. The Training Wing of the Department formulates policies and implements its training programmes by identifying areas of training, designing training programmes, development of trainers and training
capabilities and administering policies in training. Major training activities undertaken during the year are (i) In-service training of AIS/CSS/CSSS officers (ii) Mid-Career Training of IAS Officers (iii) Post Graduate Programmes in Public Policy/Sustainable Development/Management (iv) State Category Training Programme (SCTP); (v) Trainer Development Programme (TDP); (vi) Comprehensive Online Modified Modules for Induction Training (COMMIT); (vii) Augmentation of the Capacity of Training Institutions (ACTI); (viii)Integrated Government Online Training Programme (i-GOT); and (ix) National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB)- Mission Karmayogi.
1.6.2 The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) – Mission Karmayogi is being implemented with the goal of systematically developing the competencies of government officials, to enable them to best discharge their assigned roles. It aims to affect a signal shift towards competency driven training and Human Resource (HR) management of public officials, by transitioning from a ‘rule-based’ to a ‘role-based’ system of capacity building.
1.6.3 Through the adoption of modern technological tools such as a digital portal – the integrated Government online Training (iGOT) platform – https://igotkarmayogi.gov.in/ and with effective harnessing artificial Intelligence, machine learning and data analytics, Mission Karmayogi endeavors to break silos in capacity development and democratize knowledge on an equitable basis across civil services, by providing opportunity for need based access to world class learning, to all government officials.
Training Institutions (Chapter 8)
1.7 Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussourie, Uttarakhand and Institute of Secretariat Training and Management (ISTM), New Delhi are two premier training institutions, attached to this Department. These institutes cater to the needs of human resource development by imparting training to all officers of Central Government and AIS at regular intervals for their career progression. The Department also supports the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA) which is an autonomous organisation, in undertaking advance training programmes for administrators as well as researchers on issues relating to public administration.
e-HRMS (Chapter 9)
1.8 The NPCSCB facilitates data-driven decisions for training and personnel management through the electronic Human Resources Management System (e-HRMS), which has now been revamped as eHRMS2.0 and also integrated with the i-GOT portal. This helps the Government to digitally manage the service matters of officials leading to reduction in transaction time and cost, availability of digital records, dashboards for MIS, real time monitoring of manpower deployment as well as serving as a productivity enhancement tool amongst others.
Administrative Vigilance Division (Chapter 10)
1.9 The Department is the nodal agency responsible for the formulation and implementation of vigilance and anti-corruption policies of the Government. Administrative Vigilance Wing in the Department oversees government programme for maintenance of discipline and eradication of corruption from public service. The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) advises the Central Government on all vigilance matters. The jurisdiction of the Commission extends to all the organisations to which the executive powers of the Union of India extend.
International Cooperation (Chapter 11)
1.10 The Department of Personnel and Training is the nodal Department for formation of policies for anti-corruption in Government of India. To deal with international cooperation on these aspects an International Cooperation Cell was created in this Department. The primary tasks of this Cell emanate from the follow up to the ratification of the United Nations Convention Against Corruption (UNCAC) and
the other consequential international collaborative efforts, on global platforms. This Cell acts in conjunction with specialized agencies like the Central Bureau of Investigation, the Enforcement Directorate and the other line Ministries entrusted with the specific ancillary tasks within their respective administrative domain, viz. corporate governance, extradition matters, prevention of money laundering, mutual legal assistance treaties etc.
Central Bureau of Investigation (Chapter 12)
1.11 Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was set up by the Government of India by a Resolution dated April 1, 1963, to not only investigate cases of bribery and corruption but also the cases of violation of central fiscal laws, major frauds relating to Government of India Departments, Public Joint Stock Companies, passport frauds and serious crimes committed by organized gangs and professional criminals. CBI was further strengthened by the addition of Economic Offences Wing by the Government of India by Resolution dated February 2, 1964.
Joint Consultative Machinery (Chapter 13)
1.12 The Government provides for a Joint Consultative Machinery for joint consultation at three levels between the Central Government and its employees for promoting harmonious relations and securing the optimum level of co-operation between the Central Government and its employees in matters of common concern. The objective is to increase the efficiency of public services along with the well-being of the employees. The three tiers are:
a) National Council – at the apex level, functioning under the Department of Personnel and Training.
b) Department Councils – functioning at the level of the Ministries / Departments.
c) Office Councils – functioning at offices/organisations under various Ministries / Departments.
The Scheme has proved to be an effective forum for amicable settlement of grievances of the Central Government employees relating to their service matters etc.
Administrative Tribunal (Chapter 14)
1.13 In order to provide speedy and inexpensive justice delivery system to the employees who feel aggrieved by Government decisions, the Government set up the Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) in 1985, which deals with all cases relating to service matters. The CAT has 19 regular benches, 17 of which operate at the Principal seats of High Courts and the remaining two are at Jaipur and Lucknow.
Staff Welfare (Chapter 15)
1.14 The Central Government being the largest single employer in the country discharges its responsibility for looking after the welfare of employees through various welfare measures. The Department also extends support to various staff welfare measures. The DoPT is the nodal Department for registered societies set up for the welfare of the Government employees and their families. In addition, the Department lays down policies for Departmental Canteens and supports the Resident Welfare Associations.
Right to Information (Chapter 16)
1.15 The Department has brought out a comprehensive law to ensure the right to information of the citizens of India in almost entire matters of governance at all levels from the Central Government to the local self-government. The Law (RTI Act, 2005) has provided a mechanism where the Central Information Commission, being the apex body at the Centre, facilitates its citizenry in accessing information in a time-bound, hassle-free and affordable manner.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism & Citizens’ Charter (Chapter 17)
1.16 The Department has identified some of the core services being offered by its various divisions and their standards for the purpose in its first Citizen Charter. This has been undertaken by a Task Force in consultation with the Stakeholders. While identifying the services the focus has been on measurable and verifiable services and their standards. The charter contains a Grievance Redress Mechanism related to the services mentioned in the Citizens’/Clients’ Charter. The Charter also provides links for other grievances which are not related to the Citizens’/Clients’ Charter. Timelines have been prescribed for final disposal of the complaint arising out of the Citizens’/Client’s Charter. Information regarding steps taken by this Department for Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplac is at Annexure VI.
Progressive Use of Hindi in Official Works (Chapter 18)
1.17 The Department is fully committed to promoting the use of Hindi as the official language, in official matters and motivates compliance of the provisions of the Official Language Act, 1963, and the rules framed thereunder. The Department also ensures that the spirit of various orders and guidelines issued by the Department of Official Language is appropriately enforced for implementation of the official language policy of the Union. The Department has an Official Language Division which monitors the implementation of the Official Language policy in the Department.
Financial management (Chapter 19)
1.18 In order to promote the various programmes administered by Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, an allocation of Rs. 272.35 crore was made in the Central Sector Scheme Outlay for the year 2023-24 against the total allocation of Rs. 2493.70 crore at the Revised Estimate 2023-24 stage. The corresponding figures for RE 2024-25 are Rs. 344.65 crore as Central Sector Scheme Outlay against a total allocation of Rs. 2576.15 crore (RE 2024-25). The requirements and priorities of its attached and subordinate offices were kept in view while making budgetary allocation to them by this Department. Four C\&AG Para are pending.
Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (Chapter 20-27)
1.19 The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is the nodal agency of the Government of India for administrative reforms as well as redressal of public grievances relating to the States in general and those pertaining to the Central Government agencies in particular. The Department endeavours to document and disseminate successful governance practices by way of audio-visual media and publications. The Department also undertakes activities in the field of international exchange and cooperation to promote public service reforms.
Department of Pensions \& Pensioner’s Welfare (Chapter 28)
1.20 The Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare was set up in 1985 as part of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions to formulate policy and coordination of matters relating to retirement benefits of Central Government employees (except Defence, Railway and Post \& Telecommunication).
CHAPTER 2
MAJOR INITIATIVES/ ACHIEVEMENTS/ EVENTS DURING THE YEAR
2.1 Rozgar Mela
2.1.1 Hon’ble Prime Minister launched the National Rozgar Mela on $22^{\text {nd }}$ October 2022. Rozgar Mela is a step towards fulfillment of the commitment of the Hon’ble Prime Minister for employment generation in the country. The Rozgar Mela is expected to act as catalyst in further employment generation and provide meaningful opportunities to the youth for their empowerment and participation in National Development directly. The recruitments are largely in posts of Group-B and Group-C level. The new appointees were inducted into various Central Government Ministries/Departments/Public Sector undertakings (PSUs)/ Autonomous Bodies including Health and Educational institutes, Public Sector Banks and Administration of Union Territories (UTs) etc. Various Ministries and Departments organized Rozgar Melas at 45-50 locations across the country in which several lakh newly appointed candidates received their letters of appointment. By the end of December 2024, 14 Rozgar Mela events have been organized at National level.

Hon’ble Prime Minister launching $14^{\text {th }}$ Rozgar Mela across the country on $23^{\text {rd }}$ December, 2024

देशभर में 45 स्थायी पर सरकारी नौकरियों में चयनित 71000 । अधिक अभ्यर्थियों को नियुक्ति पत्रों का वितरण
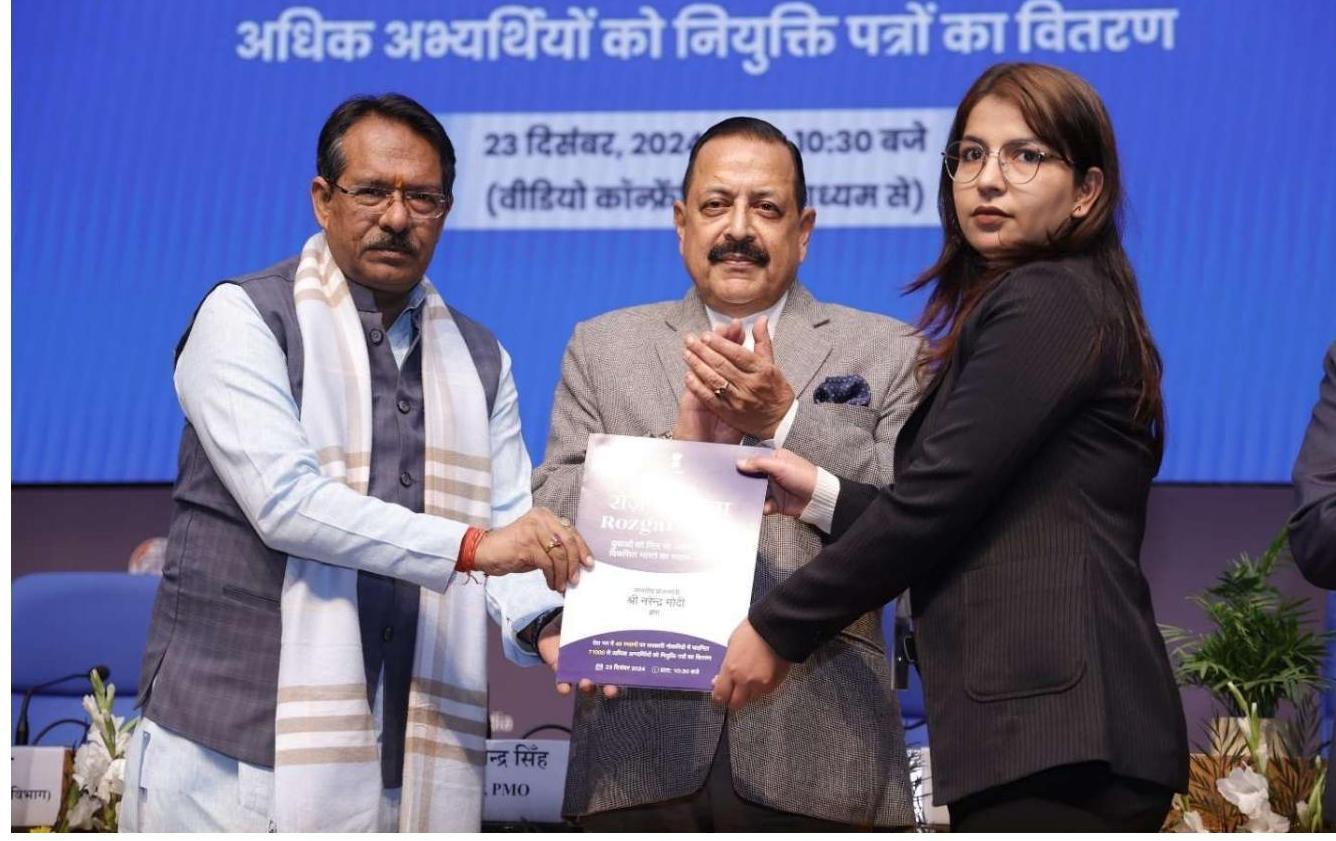

Distribution of appointment letters by Hon’ble Minister of State (P) to newly recruited officers during the $14^{\text {th }}$ tranche of Rozgar Mela held on 23th December, 2024
2.2 National Learning Week 2024
2.2.1 National Learning Week (NLW)- Karmayogi Saptah was organized from 19/10/2024 to 27/10/2024 by this Department in collaboration with Capacity Building Commission and Karmayogi Bharat. The NLW was inaugurated by Hon’ble Prime Minister on $19^{\text {th }}$ October, 2024, marking a new chapter in civil service capacity building under the Mission Karmayogi initiative. This groundbreaking effort aimed at fostering continuous skill enhancement and lifelong learning among civil servants, ensuring their competencies align with the country’s evolving goals.
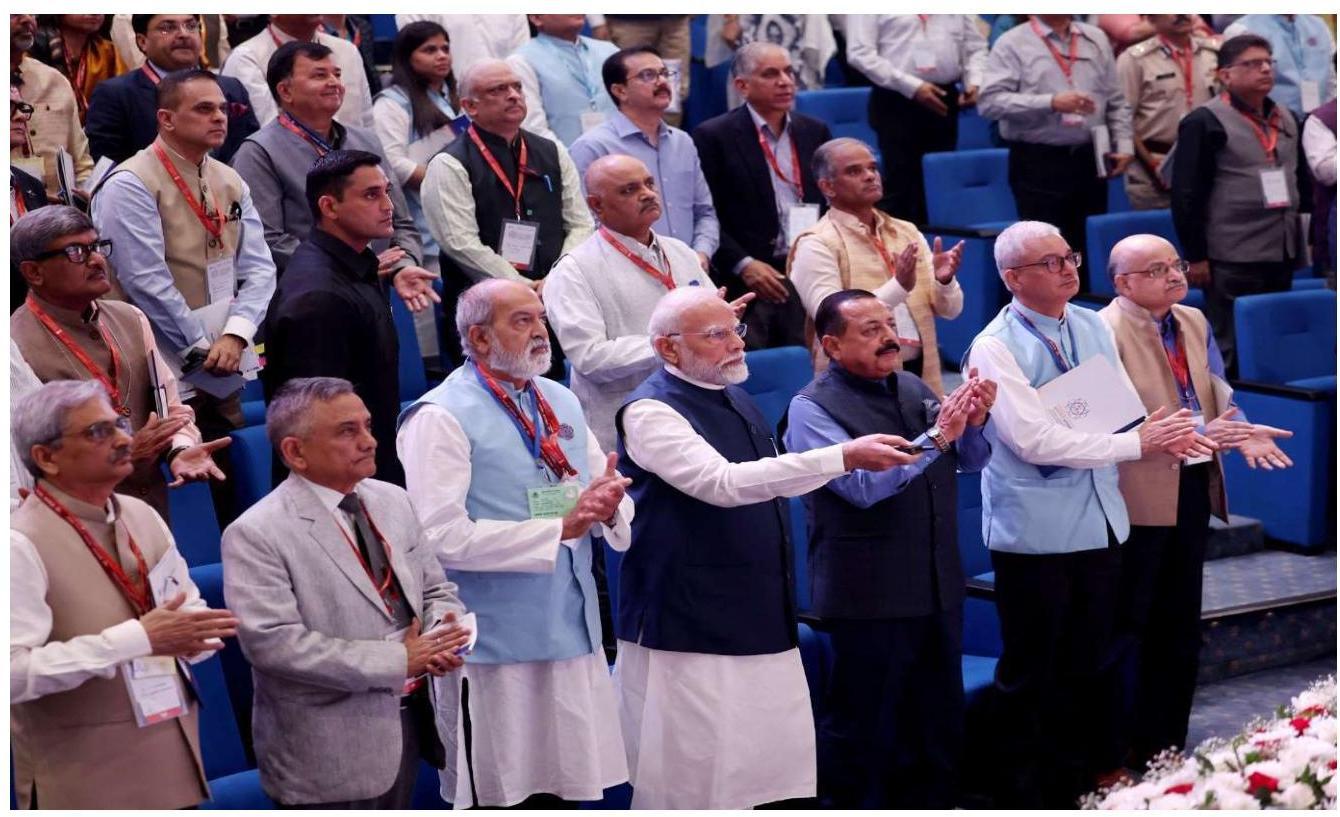

Hon’ble Prime Minister launching National Learning Week 2024
2.2.2 The iGOT Karmayogi Platform crossed the major milestone of 75 lakh cumulative on-boarded users, during the financial year 2024-25. The Karmayogi Bharat – a Special Purpose Vehicle set up as a Not for Profit $100 %$ Government owned Corporation to own, manage and maintain the digital assets of Mission Karmayogi on behalf of the Government, started functioning from August 2022 and in a short span of 28 months, the intense efforts for outreach and onboarding have yielded significant results.
The engagement of users on iGoT is also showing encouraging progress with the platform crossing more 2.26 Cr course enrolments and 2.33 Cr course completions during Financial Year 2024-25.
2.3 Women Sports Meet organized by DoP&T on 15.01.2025
2.3.1 The Women’s Sports Meet – 2025 was organized by Central Civil Services Cultural and Sports Board at Vinay Marg Sports Complex, New Delhi on $15^{\text {th }}$ January, 2025. The purpose of organizing this Women’s Sports Meet was to create awareness and to enhance Women’s participation in various cultural and sports activities organized by CCSCSB and also to inform women about the benefits, facilities and incentives provided to sportspersons by the Government.
2.3.2 The event witnessed enthusiastic participation of around 600 sportswomen from different Ministries. Ms. Rachna Shah, Secretary (Personnel), felicitated the achievers with awards and encouraged the participation of women employees in various sports activities.

2.4 Blood Donation Camp Organized by DoP&T on 01.10.2024
2.4.1 Department of Personnel \& Training organized a Blood Donation Camp on the occasion of National Voluntary Blood Donation Day on $1^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024 at North Block, New Delhi under the campaign slogan “Celebrating 20 years of giving: THANK YOU, BLOOD DONORS”.
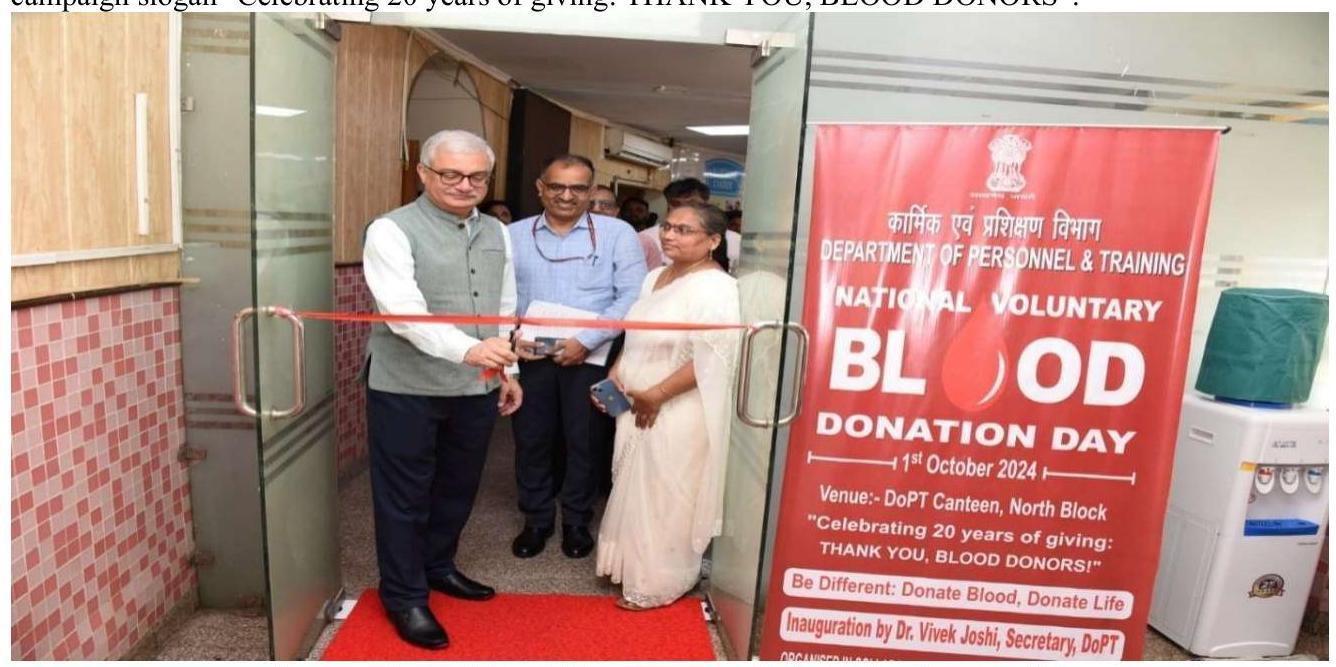

Inauguration of Blood Donation camp in DoPT by Secretary(P)

2.5 Hon’ble Prime Minister interacting with Assistant Secretaries of 2022 batch
2.5.1 Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi interacted with 181 Officer Trainees of IAS 2022 Batch who have been attached as Assistant Secretaries in various Ministries and Departments at Sushma Swaraj Bhawan in New Delhi on 11.07.2024.
2.5.2 During the interaction, various officers shared their experience of training undergone by them speaking about the Assistant Secretary programme. Hon’ble Prime Minister said that the intent behind it was to provide opportunity of experiential learning to the young officers from the top to the bottom of the administrative pyramid.
2.5.3 Shri Jitendra Singh, Minister of State (Personnel), Shri P. K. Mishra, Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister, Shri Rajiv Gauba, Cabinet Secretary and Shri A.K. Bhalla, Secretary (Home and DoPT) and other senior officers were also present during the interaction.
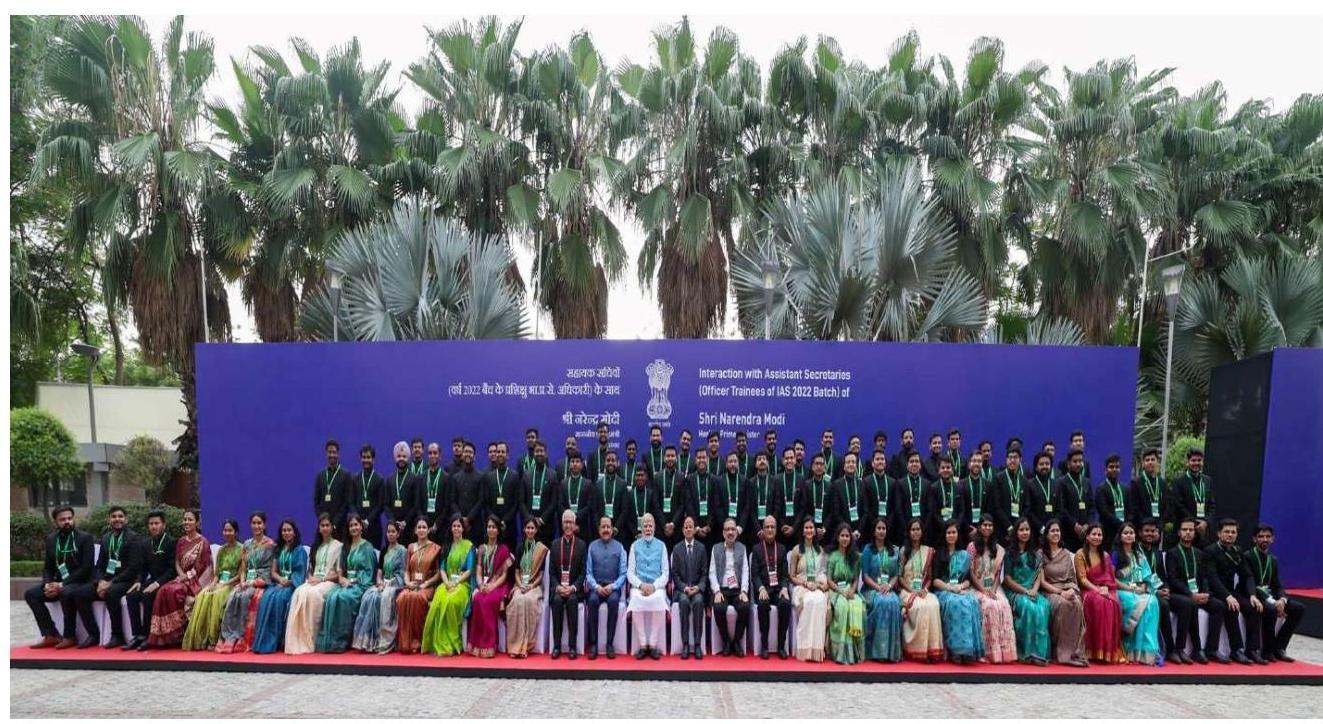

Hon’ble Prime Minister with Assistant Secretaries of 2022 batch on 11.07.2024
2.6 Swacchata Hi Seva Event organized at Grih Kalyan Kendra
2.6.1 Department of Personnel & Training organized “Swachhata Hi Seva” event on $2^{\text {nd }}$ October, 2024 at Grih Kalyan Kendra, New Delhi. Seniors officers and other officers of the department took Swachhata Pledge under the chairmanship of Secretary (P). Nukkad Natak on Swachhata theme was also organised as part of Swachhata Hi Seva event.


2.7 Special Campaign 4.0
2.7.1 Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) along with its Attached/Sub-ordinate organizations actively participated in all the activities included in the Special Campaign and fully achieved its targets of Special Campaign 4.0, which began on $2^{\text {nd }}$ October 2024 and concluded on $31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024. This campaign focused on overall cleanliness (Swachhata) of workplaces, space management, promoting sustainable practices and optimum disposal of pending matters.
Highlights \& achievements of the Department
i) Effective Disposal of Pending items: During the campaign, DOPT along with its attached \& Subordinate offices and autonomous bodies have disposed of 8 pending References from MPs, 5 Inter Ministerial References, 1902 Public Grievances (PGs), 146 PG Appeals and 14 State Government References.
ii) File Management: DOPT with its Attached, Subordinate and Autonomous Organizations has successfully achieved its target in so far it pertains to review of physical and e-office files. 48,469 Physical files, 5,217 e-office files and 75,000 documents/ dossiers have been reviewed by DOPT and its associated organizations.
iii) Revenue Generation: Revenue of Rs. 1,29,847/- has been generated.
iv) Cleanliness: 325 cleanliness campaigns have been conducted at various office sites.
v) Best Practices were adopted during this Campaign. Some of the best practices adopted e.g. Digitization \& Preservation of Records as part of Review exercise, Recording / Reviewing of files carried out in mission mode in all organizations so as to promote digital governance and freeing up of physical space. In a significant move towards enhancing civil service capabilities, the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ – National Learning Week was inaugurated by Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on $19^{\text {th }}$ October 2024 at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre in New Delhi. The initiative aims to empower government employees through continuous learning, aligning with the vision of a developed India by 2047. To protect environment and natural resources, tree plantation drive led by Secretary (P) was launched under “Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam” campaign. Nukkad Natak on Swacchata theme was organised as part of Swacchata Day on $2^{\text {nd }}$ October, 2024 in New Delhi. A workshop on Cyber Security was organized in DoPT, North Block to spread Cyber Swachhta Awareness for the employees. A Workshop for CISOs on Cyber Awareness/Security was organized by the Department. Two special informative workshops were conducted on RTI Act, 2005.

Review of Record Room, DoPT at North Block by the Secretary(P)

Before and After images of cleanliness drive at Old JNU office of DoPT
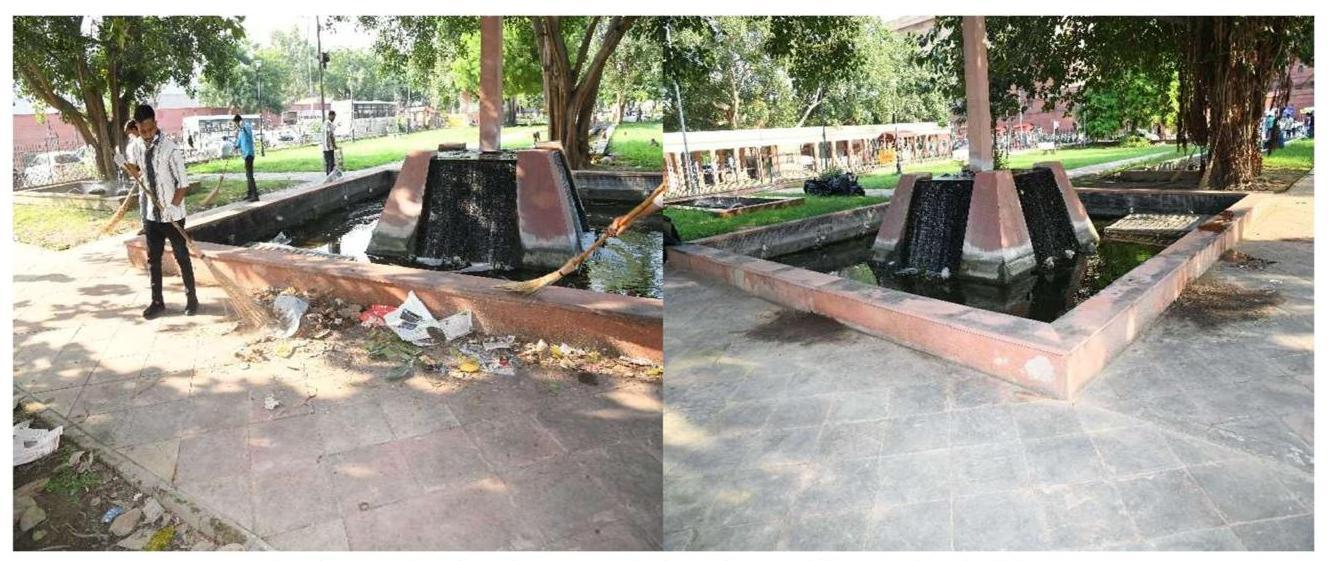

Before and After images of cleanliness drive at North Block
2.8 Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam
2.8.1 To protect environment and natural resources, tree plantation drive named Ek-Ped-Maa-Ke-Naam led by the Secretary, DoPT was launched on $13^{\text {th }}$ September 2024 alongwith the officers of DoPT in the Central Ridge Area of New Delhi.

2.9 Stakeholders Consultative Meeting with Training Institutes on 23.10.2024
2.9.1 The Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) organized a Stakeholder Consultative Meeting on $23^{\text {rd }}$ October, 2024, at CSOI, K.G. Marg, New Delhi, as a preparatory step for finalizing the In-Service Training (IST) and Long-Term Domestic Training (LTDP) programs for the 2025-26 calendar year. The meeting brought together representatives from top-ranked Indian institutes to discuss proposals and align the training themes with the objectives of Mission Karmayogi. It aimed to ensure effective collaboration with premier training institutions and to enhance the relevance and quality of capacity-building initiatives for civil servants.

Stakeholders Consultative Summit under the Chairpersonship of Joint Secretary (Training)
2.10 Cyber Awareness Programme Organized by DoP&T on 11.12.2024

Department of Personnel \& Training organized a ‘Cyber Security Awareness Workshop’ on 11th December, 2024 in North Block, New Delhi for the all the officers / officials of Department. The aim of the programmes was to achieve a clean and sanitized cyber space for ensuring a safe, secure, and trustworthy online environment.
2.11 Celebration of Good Governance Day
Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions celebrated the Good Governance Day on $25^{\text {th }}$ December 2024. During this event, Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble Minister of State (Personnel), launched various initiatives, including New Dashboard for the i-GOT Karmayogi Platform, Milestones of making available the $1600^{\text {th }}$ course on the iGOT Karmayogi Platform, Viksit Panchayat Initiative.
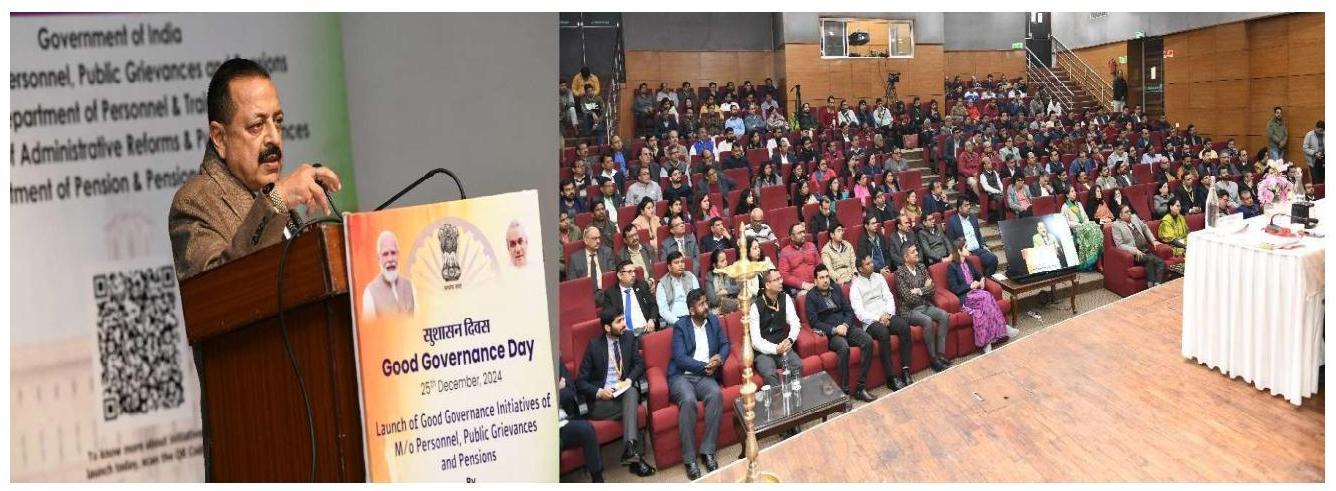

Address by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MoS (PP) on the occasion of Good Governance Day on 25.12.2024
2.12 Annual Conference of Principal Secretaries of States/UTs
The Annual Conference of Hon’ble MoS (PP)/Secretary (P) with Principal Secretaries (Personnel/GAD) of the State Governments/UTs was held on 25.11.2024 covering aspects such as Deputation Management of IAS, cadre management, recruitment matters, vigilance matters, review under Rule 16(3) of AIS (DCRB) Rules, 1958, training of AIS, and other miscellaneous DoPT matters.

Address by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MoS(PP) during the Annual Conference with Principal Secretaries (Personnel/GAD) of State Governments / UTs on 25.11.2024
2.13 Common Foundation Training Programme
A total of 653 officers (including 11 officers from the Royal Bhutan Civil Servics) participated in the $99^{\text {th }}$ Common Foundation Course conducted by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussoories, from 26 August to 29 November 2024.
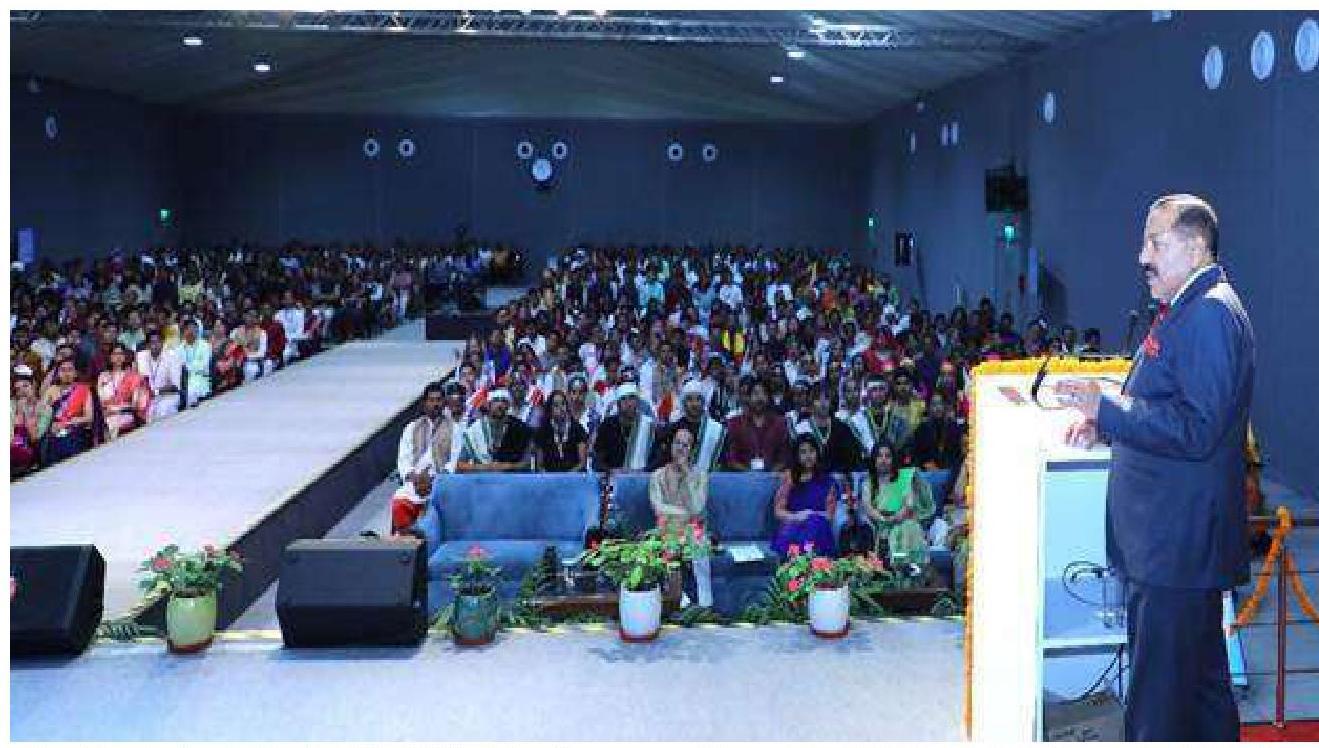

Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MoS(PP) addressing young officers at the 99th Foundation Course at Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration, Mussoorie
2.14 Uniform Functional Classification and Physical Requirement (FC&PR) criteria for the participating Services of the Civil Services Examination (CSE) from CSE-2024 onwards
With a view to maintaining uniformity in the Functional Classification and Physical Requirement (FC\&PR) criteria for all the Non-Technical participating Services of CSE as well as Indian Railways Management Service (IRMS), a decision was taken with the approval of the Competent Authority and with the concurrence of the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), that the Department of Personnel \& Training, being the Nodal Department for CSE, shall be the ‘appropriate Government’ in the context of the participating Services of CSE. As per the provisions of Section 33 \& 34 of the RPwD Act, 2016; and shall, accordingly, be competent to prescribe the FC\&PR criteria for all the Non-Technical participating Services of CSE as well as IRMS, in consultation with and involvement of the CCAs and the DEPwD. In pursuance of the above decision, an Expert Committee was constituted by this Department for rationalisation of the FC\&PR criteria for the participating Services of CSE. On the basis of the recommendations of the Expert Committee and views expressed by the CCAs of the participating Services of CSE, it was decided to implement uniform set of FC\&PR criteria for all for all the non-Technical participating Services and IRMS from the CSE-2024 onwards.
[Reference: DOPT’s OM No. 13018/04/2023-AIS-I dated $17^{\text {th }}$ November, 2023]
2.15 Central Civil Services (Leave Travel Concession) Rules, 1988 – Relaxation to travel by air to visit North East Region, Jammu \& Kashmir, Ladakh and Andaman \& Nicobar
In order to boost tourism, the Government decided to extend the Special Dispensation Concession allowing Government servants to travel by air to North East Region (NER), Union Territory of Jammu
and Kashmir (J&K), Union Territory of Ladakh and Union Territory of Andaman \& Nicobar Islands (A\&N) for a further period of two years, w.e.f. 26 September, 2024 till 25th September, 2026. This concession may be availed in lieu of the Home Town LTC or against Anywhere in India LTC.
[Reference: DoPT’s OM No. 31011/15/2022-Estt-A-IV dated 17.09.2024]
2.16 Admissibility to travel by Tejas Express, Vande Bharat Express \& Humsafar Express trains under Leave Travel Concession (LTC)
Apart from existing Rajdhani, Shatabdi and Duronto trains, travel by premium trains like Tejas Express, Vande Bharat Express \& Humsafar Express under Leave Travel Concession has also been allowed for Central Government employees.
[Reference: DoPT’s OM No. 31011/3/2022-PP.-A-IV dated 14.01.2025]
2.17 Grant of Maternty Leave, Child Care Leave and Paternity Leave on child birth through Surrogacy
Instructions were issued for extension of Child Care Leave, Maternity and Paternity for child birth through surrogacy to a government servant with less than two surviving children vide Notification no. A-24011/21/2023-ESTT-Leave dated 18.06.2024. Now, surrogate mother as well as commissioning mother can avail a maternity leave of 180 days, the commissioning mother can avail a child care leave of 730 days and the commissioning father can avail a paternity leave of 15 days.
2.18 Further liberalization of Child Care Leave
Instructions were issued to grant additional three spells beyond the existing three spells of Child Care Leave in a calendar year to a Government servant, in case the child of a government servant is admitted in a hospital as inpatient vide DOPT’s OM No.A-24011/5/2024-ESTT.-Leave dated 29.07.2024.
2.19 Instructions were issued for availing the benefit of reimbursement of Children Education Allowance and Hostel Subsidy for three classes before class one to $12^{\text {th }}$ standard (irrespective of nomenclature of class) in accordance with New Education Policy 2020 vide DOPT’s OM No. A-27012/01/2023-Pers.Policy(Allowance) dated 14.03.2024.
2.20 Increasing Children Education Allowance and Special Allowance for child care to women with disabilities
Instructions were issued for increasing Children Education Allowance and Special Allowance for child care to women with disabilities by $25 %$ consequent upon the Dearness Allowance goes up by $50 \%$ vide DOPT’s OM No. A-27012/01/2023-Pers.Policy(Allowance) dated 25.04.2024.
2.21 Inclusion of Sports Events – Khelo India University Games, Khelo India Youth Games, Khelo India Winter Games and Khelo India Para Games in the Events of National Importance for recruitment/promotions under Sports Quota
Consolidated Instructions on Recruitment/Promotions for Sportspersons in Government of India have been updated by including the Sports Events – Khelo India University Games, Khelo India Youth Games, Khelo India Winter Games and Khelo India Para Games in the list of Events of National Importance. Medal Winners in the designated sports/games under the above events would now also be eligible to the considered for recruitment/promotions under Sports Quota.
CHAPTER 3
PERSONNEL POLICIES
MANDATE
- Matters relating to framing and amendment of recruitment rules/service rules for Group “A” and “B” posts
- Framing of policy relating to the procedure for Departmental Promotion Committee(s)
- Policy on seniority
- General policy matters relating to: –
(a) Flexible complementing scheme,
(b) Modified Assured Career Progression Scheme,
(c) Lateral entry in Central Government,
(d) Leave travel concession,
(e) Deputation,
(f) Leave,
(g) Pay & allowances,
(h) Holiday policy,
(i) Age relaxation and
(j) Other matters concerning service conditions. - Administration of UPSC and SSC including exams except for the Civil Service Examination
- Policy matters of PESB
- Policy on Verification of Character and Antecedents of candidates selected for appointment to civil posts under the Government of India
- Disagreement cases with UPSC from various Ministries except on appointment cases
- UPSC (Exemption from Consultation) Regulations
- Policy on APAR.
- Commercial employment after retirement
- Policy on
(a) Retirement, extension, re-employment,
(b) Posting and transfers, Conduct and CCA Rules,
(c) Sealed Cover procedure,
(d) Status of Women in Central Government,
(e) Temporary Service Rules, etc.
(f) Lien, Probation, Confirmation,
(g) Daily Wage Casual Labourers
Pers Policy wing of the Department deals with all the matters relating to personnel policies of Central Government servants other than All India Service Officers, Joint Consultative Machinery for Central Government Employees and matters relating to the Union Public Service Commission, Staff Selection Commission and PESB.
The mandate of the Pers. Policy wing includes formulation of/amendment in policy; interpretation of Policy and subsequent issuance of executive instructions; tendering advice to the Ministries/Departments on various aspects of service matters in respect of Government servants viz. Conduct and Discipline of Government servants, Leave Travel Concession, Age of retirement, Superannuation, Voluntary Retirement, Premature Retirement, Extension in Service/Reemployment, Transfer Policy, Probation/Confirmation, Technical Resignation, Temporary Service Rules,
Regularization of Casual Labours etc. Pers Policy Wing also provides guidance to Ministries/Departments in the light of extant instructions onhandling of Court cases on the above aspects and issuance of instructions in compliance of the directions of the Courts, if required.
Pers. Policy wing in the Department has following divisions:
| Personnel Policy Wing | |
|---|---|
| a) | Cadre Review Division |
| b) | Pers. Policy Division |
| c) | Pers. Policy (Pay) Division |
| d) | Pers. Policy (Leave & Allowance) Division |
| e) | Pers. Policy (Reservation) Division |
| f) | SR Division |
| g) | RR\&DC Division |
| h) | Lateral Entry |
Pers. Policy A-III Section
3.1 Instructions regarding implementation of Aadhar Enabled Biometric Attendance System (AEBAS) for attendance of all Government employees, by various Ministries /Departments/ Organizations.
Based on the review of Implementation of AEBAS, Ministries /Departments/Organizations (MDOs) were directed to regularly monitor the attendance reports of their employees and also to ensure mandatory registration of all employees on BAS portal, reconciliation of data amongst all the relevant portals such as AEBAS, eHRMS/PFMS. In respect of Divyaang employees, it was requested to make appropriate arrangements for providing convenient and easily accessible machines for capturing biometrics through suitable alternative modes.
MDOs were also informed about rolling out of face-based authentication by UIDAI using mobile phones and given directions to configure personal mobile policy in attendance portal for the employees of their Organizations and get the geo-coordinates fed into the entry locations of the office.
[Reference DoPT OM No. 11013/13/2023-PP. A-III dated 15.06.2024]
3.2 Implementation of Actions under stage-IV (‘Severe+’ Air Quality) of revised Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) in Delhi-NCR steps to be taken-reg.
In view of the severe+ air pollution levels in Delhi, the various Ministries/Departments/Organizations (MDOs) of Central Government were advised to adopt the staggered timing measure in respect of Offices located in Delhi/NCR, as part of the Actions envisaged by the Commission for Air Quality Management under GRAP, till GRAP-IV is in force.
The officers/ staff using personal vehicles were encouraged to pool vehicles and to use public transport to minimize the vehicular pollution. MDOs were also requested to adopt these measures as per their functional requirements ensuring that it should not have an adverse impact on efficiency and productivity in their organisations.
[Reference DoPT OM No. 43020/21/2024-PP. A-III dated 21.11.2024]
3.3 Instructions on Timely submission of Annual Immovable Property Return by the members of Central Civil Services/Posts.
All Ministries/Departments/Organizations of GoI were instructed to issue necessary directions to the concerned officers to ensure that all the officers/officials working in their
Ministries/Departments/Organizations submit their IPR in the prescribed mode of submission within the stipulated time e.g. latest by 31.01 .2025 in respect of the year 2024.
[Reference DoPT OM No. 11013/17/2023-PP. A-III dated 30.12.2024]
Pers. Policy A-IV Section
3.4 Central Civil Services (Leave Travel Concession) Rules, 1988 – Relaxation to travel by air to visit North East Region, Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh and Andaman \& Nicobar extension beyond 25.09 .2024 – regarding.
In order to boost tourism, the Government decided to extend the Special Dispensation Concession allowing Government servants to travel by air to North East Region (NER), Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir (J\&K), Union Territory of Ladakh and Union Territory of Andaman \& Nicobar Islands (A\&N) for a further period of two years, w.e.f. 26 September, 2024 till 25th September, 2026. This concession may be availed in lieu of the Home Town LTC or against Anywhere in India LTC.
(Reference DoPT’s OM No. 31011/15/2022-Estt-A-IV dated 17.09.2024)
3.5 Admissibility to travel by Tejas Express, Vande Bharat Express \&Humsafar Express trains under Leave Travel Concession (LTC)-reg.
Apart from existing Rajdhani, Shatabdi and Duronto trains, travel by premium trains like Tejas Express, Vande Bharat Express \&Humsafar Express under Leave Travel Concession has also been allowed for Central Government employees.
[Reference DoPT’s OM No. 31011/3/2022-PP.-A-IV dated 14.01.2025]
3.6 Periodic Review of Central Government Employees for strengthening of administration under FR 56(j)/(l) and Rule 48 of CCS (Pension) Rules, 1972
In order to bring efficiency in Government machinery, all the Ministries/Departments/Organisations were sensitized to undertake the exercise of review of performance of the Government servants and for the employees of PSUs/Banks/autonomous institutions/statutory organisations under their administrative control on regular basis.
Pers Policy (Leave) Section
3.7 Instructions were issued for extension of Child Care Leave, Maternity and Paternity for child birth through surrogacy to a government servant with less than two surviving children vide Notification no. A-24011/21/2023-ESTT-Leave dated 18.06.2024. Now, surrogate mother as well as commissioning mother can avail a maternity leave of 180 days, the commissioning mother can avail a child care leave of 730 days and the commissioning father can avail a paternity leave of 15 days..
3.8 Instructions were issued to grant additional three spells beyond the existing three spells of Child Care Leave in a calendar year to a Government servant, in case the child of a government servant is admitted in a hospital as inpatient vide DOPT’s OM No.A-24011/5/2024-ESTT.-Leave dated 29.07.2024.
Pers Policy (Allowance) Section
3.9 Instructions were issued for availing the benefit of reimbursement of Children Education Allowance and Hostel Subsidy for three classes before class one to $12^{\text {th }}$ standard (irrespective of nomenclature of class) in accordance with New Education Policy 2020 vide DOPT’s OM No. A-27012/01/2023-Pers.Policy(Allowance) dated 14.03.2024.
3.10 Instructions were issued for increasing Children Education Allowance and Special Allowance for child care to women with disabilities by $25 %$ consequent upon the Dearness Allowance goes up by 50\%vide DOPT’s OM No. A-27012/01/2023-Pers.Policy(Allowance) dated 25.04.2024.
3.11 Instructions were issued to allow reimbursement of Child Education Allowances and Hostel Subsidy to all affected employees posted in various Central Government Offices of UT of J&K, for additional period of 05 months w.e.f. November 2022 to March 2023, owing to extension of academic session by UT of J\&K.
3.12 During the Calendar year 2024, total of 1658 RTI and 169 PG has been disposed by Pers. Pol. (L\&A) Division.
Pers. Policy (Pay) Division
3.13 Following OMs/Instructions have been issued by Pers. Policy (Pay) Division, during the period of 2024-25:
| Sl. No. | Subject/Details | Date of issuance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Deputation of Group ‘B’ Officers of the Central Government to State Governments/UTs – Modification in guidelines – regarding |
$\mathbf{3 0 . 0 8 . 2 0 2 4}$ |
| 2. | Deputation of Group ‘C’ employees of the Central Government to State Government/UTs Admn. – Modification in guidelines – regarding |
$\mathbf{2 4 . 0 9 . 2 0 2 4}$ |
| 3. | Grant of notional increment on $1^{\text {st }}$ July/1 $1^{\text {st }}$ January to the employees who retired from Central Govt. Service on $30^{\text {th }}$ June/31 $1^{\text {st }}$ December respectively for the purpose of calculating their pensionary benefits – regarding |
$\mathbf{1 4 . 1 0 . 2 0 2 4}$ |
Pers. Policy (RR) Branch
3.14 As a major reform measure, the entire process of framing/ amendment of Recruitment Rules (RRs) for Group ‘A’ and ‘B’ posts involving approval of Department of Personnel \& Training, consultation with Union Public Service Commission, has been automated through the Recruitment Rules Formulation, Amendment Monitoring System (RRFAMS) portal. Resultantly, the earlier system of sending physical files, which often resulted in considerable delay in finalization of recruitment rules, has been replaced by an online mechanism. The RRFAMS portal was formally launched on 25.12.2016 by Hon’ble Minister of State in the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
3.15 At present, in the process of framing/ amendment of Recruitment Rules for Group ‘A’ and ‘B’ posts, the modules relating to approval by Department of Personnel \& Training and Union Public Service Commission, have been operationalised on the RRFAMS portal. The system of processing proposals for framing and amendment of RRs in the physical mode has been dispensed with.
3.16 To further facilitate user Ministries/ Departments in operation of the RRFAMS portal, a user guide was published in September 2020 on the RRFAMS portal. The launching of RRFAMS portal has significantly improved the timelines for framing the RRs, besides streamlining the process. Also, Ministries/Departments have been allowed to request meetings for discussions on their proposals through this portal. The average time taken by DoPT for final approval of the draft RRs has been significantly reduced. As on 23.01.2025, approximately 3400 proposals for framing/ amendment of RRs have been received on the RRFAMS portal, out of which over 2150 proposals have been approved by DoPT.
3.17 Revised Flexible Complementing Scheme (RFCS) for Scientists replaces the Modified Flexible Complementing Scheme in force in Scientific Ministries/Departments/Organisations of the Government of India and the Personnel Policy for Group A S& T Officers of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology w.e.f 1.7.2024.
Lateral Entry
3.18 Lateral recruitment is an initiative of the Government to achieve the twin objective of bringing in fresh talent as well as augment the availability of manpower at middle management levels by appointing persons, at the level of Joint Secretary, Director and Deputy Secretary, for specific assignments keeping in view their specialized knowledge and expertise in their domain area. A total of 45 officers comprising 6 Joint Secretaries, 29 Directors and 10 Deputy Secretaries, appointed through Lateral Recruitment are in position in various Ministries/Departments.
3.19 During the year 2024, 25 candidates from LE-2023 batch were appointed in the Government of India (3 Joint Secretary, 15 Director \& 7 Deputy Secretary).
Pers. Policy D Section:
Inclusion of Sports Event in the list of events of National Importance for recruitment of meritorious sports persons to any post in Group ‘ $C$ ‘ in Ministries/ Department of Government of India regarding.
3.20 Consolidated Instructions on Recruitment/Promotions for Sportspersons in Government of India have been updated vide DoPT’s OM No.- 1711450898768 dated 04.03.2024 by including the Sports Events – Khelo India University Games, Khelo India Youth Games, Khelo India Winter Games and Khelo India Para Games in the list of Events of National Importance. Medal Winners in the designated sports/games under the above events would now also be eligible to the considered for recruitment/promotions under Sports Quota.
RECRUITMENT AGENCIES
3.21 The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) and the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) are the two designated recruitment agencies administered by the Department of Personnel and Training. While the UPSC is a Constitutional body set up under Article 315 of the Constitution, the Staff Selection Commission has been set up by Resolution of the Government and it has the status of an attached office of the Department of Personnel and Training. Both these agencies enjoy the reputation for selecting candidates for the Government services in a fair, objective, and impartial manner. The candidates for the various examinations come from a variety of social environment and having studied in different disciplines.
3.22 UNION PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION *
3.22.1 The Union Public Service Commission comprises a Chairman and ten Members. The UPSC makes recruitment for recruitment for All India Service, Group ‘A’ Central Civil Services /posts, and Group ‘B’ Gazetted posts in Ministries/Departments of the Central Government. The Commission also conducts the examination for recruitment of Commissioned officers in the Defence forces. Some Union Territories (UTs) also avail the services of the chapter Service Commission for recruitment to the posts under the UT.
3.22.2 The functions of the Commission are as specified in Article 320 of the Constitution. By the exercise of powers conferred by the proviso to Article 320 (3) of the Constitution the President has made the UPSC (Exemption from Consultation) Regulations, 1958 as amended from time to time, as respects the All India
Services and also as respects other services and posts in connection with the affairs of the Union specifying the matters in which it shall not be necessary for the UPSC to be consulted.
3.22.3 Examination
(a) During the year 2023-24, the Commission conducted a total of 22 Examinations under the method of Recruitment by Examination, i.e. 18 examinations for selection to Civil Services/Posts and 04 for Defence Services, against which a total of $25,70,244$ applications were received and processed.
Table: Candidates interviewed and recommended
| Particulars | Number of Candidates interviewed | Number of Candidates recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Civil Services/Posts | 15,488 | 6074 |
| Defence Services | 20,230 (interviews conducted by Services Selection Board) |
1925 |
| Total | $\mathbf{3 5 , 7 1 8}$ | $\mathbf{7 9 9 9}$ |
(b) Against 3,122 posts reserved for SC, ST, OBC and EWS candidates to be filled up under method of Recruitment by Examinations, the Commission recommended 2,924 Candidates, including 115 SC, ST, OBC and EWS candidates, who were recommended against the post reserved for them but at general standard in cases where Reserve List is maintained. The final status will be known after allocation of service upon applying the Reserve List Rule. In addition to above, 365 candidates were recommended at General Standard against the unreserved posts, in respect of Examinations having no provision of Reserve List.
(c) Under the method of Recruitment by Examination, the offer of appointment is made by the Ministry/Department concerned. A delay in the issues of offer of appointment was reported in 04 cases.
(d) During the year 2023-24, 03 cases of malpractices, committed by the candidates were reported to the Commission relating to cheating, possession of mobile phones etc. The Commission took serious note of such cases and, after following due process, imposed penalties on the delinquent candidates, ranging from cancellation of their candidature to their debarment up to a period of 10 years from future Examination/ Selections, conducted by the Commission.
(e) Changes implemented during the year 2023-24:
(1) The Commission had decided to open two New Centres for its various Examinations as under:
i) Kargil in UT of Ladakh for Civil Services (Preliminary) including Indian Forest Service (Preliminary), NDA & NA, CDS and CAPF (ACs) Examination.
ii) Leh in UT of Ladakh for CAPF (ACs) Examination.
(2) In pursuance of a proposal from the Government (DoP\&T), CBI Limited Departmental Competitive (LDC) Examination for selection to the post of Deputy Superintendent of Police included in the Commission’s Annual Programme of Exam and for the first time the Exam was notified on 20.12.2023 and conducted on 16.03.2024 and 17.03.2024 ( 02 days).
3.22.4 Direct Recruitment by Selection
(a) The Commission received 305 requisitions for 4,398 posts from various Ministries/ Departments. A total of 4,026 posts against 208 requisitions were advertised during the year and 5,97,242
applications were received. The recruitment process was cancelled in respect of six requisitions for nine posts (including one post reduced), subsequent to the publications of advertisement.
(b) During the year, a total of $1,67,982$ applications were finalized including applications received in the preceding year; 5,821 candidates were called for interview and 4,407 candidates actually appeared for interview. 1,266 candidates were recommended against 1,420 posts requisitioned in 199 cases. The applicant to Post Ratio was 118 and the Recommendation to Post Ratio was 0.89 .
(c) Recruitment Tests were conducted in 59 cases (including one proficiency skill retest), where the number of applicants was disproportionately high vis-à-vis the number of vacancies.
(d) The process of selection to 154 posts became infructuous due to non-availability of suitable candidates. Most of these posts required specialized medical or engineering qualifications.
(e) As against 707 reserved posts, a total of 606 candidates ( 162 SC, 63 ST, 303 OBC and 78 EWS) were recommended. Thus 85.7 percent of the posts for reserved category were filled up. Besides, 15 SC , five ST, 97 OBC and 27 EWS candidates were recommended for selection against the unreserved post.
(f) The Commission recommended 31 Person with Benchmark Disability candidates against 66 posts reserved for them. Further, six more PwBD candidates were also recommended for posts suitable for them.
(g) A delay was reported in 58 cases in issue of offer letters of appointment, by the Ministry/Department concerned, to the candidates recommended by the Commission. In certain cases, the Ministry/Department concerned did not provide information regarding the issuance of the offer letters of appointment to the recommended candidates.
3.22.5 Appointments
(a) The Commission considered the service records of 24,581 officers and made recommendations regarding the suitability of candidates/officials for promotion, deputation, absorptions etc. in respect of 13,423 officers i.e.
(i) 13,294 officers for promotion in Central Services and
(ii) 129 officers for appointment on Deputation (ISTC)/Absorption.
Advice letters were issued to the Ministries/Departments concerned in 634 DPC cases and in 152 Deputation cases (including 51 infructuous cases).
3.22.6 Recruitment Rules
(a) Advice of the Commission on 361 proposals relating to framing/amendment of Recruitment Rules (including 1 Service Rule and 6 one time mode of recruitment) were issued during the year.
(b) Out of 361 proposals, 345 proposals were processed online on Recruitment Rules Formulation, Amendment and Monitoring System (RRFAMS) portal and 16 proposals were processed in offline mode.
3.22.7 Disciplinary Cases
(a) During the year 2023-24, 750 cases were received at Single Window. Out of these, 523 cases were accepted and 227 cases were returned due to deficiencies in the documents. Further, five cases were received directly through post. Thus, a total of 528 cases were accepted in the Commission.
(b) On including the 231 cases brought forward from the previous year i.e. 2022-23 which were pending with the Commission as on April 1, 2023, the total number of cases with the Commission during the year was 759 . Out of these 759 cases, advice of the Commission was tendered in 446 cases and 77 cases were returned on account of procedural deficiencies, leaving a balance of 236 cases at the close of the year.
3.22.8 Visit of Foreign Delegation
Four-member delegation led by Mr. Ozias Hove, Commissioner, Zimbabwe Public Service Commission visited the Commission on 05.07.2023.
3.22.9 Progressive use of Hindi in official work
Hindi Branch of Union Public Service Commission has been engaged in making sincere and concerted efforts to ensure the compliance of the provisions of Official Language Act/Rules and orders/ instructions issued by Department of Official Language from time to time regarding the progressive use of Hindi for official use.
3.22.10 Implementation of Government’s Language Policy and programme
Hindi Branch in the UPSC is under the charge of a Director (Official Language) with two Deputy Directors (Official Language), four Assistant Directors (Official Language) and other support staff. Apart from guiding and monitoring the implementation of the Official Language policy and programmes of the Government, this Branch also performs the work relating to the translation of documents, which are required to be issued in Hindi or bilingually as per requirements of the office.
3.22.11 Official Language Implementation Committee
There is an Official Language Implementation Committee in UPSC duly constituted under the chairmanship of Secretary and all the branch-heads of UPSC are its members. All the decisions regarding use of Hindi in Office and discussions on shortcomings, if any, in achieving the target fixed every year by Department of Official Language are done in this meeting. During 2023-24, four meetings of the Official Language Implementation Committee were held in the Commission and necessary follow up actions were taken to implement the decisions of the Committee.
3.23 Staff Selection Commission
A. Introduction
3.23.1 The Staff Selection Commission is one of the largest recruiting agencies in India in terms of the number of candidates who apply for various posts in the Central Government.
The Staff Selection Commission is mandated with the task of making recruitment to all Group ‘B’ (Non-Gazetted) and Group ‘C’ (Non-Technical) posts in various Ministries / Departments of the Government of India and their Attached and Subordinate Offices except those posts which are specifically exempted from the purview of the Commission. In addition, the Commission, from the year 2016, has been assigned the additional responsibility of making recruitments to Group ‘B’ (Gazetted) posts of
Assistant Accounts Officer and Assistant Audit Officer for the Indian Audit and Accounts Department. Further, in the year 2021, the Staff Selection Commission has been entrusted with the responsibility of conducting recruitment examinations for the vacant Group ‘B’ (Non-Gazatted) and Group ‘C’ posts in Constitutional / Statutory bodies and the Union Territory (UT) of Ladakh.
B. EXAMINATIONS CONDUCTED BY THE COMMISSION
3.23.2 The Commission is mandated to conduct the following Examinations:
I. Combined Graduate Level Examination;
II. Combined Higher Secondary (10+2) Level Examination;
III. Junior Engineer (Civil, Mechanical and Electrical) Examination;
IV. Sub Inspectors in Delhi Police, and Central Armed Police Forces Examination;
V. Junior Hindi Translator, Junior Translator and Senior Hindi Translator Examination;
VI. Stenographer’s Grade ‘C’ & ‘D’ Examination; and
VII. Multi-Tasking (Non-Technical) Staff Examination.
3.23.3 Non-mandated Examinations: In addition to the above, the Commission also conducts nonmandated Examinations on the specific directions of the Government. Such Examinations are conducted on Memorandum of Understanding basis.
3.23.4 Departmental Examinations: Besides, the Commission also conducts three Limited Departmental Competitive Examinations.
(i) Junior Secretariat Assistant / Lower Division Clerk Grade Limited Departmental Competitive Examination.
(ii) Senior Secretariat Assistant / Upper Division Clerk Grade Limited Departmental Competitive Examination.
(iii) Grade ‘C’ Stenographers Limited Departmental Competitive Examination.
3.23.5 Selection Posts: The Commission is also mandated to conduct examinations for recruitment to Selection Posts, which are isolated posts (not covered under All India Open Competitive Examinations) for Group ‘B’ (Non-Gazetted) and Group ‘C’ (Non-Technical) posts in different Ministries / Departments of the Government of India and their Attached and Subordinate Offices. These posts were earlier filled only through interviews. As interviews for lower level posts have been dispensed with by the Government of India w.e.f. 01.01.2016, the said posts are now filled through written examinations conducted in the format of Objective Type Multiple Choice Questions in Computer Based Mode (CBM).
C. MEASURES ADOPTED IN THE EXAMINATION SYSTEM
3.23.6 Introduction of Computer Based Mode (CBM) of Examination for conduct of various examinations by the Staff Selection Commission.
In June 2016, the Commission adopted the Computer Based Mode for the conduct of its Objective Type Multiple Choice Examinations. Earlier these examinations were conducted in the conventional Optical Mark Reader (OMR) Based Mode. The Computer Based Mode of examination has the following strategic advantages: –
(i) The Computer Based Mode of Examination is more effective and with adequate safeguards in place, the said modality is more reliable, efficient and robust.
(ii) Human intervention is minimal which reduces the chances of the examination being compromised.
(iii) There is greater flexibility and higher confidentiality in the administration and management of Question Papers.
(iv) There is greater accuracy and faster processing of results.
(v) This mode also facilitates better data management and analysis for generating reports.
3.23.7 Online System for receipt of applications, vacancy collection, declaration of results and related activities
(i) As an initiative to achieve full digitization, the Commission introduced the system of online application, in phases from the year 2010. At present, the Commission receives applications for all its examinations only online.
(ii) The Commission uploads notices of various examinations on its website. Starting with Combined Graduate Level Examination, 2021, the Commission has started providing a Window for Application Form Correction after the closing date for receipt of online applications to enable the candidates to correct / modify online application parameters. During the Window for Application Form Correction, the candidates are allowed to submit applications after making requisite corrections / changes in the one-time registration / online application data as per their requirement.
(iii) The online collection of vacancies from various Ministries / Departments of the Government of India has been made mandatory.
(iv) Admit Cards of the candidates are hosted on the websites of the Regional Offices of the Commission.
(v) Similarly, after the conduct of the written examination in the CBM, challenges on the Tentative Answer Keys are invited online. Thereafter, Final Answer Keys are hosted on the website of the Commission.
(vi) Results of all examinations, including results of intermediary stages / tiers are also declared on the website of the Commission. In addition, intimations regarding Document Verification and Skill Test, wherever applicable, are uploaded on the website.
(vii) The responses of candidates, Final Answer Keys and scores of the candidates for their Computer Based Examinations are also uploaded on the website of the Commission. Candidates can view their response sheets and scores individually by logging in using their unique credentials.
(viii) The comprehensive adoption of the online mode for various exam related activities of the Commission has brought about systemic improvements in the examination process contributing to higher standards of diligence and efficiency in the conduct of examinations.
(ix) In addition, communication with the candidates, if required at short notice, is also done through emails / SMS, etc.
3.23.8 Reforms in the Recruitment Process
(i) The Staff Selection Commission (SSC), with the approval of Department of Personnel & Training (DoP\&T), had constituted an Expert Committee (EC) for review of scheme and syllabus of examination to be conducted by SSC. The Committee submitted its report on 08.08.2022. After the approval of DoP\&T, the recommendations of the Committee were adopted and the same was applied with effect from the notice of Combined Graduate Level Examination, 2022 published on 17.09.2022. The major changes following the implementation of the recommendations of the Committee are as under.
a) The number of tiers of the examinations conducted by SSC has been reduced.
b) The Commission has removed descriptive paper from All India open competitive examinations except Junior Hindi Translator Exam.
c) The scheme and syllabus of examinations have also been changed.
d) The Commission has started conducting 12th level and 10th level examinations in multiple languages.
e) Starting from 2022 series of exams, Document Verification (DV) is being conducted by User Departments only.
(ii) Due to cumulative effects of the various reform measures taken, including the ones following the recommendations of the Expert Committee, there has been a reduction in the recruitment cycles of various examinations. Whereas earlier, The average time taken for Combined Graduate
Level and Combined Higher Secondary Level Examination right from the Tier-1 stage to the declaration of final result has been approximately 12 – 15 months, this has now come down to 6 7 months during the mission mode recruitment.
(iii) Starting with Selection Post (Phase XII) Examination, 2024, the online application module has been upgraded to capture live photograph of the candidate filling up the application form so as to prevent applications with bogus photographs, superimposed AI photographs etc.
(iv) Commission has started One Time Registration (OTR) process for own scribes. The candidate can provide OTR details of his/her scribe and can download entry pass of the scribe along with his/her admission certificate to the examination venue
3.23.9 Measures for the benefit of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan)
The Commission extends the facility of scribes for Written / CBM to the candidates having benchmark disabilities in the category of blindness, locomotor disability (Both Arms Affected-BA) and Cerebral Palsy, if desired by the candidates in their online applications. In addition, for the remaining categories of persons with benchmark disabilities (as prescribed in DoP&T OM No.36035/02/2017Estt.(Res) dated $15^{\text {th }}$ January, 2018), if desired by the candidates in his / her online application, a scribe is provided on production of a certificate from the Chief Medical Officer / Civil Surgeon / Medical Superintendent of a Government Health Care Institution in the specified proforma at the time of the examination to the effect that the person concerned has physical limitation and scribe is essential to write the examination on his / her behalf. Compensatory time of 20 minutes per hour is also provided to such candidates. The VH candidates are also provided with the facility of Passage Readers during the Skill Test.
The Commission ensures that the VH candidates are administered separate sets of questions on Quantitative Aptitude and General Intelligence which do not have components of Maps, Graphs, Statistical data, Diagrams, etc.
The Commission makes a conscious effort to provide PwD candidates, an easy, safe and hassle free access to the venues of examination. To ensure this, the PwD candidates are allocated to such venues which are provided with user friendly facilities like elevators/lifts and ramps, etc. PwD candidates, who seek assistance of scribes, are allotted specific venues on a separate date.
3.23.10 Transparency in Governance
As a premier Recruiting Agency, the Commission maintains a high standard of integrity, discipline and efficiency in the conduct of its examinations to ensure merit-based selection.
The Commission also maintains transparency in its processes. The Commission has put in place a robust grievance redressal mechanism wherein references received through CPGRAMS, RTI or any other mode of communication are addressed on priority with due weightage assigned to the quality of replies.
3.23.11 Candidates registering with the Commission
Total number of candidates registered for various Examinations of the Commission during the financial year 2024-25 (as on 31.12.2024) is as under:
| Sl. No. | Name of Examination | Dates of Examinations | Registered Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grade ‘C’ Stenographer Limited Departmental Competitive Examination, 2023-2024. |
09.05 .2024 | 609 |
| 2 | JSA/ LDC Grade Limited Departmental Competitive Examination, 2023-2024. |
10.05 .2024 | 837 |
| 3 | SSA/ UDC Grade Limited
Departmental Competitive
Examination, 2023-2024. | 13.05.2024 | 231 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 4 | Junior Engineer (Civil, Mechanical, Electrical and Quantity Surveying & Contracts) Examination, 2024. | 05.06.2024 to 07.06.2024 | $4,62,128$ |
| 5 | Selection Post Examination, Phase-XII, 2024. | 20.06.2024 to 21.06.2024, \& 24.06.2024 to 26.06.2024 | $12,90,227$ |
| 6 | Sub-Inspector in Delhi Police and Central Armed Police Forces Examination, 2024. | 27.06.2024 to 29.06.2024 | $7,18,453$ |
| 7 | Combined Higher Secondary (10+2) Level Examination, 2024 | 01.07.2024 to 05.07.2024 \& 08.07.2024 to 11.07.2024 | 28,59,345 |
| 8 | Combined Graduate Level Examination, 2024 | 09.09.2024 to 13.09.2024 \& 17.09.2024 to 19.09.2024 | 35,94,257 |
| 9 | Multi-Tasking (Non-Technical) Staff and Havaldar (CBIC \& CBN) Examination, 2024 | 30.09.2024 , 01.10.2024, 07.10.2024 to 09.10.2024, 14.10.2024 to 18.10.2024, 21.10.2024 to 23.10.2024, 28.10.2024 to 30.10.2024, 04-05.11.2024, 11.11.2024 to 14.11.2024 | 55,99,291 |
| 10 | Combined Hindi Translator Exam, 2024 | 09.12.2024 | 13,687 |
| 11 | Stenographer Grade ‘C’ \& ‘D’ Examination, 2024 | 10.12.2024 to 11.12.2024 | $4,53,930$ |
| | | Total | 1,49,92,995 |
Projection:
| 1 | Constable (GD) in CAPFs \& SSF, Rifleman (GD) in Assam Rifles and Sepoy in NCB Exam, 2025 | 04.02.2025 to 07.02.2025, 10.02.2025 to 13.02.2025, 17.02.2025 to 21.02.2025 \& 25.02.2025 | 52,69,512* |
|---|---|---|---|
Candidates selected by the Commission
3.23.12 During the Financial Year 2024-25 (as on 31.12.2024), the Commission has recommended 48,857 candidates to various User Ministries/Departments. Details in this regard are given in the table below: –
| Sl.
No. | Name of Examination | Date of Declaration of Result | Candidates
Selected |
| — | — | — | — |
| 1 | Sub-Inspector in Delhi Police and CAPFs Examination, 2022 | 05.04 .2024 | 1865 |
| 2 | Constable (GD) in Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs), SSF, Rifleman (GD) in Assam Rifles and Sepoy in Narcotics Control Bureau Examination, 2024 | 13.12 .2024 | 44,266 |
| 3 | Selection Posts/ Phase-VI/ 2018 | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 46 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Selection Posts/ Phase-IX / 2021 Examination | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 815 |
| 5 | Selection Posts/ Phase-X/ 2022 Examination | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 548 |
| 6 | Selection Posts/ Phase-XI/ 2023 Examination | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 1201 |
| 7 | Selection Post Phase/Ladakh/2022 Examination | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 01 |
| 8 | Selection Post Phase/Ladakh/2023 Examination | Final results is declared post wise by Regional Offices | 115 |
| Total | 48,857 |
3.23.13. Progressive use of Hindi in Commission’s work
During the period under review, provision of section 3(3) of Official Language Act, 1963 and Official Language Rule, 1976 were duly complied with. All the notices of various examinations published during the period were issued bilingually and the emphasis was laid on increasing the original correspondence in Hindi with three regions namely A, B and C as per target prescribed by the Department of Official Language.
Three Regional Offices of Staff Selection Commission namely Raipur (Region-A), Chandigadh (Region-B) and Guwahati (Region-C) were awarded the Rajbhasha Shield under the scheme of commendable work in Official Language Hindi for the year 2023-24. In the year 2023-24, Five officials were awarded under the scheme of Original Work in Hindi and Establishment Section of this Commission was awarded Rajbhasha Running Shield for the year 2023-24.
In order to encourage the progressive use of Hindi in the Official work and to create interest among officers/officials for its usage, Hindi Software supported by Unicode compliance is being used. All Regional offices of the Commission along with Headquarters are using this Hindi Software/Fonts. The Hindi Fortnight event was organized from 14th September, 2024 to 28th September, 2024. During the fortnight various competitions like Hindi Typing, Hindi Question-Answer, Noting and Drafting, Hindi Dictation, Hindi Essay and Debate competitions were organized. These winners were awarded by the Hon’ble Chairman, SSC (HQ) in a prize distribution function organized on 1st October, 2024. During the period under review, Hindi workshops were also organized on 19.06.2024, 11.09.2024 and 03.12.2024 in which 18,17 and 22 Officers/Officials respectively participated.
In a major initiative taken by the Commission towards Rajbhasha implementation, an e-Magazine of the Commission named “Naya Jharokha” was launched during the year 2022-23. Publication of the fourth edition of this e-magazine is under process.
3.24 NATIONAL RECRUITMENT AGENCY
A. Introduction
3.24.1 The National Recruitment Agency (NRA) has been registered as a Society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 with its HQ in Delhi. NRA has been set up to conduct the Common Eligibility
Test (CET) for subordinate posts as per the DoPT order dated 28.08.2020. NRA aims to conduct Common Eligibility Tests (CET) to shortlist the candidates for vacancies of Group B Non Gazetted posts, Group B Gazetted posts which are exempted from consultation with UPSC; Group C posts in the Government and equivalent posts (where no such classifications exist) in instrumentalities of the Government, through a computer-based test (Tier-1 Examination).
B. Major Objectives of NRA
- To mitigate the hardship faced by candidates who have to appear for multiple examinations conducted by multiple agencies, where similar eligibility conditions have been prescribed.
- To bring in savings to the candidates towards multiple application fees and travelling cost to appear in these examinations.
- To reduce the time taken in the selection process.
- To facilitate employment generation- In the longer run, the CET score could be shared with other recruiting agencies in the Central Government, State Governments/ Union Territories, Public Sector Undertaking and Private Sector on MOU/Cost sharing basis, for appointment in their organizations. This would help such organizations in saving costs and time spent on recruitment.
C. General Body of NRA
The General Body (GB) of NRA has the following members has been fully set up as stated below:
- Chairman, NRA
Chairman
2. Secretary, DoPT or his representative
Member
3. Representative of Ministry of Finance (DFS)
Member
4. Representative of Ministry of Railways
Member
5. Chairman, Staff Selection Commission
Member
6. Executive Director (ED), Estt., RRBs
Member
7. Director, Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS)
Member
8. Chairman, All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE)
Member
9. Director General (DG), National Testing Agency (NTA)
Member
10. Secretary and Controller of Examinations, NRA
Member-Secretary
D. ACTIVITIES DURING THE YEAR 2024-25
a. Rule 5 of the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Rules, 2024 notified under the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 mandates NRA to formulate Norms, Standards, and Guidelines for CBT mode of examinations. Accordingly, NRA is in the process of formulating Norms, Standards and Guidelines for the conduct of CBT examinations.
b. The $5^{\text {th }}$ General Body meeting was held on $7^{\text {th }}$ November 2024.
3.25 Public Enterprises Selection Board
3.25.1 The Public Enterprises Selection Board (PESB) is a high powered body set up by a Resolution of Government of India, Ministry of Finance dated 30.08.1974 to evolve a sound managerial policy for
Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSE) and in particular, to advise the Government on appointments to the top management posts. The PESB functions as a professional body with a large measure of autonomy. The PESB is headed by Chairperson and has three Members.
3.25.2 As per the policy of the Government, PESB has been entrusted with the job of recommending for appointment, through a fair and objective selection procedure, outstanding professional managers to Chairman, Managing Director or Chairman-Cum-Managing Director (Level-I) and Functional Director (Level-Il) posts and posts at any other level in CPSEs, as may be decided by the Government from time to time.
3.25.3 Government has recognised the need to develop a cadre of professional managers within the public sector. Hence, unless markedly better candidates are available from outside, internal candidates, employed in CPSEs, are to be preferred for appointment to Board Level posts. However, if internal candidates are not available, preference is to be given to candidates working in other CPSEs, either in the same area of business or in the other areas. Mobility of managerial personnel among CPSEs within the same sector or group, failing which mobility within the public sector as a whole will be encouraged, subject to certain limitations.
3.25.4 With effect from 10.06.2021, candidates from State Public Sector Enterprises and the private sector, subject to fulfilling the eligibility criteria, can also be considered as non-internal candidates along with the candidates of other public sector enterprises for a period of five years.
3.25.5 Vide GoT notification dated 20.06.2023, Group ‘A’ officers of the Central Government including All India Services (AIS) & Armed Forces of India and officers in equivalent rank / grade from Public Sector Bank / Financial Institutions / Autonomous Bodies, etc. subject to fulfilling the eligibility criteria, can also be considered as non-internal candidates.
3.25.6 Under special circumstances, the appointment to a particular post or posts in a CPSE may be made other than through PESB with the prior and specific approval of the Government.
3.25.7 For sick and potentially sick CPSEs, the Administrative Ministry / Department concerned, in consultation with PESB could take a decision at any stage in the process of recruitment to the post of Chairman, Managing Director or Chairman-cum-Managing Director of the CPSE, to take a person on deputation from any of the All India or Group ‘A’ Central Services without insisting on the rule of immediate absorption.
Constitution of the Board
3.25.8. The PESB consists of a part-time or full-time Chairperson and three full-time Members. The Chairperson and Members are persons who have had a long and distinguished career in management of Public or Private Corporation or Public Administration and have proven record of achievements, preferably, in the field of personnel, finance, production or marketing. The three full-time Members of PESB may be:
(i) A distinguished serving or former Chief Executive of a Public Sector or Private Sector or Joint Sector Enterprises.
(ii) A distinguished person with experience in selection of Top Management personnel.
(iii) A distinguished serving or former Civil Servant with experience in management of PSEs or in areas of finance, industry or economic affairs.
3.25.9 The specific functions assigned to the PESB include the following:
(i). To be responsible for the selection and placement of personnel in the posts of Chairman, Managing Director or Chairman-cum-Managing Director (Level-I), and functional Directors (Level-IT) in CPSEs as well as in posts at any other level as may be specified by the Government.
(ii). To advise the Government on matters relating to appointments, confirmation or extension of tenure and termination of services of the personnel of the above mentioned levels.
(iii). To advise the Government on the desired structure at the Board Level, and for senior management personnel, for each CPSE or group of CPSEs.
(iv). To advise the Government on a suitable performance appraisal system for both the PSEs and the managerial personnel in such enterprises.
(v). To build a data bank containing data relating to the performance of PSEs and its officers.
(vi). To advise the Government on formulation and enforcement of code of conduct and ethic for managerial personnel in PSEs.
(vii) To advise the Government on evolving suitable training and development policies for management personnel in PSEs.
3.25.10 Action taken by PESB during the year 2024-25 from April 1, 2024 to 31.03 .2025 .
The achievements made during the period under report are as follows:
| S.No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Selection Process | No. of Advertisements issued |
No. of Selection Meetings held |
No. of Posts where recommendations were made |
| 124 | 103 | 97 | ||
| 2 | Joint Appraisal for non- extension / non- confirmation of tenure |
01 | ||
| 3 | Creation of posts / bifurcation of Board |
Nil | ||
| 4 | Creation / Categorization of CPSEs |
Nil |
CHAPTER: 4
RESERVATION IN THE CENTRAL GOVERNMENT SERVICES
MANDATE
Based on the policy decision taken by the concerned nodal Ministries/Departments, DoPT issues instructions on the matters regarding reservation in posts and services in Central Government for the following:-
- Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes & Other Backward Classes;
- Economically Weaker Sections who are not covered under the scheme of reservation for SCs, STs and OBCs;
- Persons with Benchmark Disabilities;
- Ex-servicemen.
The Government has taken several steps for the upliftment and welfare of the Scheduled Castes (SCs), the Scheduled Tribes (ST) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs). One such welfare measure, as per Constitutional provisions, is to give them reservation in services under the State. Persons with Benchmark Disabilities (PwBDs), Ex-servicemen and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS), also get the benefit of reservation in services.
RESERVATION FOR SCs, STs AND OBCs:
4.1 Clause (4) of Article 16 of the Constitution of India enables the State to make provision for reservation in appointments or posts in favour of any backward class of citizens which, in the opinion of the State, is not adequately represented in the services under the State. Clause (4A) of the same Article enables the State to provide reservation for the members of the SC and ST in the matters of promotions. Article 335 provides that the claims of the members of the SC and the ST shall be taken into consideration, consistently with the maintenance of efficiency of administration, in the making of appointments to services and posts in connection with the affairs of the Union or of a State.
4.2 In consonance with the powers given by the Constitution, the Government has issued various instructions, from time to time, providing for reservation in services for the members of the SCs, the STs and the OBCs. Such members of OBC, who fall in creamy layer, however, do not get the benefit of reservation. The income limit for determining the creamy layer status amongst the OBCs to exclude the socially advanced persons/sections is presently Rs.8.0 lakh per annum.
4.3 Reservation to SCs, STs, OBCs and EWS, in case of direct recruitment, is available in all groups of posts. When direct recruitment is made on all India basis by open competition, reservation for SCs, STs and OBCs is $15 %, 7.5 \%$ and $27 \%$ respectively, and when direct recruitment is made on all India basis otherwise than by open competition, it is $16.66 \%, 7.5 \%$ and $25.84 \%$, respectively.
4.4 In case of direct recruitment to Groups C and the erstwhile Group D posts, normally attracting candidates from a locality or a region, percentage of reservation for SCs and STs is generally fixed in proportion to the population of SCs and STs in the respective States/UTs. Reservation for OBCs, in such cases, is fixed keeping in view their proportion in the population of the State/UT subject to the maximum at $27 \%$. Further it is subject to the condition that total reservation for SCs, STs and OBCs does not exceed the limit of $50 \%$, prescribed by the Nine Judges Constitutional Bench of the Hon’ble Supreme Court in the Indira Sawhney Judgment.
4.5 Relaxations and concessions are given to SC and ST candidates with a view to increasing their representation in services. They get relaxation in upper age limit upto five years and exemption from payment of fees. They also get unlimited number of chances within the relaxed age limit prescribed for appearing in the competitive examinations.
4.6 Likewise, the OBC candidate get concession like relaxation in upper age Limit upto three years, relaxation in number of chances up to nine within the relaxed age limit for appearing in the Civil Services Examination etc. The SC/ST/OBC candidates appointed on their ‘own merit’ are adjusted against unreserved vacancies.
4.7 In case of promotion, the reservation is provided to SCs and STs only which is $15 %$ and $7.5 \%$ respectively. Further, SC and ST candidates appointed by promotion on their own merit and seniority and not owing to reservation or relaxation of qualifications will be adjusted against unreserved points of reservation roster, irrespective of the fact whether the promotion is made by selection method or nonselection method. However, the Office Memorandum, dated 13.8.1997, providing ‘reservation in promotions’ and the Office Memorandum, dated 10.8.2010, relating to ‘promotion of SCs/STs on own merit’ are under challenge and presently subjudice before the Hon’ble Supreme Court. In the SLP No. 30621/2011 titled “Jarnail Singh & Ors. vs. Lachhmi Narian Gupta \&Ors. Hon’ble Supreme Court has delivered a judgement in Jarnail Singh Case on 28/01/2022 in which Hon’ble Supreme Court has clarified some issues which have emanated from its erstwhile judgment in M. Nagaraj case. However, the Hon’ble Supreme Court has not expressed any opinion on the merits of any individual case. In pursuance of the aforesaid judgment in Jarnail Singh Case, an OM dated 12/4/2022 has been issued by DoPT vide which Ministries/Departments has been requested to fulfil certain conditions before making reservation in promotion which inter alia include, collection of quantifiable data regarding inadequacy of representation of SC \& ST and applicable of the said data to each cadre separately.
4.8 As per data received from 80 Ministries/ Departments, updated information on representation of SCs, STs and OBCs in the posts and services of the Central Government, as on 01.01.2024, is as under:-
| Data as on 01.01.2024 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GROUP | Total Number of Employees | SC | ST | OBC | |||
| Number | $\%$ | Number | $\%$ | Number | $\%$ | ||
| A | 119178 | 16920 | 14.20 | 7793 | 6.54 | 22807 | 19.14 |
| B | 364307 | 59006 | 16.20 | 27789 | 7.63 | 79952 | 21.95 |
| C (excluding Safai Karamchari) |
2727930 | 456925 | 16.75 | 243872 | 8.94 | 744527 | 27.29 |
| C (Safai Karamchari) |
40737 | 14971 | 36.75 | 3331 | 8.18 | 8614 | 21.15 |
| Total | 3252152 | 547822 | 16.84 | 282785 | 8.70 | 855900 | 26.32 |
4.9 Quantum of reservation for the SCs, STs and OBCs in any grade/cadre is determined on the basis of number of posts in the grade/cadre. However, in small cadres having less than 14 posts, where it is not possible to give reservation to all the three categories on the basis of this principle, reservation is provided by rotation by way of L-Shaped 14-Point rosters prescribed by Department of Personnel and Training Office Memorandum No.36012/2/96-Estt.(Res.), dated 2.7.1997.
4.10 As per the guidelines or instructions issued by DoPT, all Ministries/Departments are required to appoint/nominate Liaison Officers at the least the rank of Deputy Secretary and setting up of special Reservation cell for enforcement of orders of reservation in posts and services of the Central Government. The Liaison Officer has been assigned the duty of ensuring proper implementation of reservation orders, conducting annual inspection of reservation register/roster registers maintained in the Ministries/Departments/Offices, reporting the case of negligence or lapses in the matter of following reservation and orders relating to it coming to light through inspections carried out by him/her to the concerned Secretary/Additional Secretary/Head of Department etc. In offices and organizations under the control of the Ministries/Departments also, a Liaison Officer is required to be nominated in the same matter as is existing in the Ministries/Departments.
4.11 Instructions have been issued on $13^{\text {th }}$ February, 2014 wherever a Selection Committee/Board exists or has to be constituted for making recruitment to 10 or more vacancies in any level of posts or services, it is mandatory to have one member belonging to SC/ST, one member belong to OBC and one member belonging to Minority Community in such Committees/Boards. One of the members of the Selection Committee/Board, whether from the general category or from the minority community or from SC/ST/OBC, should be a lady failing which a lady member should be co-opted on the Committee/Board. It is also to be ensured that where the number of vacancies against which selection is to be made is less than 10 , no effort should be spared in finding a Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribe/Other Backward Class Officer, a Minority Community officer and a lady officer for inclusion in such Committees/Boards.
4.12 Reservation for ex-servicemen and Persons with Benchmark Disabilities is termed as “horizontal” reservation and reservation for SCs, STs and OBCs is termed as “vertical” reservation. Horizontal reservation cuts across vertical reservation (in what is called interlocking reservation) and persons selected against the quota have to be placed in the appropriate category viz. SC/ST/OBC/Unreserved depending upon the category to which they belong in the roster.
RESERVATION FOR PERSONS WITH BENCHMARK DISABILITIES:
4.13 With enactment of ‘The Right of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016’ and notification of ‘The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Rules, 2017’ issued by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities, the Department of Personnel and Training issued instructions, vide OM No. 36035/2/2017-Estt.(Res), dated 15.01.2018, providing reservation to Persons with Benchmark Disabilities in the posts/services of the Central Government in direct recruitment as follows:-
In case of direct recruitment, four per cent of the total number of vacancies to be filled up by direct recruitment, in the cadre strength in each group of posts i.e. Groups A, B and C shall be reserved for persons with benchmark disabilities.
Against the posts identified for each disability, of which, one per cent each shall be reserved for persons with benchmark disabilities under clauses (a), (b) and (c) and one per cent, under clauses (d) and (e), namely:-
(a) blindness and low vision;
(b) deaf and hard of hearing;
(c) locomotor disability including cerebral palsy, leprosy cured, dwarfism, acid attack victims and muscular dystrophy;
(d) autism, intellectual disability, specific learning disability and mental illness;
(e) multiple disabilities from amongst persons under clauses (a) to (d) including deaf-blindness.
4.14 As per, data received from 80 Ministries/Departments, updated information on representation of Persons with Benchmark Disabilities in the posts and services of the Central Government services, as on 01.01.2024, is as under:-
| GROUP | Number of Persons with Benchmark Disabilities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A* | B** | C*** | D&E**** | Total | |
| A | 130 | 175 | 1017 | 6 | 1328 |
| B | 700 | 1133 | 3075 | 183 | 5091 |
| C (Excluding Safai Karmchari) |
3612 | 3842 | 12804 | 163 | 20421 |
| C (Safai Karmchari) | 286 | 189 | 341 | 37 | 853 |
| Total | 4728 | 5339 | 17237 | 389 | 27693 |
- ‘A’ (blindness and low vision)’,
** ‘B’ (deaf and hard of hearing)’,
*** ‘C’ (locomotor disabilities including cerebral palsy, leprosy cured, dwarfism, acid attack victims and muscular dystrophy)’ and
**** ‘D&E’ (D: autism, intellectual disability, specific leaning disability and mental illness \&E: multiple Disabilities from amongst persons under clauses (A) to (D) including deaf-blindness)’.
4.15 As per OM dated 31.3.2014, DoPT has issued detailed guidelines conveying the additional facilities/amenities which are required to be provided to the Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) to enable them to effectively discharge their duties. Vide this OM, facilities such as identification of jobs, post recruitment and pre-promotion training, assistive devices, preference in transfer/posting, special casual leave, etc. have been identified as areas which require special attention. Further, vide OM dated 8.10.2018, exemption from the routine exercise of transfer/rotational transfer has also been extended to the employees, who are caregiver of Persons with Disability dependents. These instructions have been further reiterated vide OM dated 2.2.2024.
4.16 Orders have been issued by DoP\&T for exemption of Persons with Benchmark Disabilities from payment of examination and application fee prescribed for competition examination held by SSC/UPSC.
4.17 DoPT has issued OM No. 36012/1/2020-Estt.(Res.-II), dated 17.05.2022 providing reservation in promotion to Persons with Benchmark Disabilities (PwBDs). The applicability of this OM has been made effective from 30.6.2016, vide OM No. 36012/1/2020-Estt.(Res.-II), dated 28.12.2023.
4.18 This Department has issued OM dated 27.9.2022 providing that facility of scribe taken by a PwBD candidate along with compensatory time shall not be treated as relaxed standard and disability of a person which he is suffering from shall not be treated as relaxed standard in medical fitness test for the purpose of ‘own merit’.
RESERVATION FOR ECONIMICALLY WEAKER SECTIONS (EWSs) WHO ARE NOT COVERED UNDER THE SCHEME OF RESERVATION FOR SCs, STs AND OBCs.
4.19 In pursuance of insertion of clauses 15(6) and 16(6) in the Constitution by One Hundred and Third Amendment Act, 2019 and in order to enable the Economically Weaker Sections (EWSs) who are not covered under the scheme of reservation for SCs, STs and OBCs, Office Memoranda, dated 19.01.2019 and 31.01.2019, have been issued for providing $10 %$ reservation to them in direct recruitment in civil posts and services in the Government of India.
RESERVATION FOR EX-SERVICEMEN:
4.20 Reservation for ex-servicemen is available in terms of the Ex-servicemen (Re-employment in Central Civil Services and Posts) Rules, 1979, as amended from time to time. As per these Rules, ten percent of the vacancies in the posts upto of the level of Assistant Commandant in para-military forces, ten percent of the vacancies in Group ‘ C ‘ posts, and twenty per cent of the vacancies in Group ‘D’ posts are reserved for ex-servicemen to be filled by direct recruitment in any year. The DG (Resettlement), Ministry of Defence monitors the implementation of guidelines for resettlement of ex-servicemen.
4.21 As per Office Memorandum dated 14.08.2014, if an ex-serviceman applies for various vacancies before joining any civil employment, he/she can avail of the benefit of reservation as ex-serviceman for any subsequent employment, which are filled through direct recruitment and wherever reservation is applicable to the ex-servicemen. However, to avail of this benefit, an ex-serviceman, as soon as (s)he joins any civil employment, should give self-declaration/undertaking to the concerned employer about datewise details of application for various vacancies for which (s)he had applied for before joining the initial
civil employment. These Orders took effect from the date of the Office Memorandum i.e. $14^{\text {th }}$ August 2014.
4.22 Definition of Ex-servicemen has been amended to cover the Short Service Commissioned officers who have been released from service after completion of the initial terms of engagement and have been given gratuity. However, such release should not be by way of dismissal or discharge on account of misconduct or inefficiency.
4.23 An OM No. 36034/2/2017-Estt.(Res.), dated 31.12.2021 was issued by this Department regarding “Nomination of Liaison Officer for implementation of orders of reservations relating to Ex-Servicemen in the posts and services of the Central Government”. The instructions relating to Liaison Officer for ExServicemen have been reiterated vide OM dated 8.12.2002.
CHAPTER 5
CADRE MANAGEMENT
5(A)- ALL INDIA SERVICES(AIS)
MANDATE OF SERVICES DIVISION
The Services Division is responsible for Cadre Management of All India Services (IAS, IPS and IFS) which includes framing and revising rules and regulations regarding service conditions of the employees, in consultation with the Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of Environment and Forests. Matters relating to framing and amendment of recruitment rules, clarification related to rules etc., are examined and processed in this Division.
5.1 Amendments in AIS Rules
(i) Amendment in IAS (Probationer’s Final Examination) Regulation, 1955 was notified on 05.04.2024.
(ii) Reconstitution of Joint Cadre Authority for All India Service of AGMUT under Rule 4 of the All India Services (Joint Cadre) Rules, 1972, was notified on 05.11.2024.
(iii) Amendment in Rule 8 of the All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958 was notified on 06.02.2024 vide Notification G.S.R.102(E).
(iv) During the Calender year 2024, following instructions were issued by AIS-II and AIS-III Sections:
a) Enhancement of maximum limit of retirement gratuity and death gratuity admissible from 20 lakh to 25 lakh with effect from 01.01 .2024 vide letter No. 25014/01/2024-AIS-II(Pension) dated 28.06.2024
b) Grant of notional increment on $1^{\text {st }}$ July / $1^{\text {st }}$ January to All India Services officers who retire on $30^{\text {th }}$ June / $31^{\text {st }}$ December respectively for the purpose of calculation of pensionary benefits vide letter No.29018/12/2023-AIS-II(Pension) dated 28.10.2024
c) Review of suspension when under deemed suspension under Rule 3(8) (b) of AIS (D&A) Rules, 1969 was issued on 03.12 .2024
d) Grant of Leave salary for AIS officers on Central Deputation during Study Leave and grant of exIndia Study Leave for pre or post course formalities under AIS (Study Leave) Regulations, 1960 was issued on 18.09.2024.
e) Extension of timelines for recording of PARs for the year 2023-24 in respect of AIS officers by the Reporting and the Reviewing Authority was issued vide letters dated 27.05.2024, 28.06.2024, 31.07.2024 \& 25.10.2024.
Cadre strength of IAS
5.2 The Total Authorized Cadre Strength of the IAS as on 01.01 .2024 was 6858 and the number of officers in position was 5542 . The corresponding figures are 6877 and 5578 as on 01.01 .2025 respectively. The authorized cadre strength and the number of officers in position in different years since 1951 is as given below:
| Year | Authorized
cadre strength | Number of officers in position
(As on $1^{\text {st }}$ January) |
| — | — | — |
| 1951
(At the time of the initial
constitution of the service) | 1232 | 957
(Including 336 officers of the Indian Civil Service) |
| 1961 | 1862 | 1722
(Including 215 officers of the Indian Civil Service) |
| 1971 | 3203 | 2754
(Including 88 officers of the Indian Civil Service) |
| 1981 | 4599 | 3883 |
| 1991 | 5334 | 4881 |
| 2001 | 5159 | 5118 |
| 2002 | 5159 | 5051 |
| 2003 | 5159 | 4871 |
| 2004 | 5159 | 4791 |
| 2005 | 5261 | 4788 |
| 2006 | 5337 | 4790 |
| 2007 | 5422 | 4731 |
| 2008 | 5460 | 4761 |
| 2009 | 5671 | 4572 |
| 2010 | 5689 | 4534 |
| 2011 | 6077 | 4456 |
| 2012 | 6154 | 4377 |
| 2013 | 6217 | 4737 |
| 2014 | 6270 | 4619 |
| 2015 | 6375 | 4802 |
| 2016 | 6396 | 4926 |
| 2017 | 6500 | 5004 |
| 2018 | 6553 | 5104 |
| 2019 | 6699 | 5205 |
| 2020 | 6715 | 5205 |
| 2021 | 6746 | 5231 |
| 2022 | 6789 | 5317 |
| 2023 | 6829 | 5464 |
| 2024 | 6858 | 5542 |
| 2025 | 6877 | 5578 |
5.3 There is a provision for quinquennial cadre review in respect of every cadre of the three All India Services under the relevant Cadre Rules. 5.4 In the calendar year 2024, notifications have been issued revising the strength and composition of the following cadres participating in the All India Services:
| Indian Administrative Service | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Nagaland |
| 2 | Rajasthan |
| Indian Police Service | |
| 1 | Himachal Pradesh |
| 2 | Andhra Pradesh |
| 3 | Maharashtra |
Commercial Employment
5.5 As per Rule 26 of the All India Services (Death-Cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958 a pensioner shall not accept any commercial employment before the expiry of one year from the date of his retirement, except with the previous sanction of the Central Government by submitting an application in Schedule ‘L’.
Resignation of AIS Officers
5.6 The issue of resignation of AIS officers is governed by Rule 5 of AIS (DCRB) Rules, 1958. Rule 5 of AIS (DCRB) Rules, 1958 provides that no retirement benefits may be granted to a person who has been dismissed or removed from the service or who has resigned from the service. Further, the issue of deemed to have resigned from service cases are governed under Rule 7 of AIS (Leave) Rules, 1955.
5.7 During the year 2024, 03 (Three) resignation cases of IAS officers have been approved by competent authority as per the resignation guidelines issued vide O.M. No. 24012/10/2010-AIS-II dated 16.08.2011.
Instructions issued under AIS Rules by AIS-II Section
5.8 During the calendar year 2024, the following instructions have been issued.
(i) Instruction issued vide letter No.25014/01/2024-AIS-II(Pension) dated 28.06.2024 regarding enhancement of maximum limit of retirement gratuity and death gratuity admissible from 20 lakh to 25 lakh with effect from 01.01.2024.
(ii) Instruction issued vide letter No.29018/12/2023-AIS-II(Pension) dated 28.10.2024 regarding grant of notional increment on 1stJuly/1stJanuary to All India Services officers who retire on $30^{\text {th }}$ June $/ 31^{\text {st }}$ December respectively for the purpose of calculation of pensionary benefits.
Instructions issued under AIS Rules by AIS-III Section
5.9 During the calendar year 2023, the following instructions have been issued.
(i) Instruction under Rule 3(8) (b) of AIS (D&A) Rules, 1969 was issued on 03.12.2024 regarding review of suspension when under deemed suspension.
(ii) Instructions under AIS (Study Leave ) Regulations, 1960 regarding Leave salary for AIS officers on Central Deputation during Study Leave and grant of ex-India Study Leave for pre or post course formalities was issued on 18.09.2024.
(iii) Extension of timelines for recording of PARs for the year 2023-24 in respect of AIS officers by the Reporting and the Reviewing Authority was issued vide letters dated 27.05.2024, 28.06.2024, 31.07.2024 & 25.10.2024.
Data regarding Service Allocation on the basis of Civil Services Examination (CSE) – 2023
5.10 In 2023-2024, Union Public Service Commission conducted the Civil Services Examination (CSE)-2023 for recruitment to 21 participating services (as mentioned below) out of which 16 are Group ‘A’ Services and the remaining 5 services are Group ‘B’ Services.
5.11 After the completion of $6^{\text {th }}$ iteration of Service Allocation, 996 candidates have been allocated service against 1143 advertised vacancies for CSE-2023 in the following 19 participating services:
| Sl. No. |
Service | SC | ST | OBC | EWS | UR | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indian Administrative Service | 27 | 14 | 50 | 17 | 73 | 181 |
| 2 | Indian Foreign Service | 5 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 15 | 36 |
| 3 | Indian Police Service | 32 | 13 | 55 | 20 | 80 | 200 |
| 4 | Indian Audit and Accounts Service, Group-A | 3 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 19 |
| 5 | Indian Civil Accounts Service, Group-A | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 10 |
| 6 | Indian Corporate Law Service, Group-A | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | Indian Defence Accounts Service, Group-A | 4 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 23 |
| 8 | Indian Defence Estates Service, Group-A | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 14 |
| 9 | Indian Information Service, Group-A | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 19 |
| 10 | Indian P\&T Accounts and Finance Service, Group-A | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| 11 | Indian Postal Service, Group-A | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 9 |
| 12 | Indian Railway Management Service, Group-A | 21 | 11 | 32 | 13 | 58 | 135 |
| 13 | Indian Railway Protection Force Service, Group-A | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 8 |
| 14 | Indian Revenue Service (Customs \& Indirect Taxes), Group-A | 15 | 8 | 31 | 11 | 42 | 107 |
| 15 | Indian Revenue Service (Income Tax), Group-A | 29 | 14 | 54 | 19 | 72 | 188 |
| 16 | Indian Trade Service, Group-A | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 9 |
| 17 | Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, DD \& NH Civil Service, Group-B | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 | 21 |
| 18 | Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, DD \& NH Police Service, Group-B | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 5 |
| 19 | Pondicherry Civil Service, Group-B | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 147 | 76 | 261 | 94 | 418 | 996 |
5.12 Cadre Allocation of candidates selected for IAS through CSE-2023:
Cadre allocations of 181 candidates allocated to IAS on the basis of CSE-2023 have been made on 12.12.2024 vide DoP\&T’s letter No. 13013/06/2023-AIS (I). State-wise details of the candidates allocated to various cadres /joint cadres are as follows:
| S. No. | Cadre/ Joint Cadre | No. of officers allocated |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A G M U T | 9 |
| 2. | Andhra Pradesh | 7 |
| 3. | Assam Meghalaya | 9 |
| 4. | Bihar | 11 |
| 5. | Chhattisgarh | 4 |
| 6. | Gujarat | 8 |
| 7. | Haryana | 5 |
| 8. | Himachal Pradesh | 2 |
| 9. | Jharkhand | 4 |
| 10. | Karnataka | 8 |
| 11. | Kerala | 5 |
| 12. | Madhya Pradesh | 9 |
| 13. | Maharashtra | 8 |
| 14. | Manipur | 1 |
| 15. | Nagaland | 1 |
| 16. | Odisha | 10 |
| 17. | Punjab | 10 |
| 18. | Rajasthan | 13 |
| 19. | Sikkim | 1 |
| 20. | Tamil Nadu | 13 |
| 21. | Telangana | 5 |
| 22. | Tripura | 5 |
| 23. | Uttar Pradesh | 17 |
| 24. | Uttarakhand | 3 |
| 25. | West Bengal | 13 |
| Grand Total | 181 |
Civil Services Examination-2023-Personality Test/Interview and Medical Examination of the Candidates
5.13 Personality Test/Interview of the 2844 candidates who qualified the written part of the Civil Services (Main) Examination – 2023 was scheduled from 03.01.2024 to 12.04.2024 and their Medical Examination was conducted on the next working day of their interview.
Promotion SCS to IAS
5.14 During 2024, this Department made concerted efforts to make appointment from SCS/Non-SCS category to IAS. As a first step towards that, all the proposals for determination of vacancies received from cadres/ segments were finalized. As on 01.01.2024, against 2077 posts earmarked for being filled through Promotion/ Selection to IAS, a total of 1555 officers were in position. Against the shortfall of 552, this Department has made 138 appointments till 31.12.2024.
5.15 Inter cadre deputation: –
Inter-cadre deputation will be available to the officers only after completion of nine years of service in his or her cadre and before reaching pay at Level 14 of the Pay Matrix in his or her home cadre. The total allowable period of inter-cadre deputation in the entire career of the officer shall be five years.
During the period from January 2024 to December 2024, approval of the Competent Authority has been obtained on ten proposals of fresh/extension of inter cadre deputation.
5.16 Inter cadre transfer: –
Inter-cadre transfer shall be permitted for members of All India Service officers on marriage to another member of an All India Service, where the officer or officers concerned have sought a change. Inter-cadre transfer shall also be permitted on grounds of extreme hardship in the rarest of cases. All India Service officers belonging to North East State and borne on any Cadre including North East Cadres may be allowed change of cadre to one of the cadres in North East except their Home State subject to availability of deficit in the insider quota. However, no officer shall be allowed change of cadre to any joint cadre in case he/she belongs to one segment of such joint cadre. Further, Inter-cadre transfer shall not be permitted to the home State of the officer.
During the period from January 2024 to December 2024, approval of the Competent Authority has been obtained for 17 Inter cadre transfer proposals.
5.17 Smart Performance Appraisal Report Recording Window (SPARROW):
5.17.1 SPARROW is an online system based on the comprehensive performance appraisal dossier maintained for IAS officers. The system aims at bringing greater transparency in the recording of performance appraisals of the officers, eliminating loss of Performance Appraisal Reports (PARs) during transition, ensuring better monitoring and timely completion of PARs and providing easy and real time access to the PARs by authorized stakeholders. This system is not only user friendly but can be accessed uninterruptedly through an internet enabled computer system from anywhere, anytime, which reduces the delays in processing of PARs by officers concerned. The system was launched with effect from 01.04.2014 and was initially linked to the intra-IAS database enabling the PAR form to be pre-populated with the existing information. Subsequently the responsibility to update the requisite details in respect of officers was passed on to the Employee Master Data (EMD) manager of the respective Ministry or Department / State Cadre. In order to make the system hassle-free and more user-friendly, the system has been enabled with e Sign (electronic Signature), an Aadhaar based authentication service.
5.17.2 For ensuring recording of PAR in a timely manner by all the authorities, auto-forwarding of PARs has been implemented vide AIS (PAR) Amendment Rules, 2007 as amended from time to time.
5.17.3 As on 31.03.2025, the total number of the electronically generated PARs for the Assessment Year 2024-25 is 9191.
Immovable Property Returns (IPR) Module
5.18 As per Rule 16(2) of AIS (Conduct) Rules, 1968, IAS officers are required to submit IPRs every year as on $1^{\text {st }}$ January and latest by $31^{\text {st }}$ January of the year, in respect of the preceding year. Since the year 2011, the IPRs of the officers are being uploaded on the Department’s website. Subsequently, an IPR Module has been introduced for filing the IPRs online by the officer’s w.e.f. 1.1.2017, the navigation tab of which has been provided in the menu on Home Page of SPARROW. The officers can access the Module
by using the login ID and password, which are already provided to them for accessing the SPARROW and after filing the return, they are required to authenticate it by using either DSC or eSign.
5.19 Cadre Review of Central Group ‘A’ Civil Services:
A. The Department of Personnel & Training is the nodal agency of the Govt. of India for personnel management policies. One of the major function envisaged for the Department of Personnel \& Training is periodical review of Central Group ‘A’ Civil Services. Cadre review encompasses several key elements of cadre management such as manpower projection, recruitment planning, training, deputation, etc. It helps to realign a service to the ever changing organizational needs and maintain congruence between functional needs and legitimate aspirations of the officers.
B. Cadre Review Division facilitates the review of 67 existing Central Group ‘A’ Services/cadres in consultation with Department of Expenditure and acts as Secretariat to Cadre Review Committee headed by Cabinet Secretary.
C. In 2024, the achievements of the Department in this regard are as under:
(i) In 2024, cadre review proposals for 6 services [Central Engineering Service (CES), Central Electrical \& Mechanical Engineering Service (CE\&MES) and Central Architects Service (CAS) in Central Public Works Department (CPWD), Central Labour Service, Indian Trade Service and Indian Postal Service] were considered and recommended by Cadre Review Committee for obtaining approval of the Cabinet.
(ii) Approval of the Cabinet was obtained on cadre review of 7 Central services [Central Geological Service Group ‘A’, Geological Survey of India Chemical Service Group ‘A’, Geological Survey of India Geophysical Service Group ‘A’, Geological Survey of India Engineering Service Group ‘A’, Indian Radio Regulatory Service, Indian Corporate Law Service and Central Engineering Service (Roads)].
(iii) Due to proactive measures and regular meetings by DoPT, the overall pendency of cadre reviews has reduced from around 25-30 few years back to 7 , at present.
(iv) The proposals of cadre review of Central Water Engineering Service, Indian Defence Accounts Service, Indian Posts \& Telegraph Accounts Finance Service are under process at various stages. Meeting of the Cadre Review Committee has been held in respect of Central Water Engineering Service in 2025.
(v) A Consultative Workshop on improvement of personnel policies was organized on 16.04.2024 in ISTM. The workshop aimed to leverage the expertise and influence of stakeholders and dignitaries from Corporate/PSUs and to gather insights and suggestions from various Government Departments for meaningful improvements in the Government’s personnel policies.
(vi) 2 modules/courses on the major functions of the Division i.e. “Cadre Review of Central Civil Services” and “Non-Functional Selection and Upgradation for Organized Group” A Services have been made available on iGoT platform in 2024.
5(B)-CENTRAL SECRETARIAT SERVICE (CSS)
MANDATE OF CS-I DIVISION
CS-I Division is one of the important Divisions in DoPT responsible for the Cadre Management of the Central Secretariat Service (CSS) comprising the grades starting from the entry grade of Assistant Section Officer, and promotional grades of Section Officer, Grade-I (Under Secretary), Selection Grade (Deputy Secretary) and Senior Selection Grade (Director). The responsibilities involve, inter alia, Cadre management of CSS officers, viz. recruitment, promotion, posting, transfer, training, cadre clearance for deputation, etc., policy making, framing/amendments in CSS Rules and Regulations, encadrement / decadrement of posts in CSS & CSSS and meeting the CSS manpower requirement of Ministries/Departments.
5.20 The details of the grades comprising CSS and the sanctioned strength of each grade as on 31.03.2025 are as under: –
| S. No. | Grade/Classification | Pay Scale and Grade Pay | Sanctioned Strength as on 31.03.2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Senior Selection Grade (Director)/Group ‘A’ (Gazetted) | Level 13 -Rs. 118500-214100; | $738 #$ |
| 2 | Selection Grade (Deputy Secretary)/ Group ‘A’ Gazetted) | Level 12- Rs. 78800-209200; | |
| 3 | Grade-I (Under Secretary)/Group ‘A’ (Gazetted) | Level 11 – Rs. 67700-208700; | 1871 |
| 4 | Section Officers’ Grade/ Group ‘B’ (Gazetted) | Level 8 – Rs. 47600 151100 ; Level 10 Rs. $56100-177500$ (after 4 years of approved service) |
3639 |
| 5 | Assistants Section Officers’ Grade/ Group ‘B’ (NonGazetted) | Level 7 – Rs. 44900-142400″. | 6720 |
| Total | 12968 |
# The strength of Deputy Secretary/ Director is operated on combined basis with inter-se flexibility. CSS officers empanelled as Joint Secretaries are given in situ promotion in SAG grade at their current places of posting till they are placed under the Central Staffing Scheme. The maximum number of Joint Secretary (in-situ) posts earmarked to CSS is 40 . In the combined strength of DS/Director, the ceiling for Director Grade is 230 .
5.21 Cadre management of the grades of Under Secretary and above of CSS is centrally administered in the CS-I Division and that of the grades of Assistant Section Officer and Section Officer is partly centralized. Functions such as conduct of DPC for promotions, cadre clearance for deputations, acceptance of resignation, voluntary retirement, disciplinary matters, etc. in respect of these two grades are looked after by the respective Ministries/Departments (cadre units). However, the issue of zone of consideration for promotions, calculation of vacancies, and maintenance of reservation roster for these grades is done centrally by the CS-I Division.
5.22 Major developments/achievements during the year
i. Revised the Selection Grade Select Lists for the years 2013-2022 in respect of 1245 officers of CSS. Finalized the Selection Grade Select List for the year 2023 in respect of 102 officers of CSS.
ii. Prepared the panel of 225 Under Secretaries for promotion to the grade of Deputy Secretary for the year 2024.
iii. Revised the Senior Selection Grade Select Lists for the years 2018-2023 in respect of 486 officers of CSS.
iv. Prepared the panel of 108 Deputy Secretaries of CSS for promotion to the grade of Director for the year 2024.
v. Consequent upon DPCs for USSL 2024, a total of 312 Section officers have been promoted as Under Secretary during the year.
vi. Massive Review exercise of USSL-2003 onwards has been undertaken during the year to correct discrepancies, if any, and Revised USSLs upto 2017 have been issued.
vii. Consequent upon implementation of CAT Order in Preeti Wadhwa case and judgment of Hon’ble Delhi High Court in Sugam Arora case, the select lists of ASOs have been reviewed for the years 2009-17 and Common Seniority Lists of ASOs were finalised for these years
5.23 Promotions/ appointments:-
5.23.1 Director: 77 CSS Officers in the grade of Deputy Secretary have been included in the Senior Selection (Director) Grade Select List for the year 2024.
5.23.2 Deputy Secretary: 110 CSS Officers in the grade of Under Secretary have been included in the Selection (Deputy Secretary) Grade Select List for the year 2024.
5.23.3 Under Secretary: 312 officers were promoted to the grade of Under Secretary during the year 2024.
5.23.4 Section Officer: On the basis of the Section Officers Limited Departmental Competitive Examination (LDCE) for the year 2023 declared by UPSC on 01.07.2024, 455 officers have been promoted as Section Officer. Section Officer Select Lists upto the year 2023 (both under Seniority Quota and LDCE quota) have been finalized. Further, on the basis of the DPC recommendations received from the cadre units, 258 ASOs have been included in Section Officer Select List-2024 (Seniority Quota).
5.23.5 Assistant Section Officer: $75 %$ Vacancies in this grade are filled by Direct recruitment through Combined Graduate Level Examination (CGLE) conducted by the Staff Selection Commission (SSC), $15 \%$ vacancies through Seniority Quota and 10\% through Limited Departmental Competitive Examination conducted by SSC in ASO grade. Around 1000 DR ASOs were nominated for mandatory Foundational Training Programme conducted by ISTM. 1433 vacancies in ASO grade have been intimated to SSC to be filled up through CGLE. The appointment procedure will then be conducted in April, 2025. 83 vacancies in the grade of ASOs at various outstation offices were circulated out of which 38 have been filled.
5.24 Annual Performance Appraisal Report of CSS officers:
CS. I Division is the custodian of APARs of Under Secretary and above level officers of Central Secretariat Service (CSS). From 2018-19, online recording of APARs in the SPARROW portal has been made compulsory in all the grades of CSS. Since then, all officers of CSS are submitting their APARs through online SPARROW portal. As on 31.03.2025, 21080 online APARs for the year 2023-24 were generated in the portal.
5.25 Cadre Training Plan for CSS
A comprehensive Cadre Training Plan (CTP) is in place for CSS officers. The training programmes under CSS (CTP) are mandatory and linked to promotions. There is also a Foundation Training for DRASOs recruited through Staff Selection Commission through CGLEs.
5.26
ISTM is the nodal agency for training of CSS officers, including foundational training for DRASOs. During the year 2024-25(as on 31.03.2025), ISTM has conducted 35 training programmes under the CSS-CTP (including foundation training for DR ASOs) and 2120 officers were nominated for these training programmes.
5(C)-CENTRAL SECRETARIAT STENOGRAPHERS’ SERVICE (CSSS)
5(D)- CENTRAL SECRETARIAT CLERICAL SERVICE (CSCS)
MANDATE OF CS-II DIVISION
CS-II Division is responsible for the cadre management of the Central Secretariat Stenographers’ Service (CSSS) comprising the grades, starting from the entry grade of Stenographer Grade ‘D’, Personal Assistant (PA), Private Secretary (PS), Principal Private Secretary (PPS), Senior Principal Private Secretary (Sr.PPS), Principal Staff Officer (PSO) and Central Secretariat Clerical Service (CSCS) comprising the grades of Junior Secretariat Assistant (JSA) and Senior Secretariat Assistant (SSA).
The Cadre Management of CSSS Cadre involves recruitment, promotion, posting, transfer, meeting manpower requirement of Ministries/Departments having CSSS cadre posts therein, nomination for training in ISTM, policy making, framing/amending of CSSS Rules and Regulations.
The cadre management of CSCS involves nomination of JSA, SSA and ASO departmental examinations qualified candidates to various cadre units, promotion in the grade of SSA and ASO through Seniority quota, imparting advice to Cadre Authorities on individual cases of promotion, confirmation, seniority and other service-related matters, transfer of CSCS personnel to other cadre units under zoning scheme and inter-cadre transfer.
The proposals related to creation of posts in the personal staff of the Union Council of Ministers and conveying approval from personnel angle as well as proposals related to relaxation in criteria for appointment in the personal staff of the Union Council of Ministers are also the responsibility of this Division.
CENTRAL SECRETARIAT STENOGRAPHERS’ SERVICE (CSSS)
5.27 The details of the grades comprising CSSS Cadre are as under: –
| Grade | Level in Pay Matrix | Sanctioned Strength as on 31.03.2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Principal Staff Officer (PSO) | Level-13 (Rs.118500-214100) | 339 |
| Senior Principal Private Secretary (Sr. PPS) | Level-12 (Rs.78800-209200) | |
| Principal Private Secretary (PPS) | Level-11 (Rs. 67700-208700) | 1217 |
| Private Secretary (PS) | Level-8 (Rs. 47600-151100) | 1547 |
| NFSG (Level-10) granted to regular PS after 4 years of approved service |
Level-10 (Rs. 56100-177500) | |
| Personal Assistant (PA) | Level-7 (Rs. 44900-142400) | 1659 |
| Stenographer Grade ‘D’ | Level-4 (Rs. 25500-81100) | 2343 |
| Level-6 (Rs. 35400-112400) |
| NFSG (Level-6) granted after 5 Years of approved service to $30 %$ of sanctioned strength of Steno Grade ‘D’ |
|
|---|---|
5.28 Cadre management of the grades of PSO, Sr. PPS and PPS in respect of promotion, maintenance of APAR and Cadre clearance for various purposes is centrally administered by the Division. The Cadre clearance to Group ‘A’ CSSS Officers (PSO, Sr. PPS, PPS) for various purposes and maintenance of their APARs are also dealt by CS.II Division.
5.29 The other three grade viz. PS, PA & Stenographer Grade ‘D’ are decentralized into 56 cadre units. The Division coordinates the process of filling up the vacancies in these grades by prescribing the zone of promotion in respect of vacancies to be filed up though seniority quota on the basis of seniority-cum-fitness as provided in CSSS Rules, 2010 and CSSS Regulations, 2010. In respect of vacancies to be filled up through direct recruitment in Stenographer Grade ‘D’ as well as Limited Departmental Competitive examination in the grade of PA, vacancies are reported by this Division to Staff Selection Commission (SSC). For PS Grade Limited Departmental Competitive Examination, the vacancies are reported to the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) which conducts the examination and nominates the successful candidates to the Division for further appointment. All other issues relating to these grades are looked after by the respective Cadre Units.
5.30 Major developments/ achievements during the year 2024-25
(i) Finalization of long pending PA LDCE for the years 2018 to 2024 and nomination of 421 officers in SLY 2018 to 2022 of PA under LDCE Quota upto 31.03.2025.
(ii) Nomination of PAs of SLY 2018 and SLY 2019 to the extra batches of Level-II Training Programme to ensure their timely promotion as PS up to 31.03.2025.
(iii) Rationalization of Scheme of Foundation Training Programme (FTP) for Steno Gr D by replacing existing pattern of 8 weeks offline training with 3 weeks online training on i-GOT and 5 weeks offline training and covering more topics for enhancement of their knowledge and efficiency.
(iv) Clearance of pending backlog of imparting FTP to Steno Gr D by nomination of 1007 officials for the said training upto 31.03.2025.
(v) Review of the performance of 297 officers (PSO/Sr. PPS-99, PPS-198) under FR 56 (j)/(l) and Rule 42 of CCS (Pension) Rules, 2021 on the basis of inputs received from respective Ministries/ Departments and ACR/APAR Gradings for the last 10 years compiled by this Division.
A. Promotions/Appointments
The following numbers of promotions were made in various grades of CSSS from 01.04.2024 to 31.03.2025:-
| Sl. No. | Name of the Grade in which promotions made $(01.04 .2024$ to 31.3 .2025$)$ |
Number of promotions made |
|---|---|---|
| (i) | From Sr. PPS to PSO | 40 |
| (ii) | From PPS to Sr. PPS | 64 |
| (iii) | From PS to PPS | $177+12($ under PwBD Quota $)=189$ |
| (iv) | From PA to PS | $236+12($ under PwBD Quota $)=248$ |
(v) From Steno Gr D to PA – SQ 180
From Steno Gr D to PA – LDCE 378 (SLY 2018 – 148, SLY 2019 – 58, SLY 2020 – 130, SLY 2021 – 42, SLY 2022-49)
B. Recruitment
Offer of appointment was issued to 411 Stenographers Grade ‘D’ recruited through Stenographers Grade C and D Examination, 2023.
C. Training:
| Name of the Programme conducted by ISTM | Batches | Number of officials/ officers nominated |
|---|---|---|
| Stenographers Direct Recruit Foundational Training Programme (SDR-FTP) |
17 | 1007 |
| Level-I (Stenographer Grade-D to PA) |
1 | 32 |
| Level-II (PA) to (PS) | 11 | 466 |
| Level-III (PS to PPS) | NIL | NIL |
| Level-IV (PPS to Sr.PPS) | 2 | 72 |
| Level-V (Sr.PPS to PSO) | NIL | NIL |
D. Transfers under Rotational Transfer Policy
(i) Sr. PPS – 12
(ii) Following number of officers were transferred under RTP (on promotion) up to 31.03 .2025 at the time of promotion:-
(a) Sr. PPS to PSO – 10
(b) PPS to Sr. PPS – 35
(c) PS to PPS – 86
(d) PA to PS – 171
E. Grant of NFSG
24 officials in the grade of Stenographer Grade D of SLY 2017 have been granted NFSG w.e.f. 01.04.2024.
F. PwBD Reservation
The guidelines contained in Reservation Division’s OM No. 36012/1/2020-Estt (Res.II) dated 17.05.2022 and 28.12.2023 are being complied with in Direct Recruitment to the post of Steno Gr D and promotions to various grades of CSSS upto lowest rung of Group ‘A’.
Pursuant to the Reservation Division’s OM No. 36012/1/2020-Estt (Res.II) dated 28.12.2023 regarding reservation in promotion to PwBD on notional basis w.e.f. 30.06.2016, 18 supernumerary posts in PS Grade and 20 supernumerary Posts in PPS Grade have been created out of which 12 posts in each grade have been filled by promoting PwBD officers.
G. e-HRMS 2.0 Portal
This Division works in close coordination with eHRMS Division to successfully develop revamped cadre management portal i.e., e-HRMS 2.0 Portal. Inputs have been given to develop various modules such as cadre clearance and rotational transfer and on several other modules such as zone of consideration, DPC etc., work is in progress. This will not only help cadre management but also minimize manual interface, and bring in transparency.
CENTRAL SECRETARIAT CLERICAL SERVICE (CSCS):-
5.31 CSCS comprises the following grades: –
| Grade | Classification | Level in Pay Matrix | Sanctioned strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior Secretariat Assistant (SSA) | Group ‘C’ (Non-Gazetted) | Level-4 Rs. $25500-81100$ |
505 |
| Junior Secretariat Assistant (JSA) | Group ‘C’ (Non-Gazetted) | Level-2 Rs.19900-63200 |
773 |
| Total | 1278 |
5.32 The Central Secretariat Clerical Service (CSCS) is a decentralized cadre spreading over 42 cadre units. This Division coordinates the process of filling up the vacancies in the grade of Junior Secretariat Assistant under Limited Departmental Competitive Examination (LDCE) and Senior Secretariat Assistant under Seniority quota (SQ) and LDCE, as reported by the cadre units. Under the existing CSCS Rules and Regulations thereon, the CS-II Division prescribes the Zone of Promotion in respect of vacancies to be filled up in Senior Secretariat Assistant grade and Assistant Section Officer grade through seniority quota on the basis of seniority-cum-fitness. This Division also compiles vacancies from cadre units and intimates the vacancy to recruitment agency for promotion under Departmental Examination Quota for Junior Secretariat Assistant, Senior Secretariat Assistant and Assistant Section Officer and consequently nominates qualified candidates to cadre units.
5.33 Matters relating to personal staff of the members of the Union Council of Ministers:
This Division deals with proposals relating to approval for creation of posts from personnel angle and relaxation in eligibility criteria with the approval of Cabinet Secretariat, as well as issue of consolidated instructions in these matters.
5.33.1 Details of posts in personal staff of Union Council of Ministers are as follows : –
| S1. No. | Name of the post | Pay Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Private Secretary | Level -13 |
| Level -12 | ||
| 2. | Additional Private Secretary | Level -11 |
| 3. | Assistant Private Secretary | Level-10 |
| Level-8 | ||
| 4. | First P.A. | Level -8 |
| 5. | Second P.A. | Level-7 |
| 6. | Hindi P.A. | Level-6 |
| 7. | LDC/Clerk | Level-2 |
| 8. | Attendant | Level-1 |
| 9. | Peon | Level-1 |
5.34 Major Achievements during 2024-2025
A. Promotion:
a. Assistant Section Officer: 506 Senior Secretariat Assistants were promoted to the grade of Assistant Section Officer under Seniority Quota
b. Senior Secretariat Assistant: 235 Junior Secretariat Assistant were promoted to the grade of Senior Secretariat Assistant under Seniority and Departmental Examination Quota.
c. Junior Secretariat Assistant: 160 Multi-Tasking Staff were promoted to the grade of Junior Secretariat Assistant under Departmental Examination Quota.
B. Grant of NFSG: 238 officials in the Grade of Senior Secretariat Assistant were granted NFSG for the NFSG Select List Year 2023 and 2024.
C. Common Seniority List (CSL)/Select list (SL): CSL for 2017 to 2020 in the grade of Senior Secretariat Assistant and Select List for 2019 to 2023 in the grade of Assistant Section Officer were finalized.
D. Annual Performance Appraisal Report: For the first time, Annual Performance Appraisal Report was devised and implemented for the use of Multi-Tasking Staff of Central Secretariat.
E. Training: A ‘Dakshta’ module for Multi-Tasking Staff and Junior Secretariat Assistant of Central Secretariat was developed in consultation with i-GoT Karmayogi and Training Division.
F. Promotion to Persons with Benchmark Disability (PwBD): 12 PwBD candidates were promoted in the grades of Assistant Section Officer, Senior Secretariat Assistant and Junior Secretariat Assistant under PwBD Quota. Pursuant to the Reservation Division’s OM No. 36012/1/2020-Estt (Res.II) dated 28.12.2023 regarding reservation in promotion to PwBD on notional basis w.e.f. 30.06.2016, 8 supernumerary post in ASO Grade has been created which is for implementing the guidelines mentioned in the aforesaid OM.
G. Appointment in the personal staff of Union Council of Ministers: 121 cases for creation of posts/ relaxation in eligibility criteria were processed.
5(E)-STATE REORGANISATION DIVISION
MANDATE OF STATE REORGANISATION DIVISION
The State Reorganization (SR) Division in the Department of Personnel & Training is entrusted with the task of allocation of the State Governments’ employees (other than All India Services) between the successor States.
5.35 Andhra Pradesh and Telangana
(i) Allocation process is complete in respect of all the identified allocable categories. Now only a few individuals remain unallocated on account of pendency of litigation before the High Court / Supreme Court.
(ii) Aggrieved by the final allocation, employees of some State cadres have filed cases in the Hon’ble High Court for Telangana and Hon’ble High Court for Andhra Pradesh for revision of the final allocation. Details of the number of court cases pending in various Courts/ Supreme Court are as under: –
| No. of court cases pending in High Courts / Supreme Court as on 01.04 .2024 |
104 |
|---|---|
| Cases filed during the period | 3 |
| Cases disposed of during the period | 9 |
| Total No. of court cases pending in High Courts / Supreme Court as on $\mathbf{0 6 . 0 2 . 2 0 2 5}$ |
98 |
5.36 Uttar Pradesh / Uttarakhand
A large number of Court Cases were filed by the employees who had been allocated to a successor State against their option/domicile. However, as on date only 47 Court cases are pending before the concerned High Court(s)/ Supreme Court in respect of such employees of Uttar Pradesh / Uttarakhand.
Details of court cases pending in the Courts are as under: –
| No. of pending court cases in High Courts / Supreme Court as on 01.04 .2024 |
52 |
|---|---|
| Court cases filed during the period | 1 |
| Court cases disposed of during the period | 6 |
| Total No. of court cases pending in High Courts/Supreme Court as on $\mathbf{0 6 . 0 2 . 2 0 2 5}$ |
47 |
5.37 Madhya Pradesh / Chhattisgarh
Final allocation of State cadre employees has been completed in these States. The Advisory Committee was wound up on 01.04.2019. As per decision taken in the last meeting of the Advisory Committee, consequent upon winding up of the Advisory Committee, to deal with representation/Courts’ Order, if any, which may arise in future in allocation matters, the following mechanism is being followed:
(i) The representations of aggrieved employees will be considered by the Central Govt./State Governments, on a case-to-case basis in compliance of Court’s directions, if, the Hon’ble Courts pass any specific directions to this effect.
(ii) If any issue regarding allocation of employees of erstwhile State of Madhya Pradesh arises in future, it will be considered by the Central Govt. in consultation with both the Successor State Governments.
The number of pending court cases filed against their final allocation by the aggrieved employees is given below: –
| No. of Court cases pending in various High Courts/ Supreme Court as on 01.04.2024 | 74 |
|---|---|
| Cases filed during the year | 4 |
| Cases disposed of during the year | 7 |
| Total No. of pending Court cases in various High Courts/ Supreme Court as on 06.02.2025 | 71 |
5.38 Bihar / Jharkhand
Final allocation of State cadre employees has been completed in these States. The Advisory Committee was wound up on 26.04.2019, as per the decision taken in the last meeting of the Advisory Committee. Representations of employees aggrieved by the allocation, if any, are being decided on case to case basis in compliance of directions of the Hon’ble High Courts.
The number of pending court cases filed by the aggrieved employees against final allocation is given below: –
| No. of pending Court cases in various High Courts/ Supreme Court as on 01.04.2024 | 4 |
|---|---|
| Court Cases filed during the year | 0 |
| Court Cases disposed of during the year | 2 |
| Total No. of pending Court cases in various High Courts/ Supreme Court as on 06.02.2025 | 2 |
5(F)-RETRAINING AND REDEPLOYMENT AND DEPARTMENTAL COUNCIL (R&R AND DC) DIVISION
MANDATE OF R\&R AND DC DIVISION
R\&R and DC Division is enstrusted with the work of redeployment of surplus staff available on surplus roll of this Department and acceptance of surplus staff on roll following winding up of Offices under CCS(RSS) Rules, 1990.
REDEPLOYMENT OF SURPLUS STAFF
5.39 The Central Government employees rendered surplus along with their posts as a result of (1) administrative and financial reforms including inter-alia, restructuring of an organization, zero base budgeting, transfer of an activity to a State Government, Public Sector Undertaking or other autonomous organization, discontinuation of an on-going activity, and introduction of changes in technology; or (2) Studies of work measurement undertaken by the Staff Inspection Unit of the Ministry of Finance or any other body set up by the Central Government or the Ministry/ Department concerned; or (3) Abolition or
winding up either in whole or in part of an organization of the Central Government, are taken on surplus rolls and redeployed in suitable vacancies by this Department under extant rules. The scheme for redeployment of personnel declared surplus has been in operation since 1966 and has undergone various modifications and improvements. Salient Provisions of the Revised Scheme for Redeployment – 1989 are:
- Surplus employees enjoy first priority for absorption against the vacancies meant for direct recruitment;
- The need of interview etc. in appointments to the posts requiring recommendations of UPSC are decided by them. However, normally, appointments to other posts including Group-C posts are not subject to any test, interview, fresh medical examination or age limit;
- Prescribed educational qualifications may also be relaxed by DoPT, if necessary for redeployment;
- The provisions of relevant recruitment rules would be deemed to have been amended to the extent required for redeployment;
- A redeployed surplus employee enjoys protection of pay;
- Past service, however, do not count for seniority and promotion;
- There is no time limit for redeployment and a surplus employee can remain on surplus roll until he is redeployed or retired.
5.40 In order to make the Scheme of redeployment of surplus staff more effective, pro-active measures have been adopted to ensure that the prior claim of surplus staff is considered before any action for fresh recruitment is initiated by the Ministries /Departments /Offices of the Government of India covered under the scheme. Whenever no suitable surplus employee is available on the surplus roll of this Department, No Objection Certificate (NOC) is issued against the vacancies for Direct Recruitment reported by various Ministries /Departments /Organisations to enable them to proceed further.
5.41: LAUNCH OF ONLINE REDEPLOYEMNT AND SURPLUS MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (RSMS) – AUTO GENERATED ISSUANCE OF NOC/NAC FOR SURPLUS EMPLOYEES: –
The Redeployment and Surplus Management System (RSMS) online platform (URL: rsms.nic.in) was developed and launched in the event of “Chintan Varta” on 08.06.2023 with an aim to facilitate the Departments/Offices of Government of India to seek Non-Availability Certificate (NAC) from Department of Personnel & Training under Rule 3 of CCS(RSS) Rules, 1990. RSMS become live on 21.06.2023 and Departments/Offices are able to report vacancy details, search the database of available surplus staff awaiting suitable redeployment against reported vacancies under Rules 4, $5 \& 6$ of CCS (Redeployment of Surplus Staff) Rules, 1990 and get auto generated Non-Availability Certificate (NAC) or auto generated redeployment -cum-NAC letter (Gazetted / Non-gazetted) from RSMS.
5.42 Details of activities from 01.04 .2024 to 31.03 .2025 in respect of surplus employees are listed below:-
| Sl. No. |
Details of Activities | No of Surplus Employee(s) |
|---|---|---|
| $\mathbf{1}$ | Surplus employees available for redeployment as on 01.04 .2024 |
$25-\mathrm{MoF}(42-\mathrm{MoWCD}, 152-$ MoI\&B were accepted later in the year $)$ |
| $\mathbf{3}$ | Surplus employees nominated for redeployment | 83 |
| $\mathbf{4}$ | Surplus employees retired on SVRS/ superannuation in period 01.04 .24 to 06.02 .2025 |
0 |
| 5 | Surplus employees available for redeployment as on
$\mathbf{0 6 . 0 2 . 2 0 2 5}$ | 132 |
| — | — | — |
| 6 | Number of NOCs issued during the period as on $\mathbf{0 6 . 0 2 . 2 0 2 5}$ | 1690 |
CHAPTER – 6
SENIOR APPOINTMENTS UNDER THE GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
6.0 The Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) is not only responsible for the personnel policy of the Government of India but also looks after appointments at senior levels in the Government. For this purpose, the Establishment Officer in the Department is the Secretary to the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC). All proposals for senior appointments under the Government of India requiring approval of the ACC, as per the Government of India (Transaction of Business Rules) 1961, are processed through the Establishment Officer. These include Board level appointments in Public Sector Undertakings and appointment to posts at the level of Joint Secretary. In addition, all appointments by promotion, which require approval of the ACC, are also processed through the Establishment Officer.
6.1 The Establishment Officer is the Member Secretary of the Civil Services Board (CSB) chaired by the Cabinet Secretary. The Establishment Officer also assists the Screening Committee chaired by the Cabinet Secretary for considering cases of Foreign Assignments for All India Service (AIS) officers under Rule 6 (2)(ii) of the AIS (Cadre) Rules 1954 and para 2.1of the Consolidated Deputation Guidelines (CDG) for members of the organized Group A and Group B Services of the Central Government (Officers of JS level \& above).
THE CENTRAL STAFFING SCHEME
6.2 The Central Staffing Scheme provides a systematic arrangement for the selection and appointment of officers to senior administrative posts at the Centre, excluding posts which are specifically encadred for the organized Group ‘A’ services or filled by recruitment through the Union Public Service Commission, by borrowing from the All India Services and participating Group ‘A’ services. The raison d’être of such a scheme is the Centre’s need for fresh inputs at senior levels in policy formulation and programme implementation from diverse sources viz. the All-India Services and the participating organized Group ‘A’ Services. The officers serve for specified periods on deputation and return to their respective cadres at the end of their tenure. This two-way movement is of mutual benefit to the service cadres and the Government of India.
PLACEMENT AT MIDDLE \& SENIOR MANAGEMENT LEVELS
6.3. 470 Officers have been appointed under the Central Staffing Scheme during the year 2024-25, out of which 42 officers are at Secretary/Equivalent level, 32 officers at Additional Secretary/Equivalent level, 105 officers at Joint Secretary/Equivalent level and 291 officers at Director and below levels. Out of these, all the above appointment at the Middle \& Senior management levels, 217 officers belong to IAS and 253 officers are from the other All India Services including IPS and IFoS and the organized Group ‘A’ Services of the Government of India. These appointments include 110 women officers.
6.4. Total 35 meetings of various Experts Panels have been held during the year 2024-25 for assessment of officers belonging to 44 different batches of participating services for empanelment for holding the posts of Joint Secretary/equivalent at the Centre. The cases of 1284 officers of various services have been considered by the CSB.
NUMBER OF APPOINTMENTS MADE UNDER CENTRAL STAFFING SCHEME DURING THE LAST FIVE YEARS
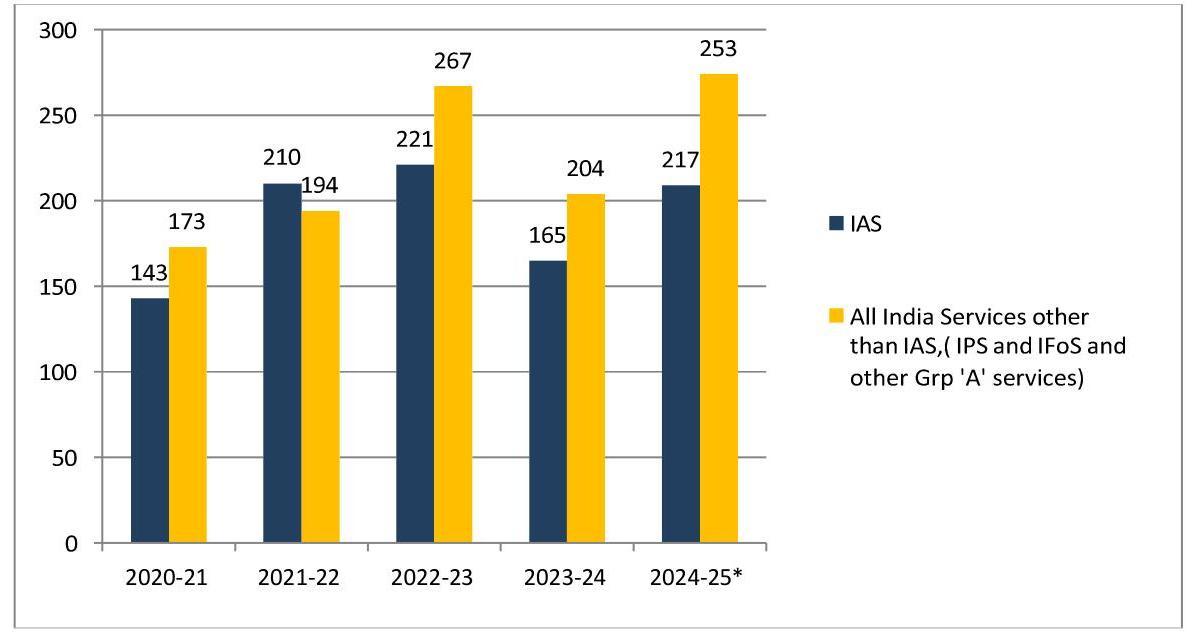
Figures for 2020-21 are up to 31/12/2020 for 2021-22 are up to 31/12/2021, for 2022-23 are up to 31/12/2022, for 2023-24 are up to 31/03/2024 and for 2024-25 are upto 31/03/2025.
CENTRAL DEPUTATION RESERVE
6.5 The Establishment Officers (EO) Division in the Department of Personnel & Training maintains an electronic database of the IAS officers \& of Group ‘A’ service officers working at the Centre under the Central Staffing Scheme. These records are maintained on the basis of orders/letters/notifications issued by the DOPT, various Central Ministries/Departments and the State Governments. The maintenance/ updation of this database is significant, as it helps in providing readily available digitized information in respect of all officers and also processing of cases for foreign appointments/assignments and training etc.
6.6. The Central Deputation Reserve statement in respect of Indian Administrative Service summarizes the state wise number of officers that are on central deputation vis-a-vis senior duty posts. It also indicates the number of officers presently on central deputation from each cadre.
CENTRAL DEPUTATION RESERVE FIGURES AS ON (31/03/2025)
| Sr. | Cadre | Total Authorized Strength |
Central Deputation Reserve |
No. of Officers at Centre |
Col. 5 as Percentage of Col.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
| 1 | A G M U T | 620 | 134 | 66 | 49 |
| 2 | Andhra Pradesh |
239 | 52 | 7 | 13 |
| 3 | Assam Meghalaya |
269 | 58 | 25 | 43 |
| 4 | Bihar | 359 | 78 | 27 | 34 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 202 | 44 | 10 | 22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Gujarat | 313 | 68 | 16 | 23 |
| 7 | Haryana | 215 | 46 | 13 | 28 |
| 8 | Himachal Pradesh | 153 | 33 | 16 | 48 |
| 9 | Jharkhand | 224 | 48 | 15 | 31 |
| 10 | Karnataka | 314 | 68 | 25 | 36 |
| 11 | Kerala | 231 | 50 | 23 | 46 |
| 12 | Madhya Pradesh |
459 | 99 | 41 | 41 |
| 13 | Maharashtra | 435 | 94 | 20 | 21 |
| 14 | Manipur | 115 | 25 | 15 | 60 |
| 15 | Nagaland | 94 | 20 | 9 | 45 |
| 16 | Odisha | 248 | 54 | 20 | 37 |
| 17 | Punjab | 231 | 50 | 19 | 38 |
| 18 | Rajasthan | 332 | 72 | 15 | 20 |
| 19 | Sikkim | 48 | 10 | 8 | 80 |
| 20 | Tamil Nadu | 394 | 85 | 26 | 30 |
| 21 | Telangana | 208 | 45 | 7 | 15 |
| 22 | Tripura | 102 | 22 | 16 | 72 |
| 23 | Uttar Pradesh | 652 | 141 | 33 | 23 |
| 24 | Uttarakhand | 126 | 27 | 10 | 37 |
| 25 | West Bengal | 378 | 82 | 7 | 8 |
| Total | $\mathbf{6 9 6 1}$ | $\mathbf{1 5 0 5}$ | $\mathbf{4 8 9}$ | $\mathbf{3 2}$ |
6.7. In addition to the appointments under the Central Staffing Scheme, 202 appointments as Chairman / CMDs / MDs / Deputy Governor / Chairman / Vice Chairman / Members / Executive Directors / Functional Directors / Non Official Directors were made on the Boards of Public Sector Undertakings and Banks/Financial Institutions during the period 01.04.2024 to 31.03.2025. During the same period, 41 appointments were made at the level of Chairman / General Managers / equivalent Members / Additional Members / Director General in the Railway Board / Zonal Railways. Besides, 440 Officers were also approved during the above period for additional charge / extension of tenure / non-extension of tenure / ad-hoc extension / rejection / termination of services of CMDs / MDs, Functional Directors, in the PSUs / Banks / Financial Institutions, and empanelment of GM/DG / AM in the Ministry of Railways. Out of these $\mathbf{6 8 3}$ appointments/Additional charge arrangements, 27 female officers were appointed.
NUMBER OF APPOINTMENTS TO THE POST OF CHAIRMAN-CUM-MANAGING DIRECTOR/MANAGING DIRECTOR ETC IN PSUs/BANKs
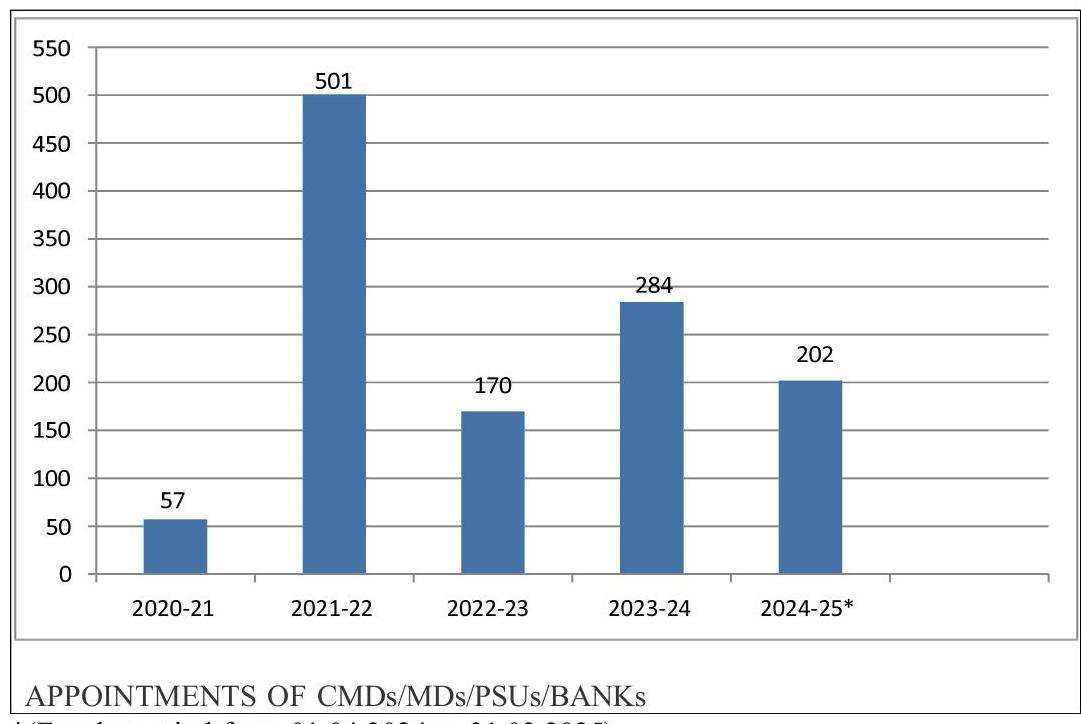
*(For the period from 01.04.2024 to 31.03 .2025 )
6.8. During the year 2024-25, 127 Member/Chairman/ Chief Executive Officer/Advisor were approved for appointment in various Autonomous Bodies, Administrative Tribunals, Labour Courts and Regulatory Bodies etc. Out of these, 17 are women officers.
6.9 A total of 2240 officers were approved for empanelment for promotion to posts of and above the level of Joint Secretary in various organized Central Services which are not included in the Central Staffing Scheme. Out of these, 288 are women officers.
6.10 During this period, based on the recommendations received from the Election Commission of India, more than 74 IAS officers posted in various Ministries/Departments on Central Deputation, have been appointed as General Observers during General election to Lok Sabha and in various States/UT Legislative Assemblies elections or Bye elections.
Chief Vigilance Officer
6.11 During the year 2024-25, 29 officers have been appointed as Chief Vigilance Officers (CVOs) in various organizations, 02 officers have been debarred and 24 officers have been given additional charge of the vacant posts of CVOs in various organizations. During the same period, 08 CVOs have been granted extension of tenure after completion of initial tenure and 07 cases of premature repatriation have been finalized.
REPRESENTATION OF WOMEN
6.12 While taking up empanelment of officers to Joint Secretary rank, it is ensured that women get adequate representation.
6.13 A total of $\mathbf{1 1 0}$ women were appointed under Central Staffing Scheme during the period 2024-25 including 38 women at Secretary/Addl. Secy. / Joint Secy. levels.
6.14 A total of 27 female officers were also approved for the period for appointment as CMDs/MDs, Executive Directors, Functional Directors, Non-official Directors in PSUs/Banks, Financial Institutions and at various post in Indian Railways.
6.15 A total of 305 women officers were appointed as Member / Chairperson / CEO, etc. in various Autonomous Bodies, Administrative Tribunals, Labour Courts, Regulatory Bodies and to posts of Joint Secretary Level and above in various organised central services excluding appointments under the Central Staffing Scheme.
6.1617 women were approved for appointment in various Autonomous Bodies, Administrative Tribunals, Labour Courts, and Regulatory Bodies etc.
CHAPTER 7
TRAINING POLICY AND PROGRAMMES
Mandate of Training Wing
7.1.1 The Training Wing of the Department of Personnel and Training is the nodal agency for training of government functionaries and is primarily responsible for formulating policies with regard to training. It also implements certain components of training directly. In the implementation of its mandate, the Wing has set the following objectives:
- Administering Policy matters in training
- Identification of functional areas of training
- Designing and implementing training programmes for officers involved in the priority development sectors
- Development of trainers and training capability
The goal of the Training Wing is to attain “Training For All”, which means that training would be imparted to all rungs of Civil Services starting from the lowest and cutting-edge to the highest in policy making.
7.1.2 Major Activities
1) Post Graduate Programmes in Public Policy/Sustainable Development/Management
2) Mid-Career Training of IAS Officers
3) Training Support under Training For All (TFA) Scheme through the following components:
State Category Training Programme (SCTP)
Trainers’ Development Programme (TDP)&Faculty Development Scheme (FDS)
Comprehensive Online Modified Modules on Induction Training (COMMIT)
Augmentation of Capacity of Training Institutions (ACTI)
4) In-service Training of IAS Officers
5) Advanced Professional Programme in Public Administration (APPPA)
6) Posting of Probationary IAS Officers as Assistant Secretary in Government of India
7) National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) – Mission Karmayogi
7.1.3 This Department is the nodal agency of Government of India for matters related to training of Civil Servants. For fulfilling this mandate, National Training Policy was formulated initially in 1996 and revamped in 2012. The 2012 policy underscores that for transforming the civil service, it is imperative to move to a strategic human resource management system, which would look at the individual as a vital resource to be valued, motivated, developed and enabled to achieve the Ministry/ Department/ Organisation’s mission and objectives.
National Program for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) – Mission Karmayogi
7.2 Union Cabinet on 02-09-2020 approved the National Program for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) – Mission Karmayogi, with the goal of securing efficient and effective public service delivery for citizens through a targeted approach of role specific capacity building of all civil service officials across the Centre and States, regardless of their ranks, cadre and geographies, transitioning from a ‘rulebased’ to a ‘role-based’ system of capacity development.
Under NPCSCB, DoPT is taking steps to build a competency model and identify the behavioural, functional and domain needs, evolving from the organization to the individual levels of the Government. An online learning platform (iGOT-Karmayogi) has also been developed to allow the Departments to provide competency linked training resources and opportunities to their employees.
NPCSCB has an overall budget of ₹510.86 crore (including Taxes), including technical assistance from the World Bank Group to the tune of ₹350 crore (approx.) in the form of loan.
Objective
7.3 Civil services are at the centre of all government activities – they are agents of policymaking and the executive hand that delivers on the ground. The skillsets and capacity of the civil servants play a vital role in service delivery, program implementation and performance of core governance functions. Recognizing this crucial responsibility, the NPCSCB aims to create a professional, well-trained and futurelooking civil service that is imbued with a shared understanding of India’s developmental aspirations, national programs and priorities.
The focus of NPCSCB is on promoting ease of living and ease of doing business, by considerably enhancing the quality and effectiveness of the citizen-government interface. This involves nurturing the continuous development and upgrading of functional as well as behavioral competencies among civil servants.
NPCSCB – Pillars & Philosophy
7.4 NITI Aayog, in its report on India@75, highlighted the need for reforms in training. The experience gained during the Covid-19 pandemic also brought forth the need for the civil service to be agile, capable of partnering with diverse stakeholders and to be up to date with new competencies. The NPCSCB is carefully crafted to lay the foundation for capacity building for future generations of civil servants so that they learn from the best practices across the world, while remaining connected to their roots.
The key philosophy of NPCSCB is to create an ecosystem of competency driven training and Human Resource (HR) management by offering holistic learning resources on iGOT Karmayogi platform, to align the knowledge, skills, and attitudes of a civil servants, based on a systematic assessment of the behavioral, functional and domain competencies required in their current role/position.
The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building has six key pillars –
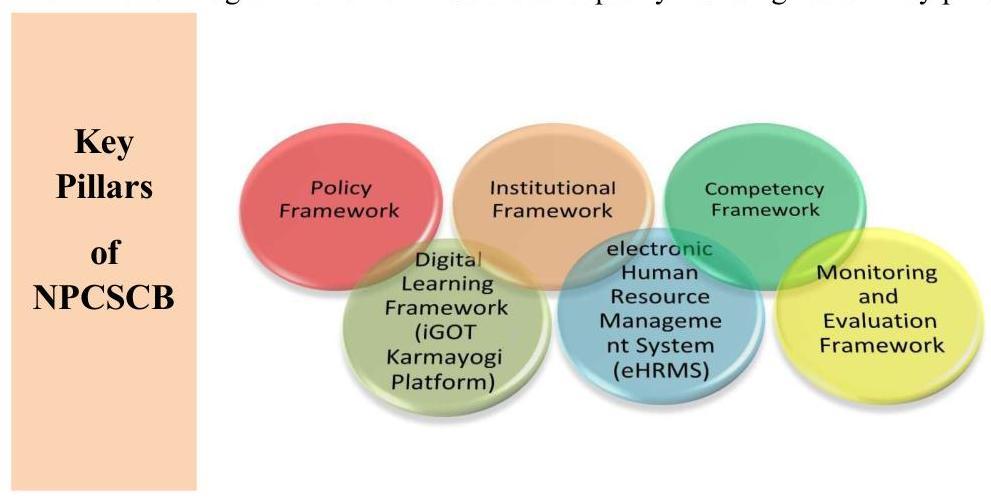
The NPCSCB aims to cover all civil servants across different Ministries, Departments, Organisations (MDOs) of the Union Government. The willing State Governments are also being enabled to align their capacity building plans on similar lines.
Policy Framework
7.5 A competency-based HR policy requires assignment of the right person to the right role at the right time. NPCSCB aims to create a robust policy framework towards implementation of such an HR policy in the Government. The policy framework will also enable adoption of modern technological tools such as a digital platform, artificial Intelligence, machine learning and data analytics for monitoring and
evaluation of the entire programme, especially quality of the learning content, assessment of user feedback and competency assessment.
Key Principles of the NPCSCB Policy Framework
To complement Physical Capacity Building with an Online Training framework.
Focus on ‘On-Site learning’ to complement ‘Off-Site learning’ whereby the civil servant learns in her job environment and only higher order learning is delivered through training institutions. To create an ecosystem of shared training infrastructure including teaching material and personnel.
To harmonise the functioning of all civil services training institutions (such as Central Training Institutions etc.) and enable them to partner with domestic and global institutions.
To calibrate all civil service tasks to a Framework of Roles, Activities and Competencies including skills (hereinafter referred to as FRACs)
To partner with all content creators including in-house sources, as well as the private sector to build a content marketplace on iGOT-Karmayogi.
To make available to all civil servants, agnostic to their geographical location and their position in the hierarchy, an opportunity to access training content in Hindi, English and other Indian languages.
To enable the individual learners to follow self-decided as well as mandated learning paths.
To make Mid-Career Training Programme (MCTP) mandatory for all services including horizontal and combined programs amongst services.
Competency Framework
7.6 The NPCSCB will facilitate delineating the Roles, Activities, and Competencies including skills by each Ministry/Department/Organisation of Union Government, for its various positions andits integration with the iGOT-Karmayogi Platform. The exercise aims to pinpoint the competencies required at each position in the government. Thereafter, work-allocation, notifications of vacancies etc. will be done through the iGOT-Karmayogi platform following the competency model. Further, capacity building content appropriate to the competency model will be provided by participating organisations on the 70:20:10 rule (an indicative $70 %$ training online, $20 \%$ on-the-job and $10 \%$ physical).
Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi Platform)
7.7 An online learning platform, i-GOT-Karmayogi, has been developed as an integral part of the Digital India stack for capacity building of all government employees. It provides anytime-anywhere-any device learning with the potential to train about 2.0 crores users which was hitherto not achievable through traditional measures. The Platform is also available as a mobile app on popular platforms for easy access
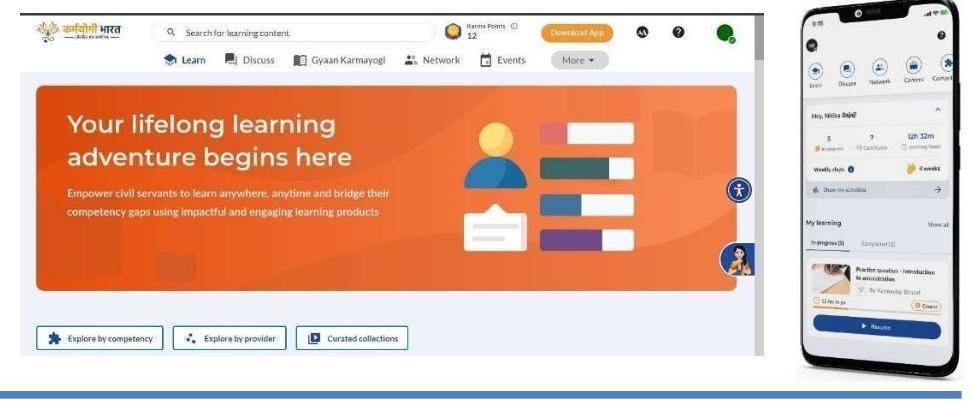
iGOT Karmayogi- Web Platform and Mobile App
The content is being curated by individual government ministries or organizations in-house or through knowledge partners. Carefully crafted and vetted content from best-in-class institutions, universities, private content providers and individual resources is also being made available as training modules. The platform is envisioned to eventually evolve into a vibrant and world class marketplace for content modelled on FRACs, supported by a robust e-learning content industry.
Institutional Framework
7.8 At present, the NPCSCB has operationalized the following institutional framework to manage the Programme and oversee its execution:

Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) – Karmayogi Bharat (KB)
7.9 The Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), Karmayogi (SPV-KB) was incorporated on 31.01.2022 under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013 as a 100% Government owned not for profit Company to own and manage the iGOT Karmayogi platform and other digital assets pertaining to the NPCSCB. The SPV-KB started functioning from July 2022 with the appointment of its CEO and the Board of Directors.
Composition of the Board of SPV – Karmayogi Bharat
Board of Directors of Karmayogi Bharat
a) Shri Subramanian Ramadorai, Former Advisor to the Prime Minister in the National Council on Skill Development:-Non-executive Director and Chairperson, Karmayogi Bharat.
b) Ms. Debjani Ghosh, President, National Association of Software & Services Companies (NASSCOM):-Non-executive Director Karmayogi Bharat.
c) Mr. Pankaj Bansal, Co-Founder and Group CEO of PeopleStrong:-Nonexecutive Director Karmayogi Bharat.
d)Dr. Nirmaljeet Singh Kalsi, IAS (retd.), Chairperson of National Council for Vocational Education and Training:-Non-executive Director Karmayogi Bharat.
e) Shri Govind Iyer (Consultant, Egon Zehnder):-Non-executiveDirector, Karmayogi Bharat.
f) Secretary, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India (Ex-officio): Non-executive Director Karmayogi Bharat.
g) Secretary, Department of Personnel and Training, Government of India (Exofficio) Director, Karmayogi Bharat.
h) Secretary, Capacity building Commission (CBC) (Ex-officio), Director Karmayogi Bharat.
i) Ms. V. Lalithalakshmi, CEO \&Director, Karmayogi Bharat.
j) CFO, Karmayogi Bharat \&Director, Karmayogi Bharat.
The Karmayogi Bharat has set about advancing its mandate to develop the i-GOT-Karmayogi Platform into a comprehensive resource for the Capacity Building of Civil Services in India.
Capacity Building Commission
7.10 Capacity Building Commission (CBC), an attached office of DoPT, has been functioning under the aegis of Mission Karmayogi since April 2021, formulating Annual Capacity Building Plans for all Ministries/Departments/Organizations (MDOs); to systematically capture the demand for training and transform and elevate the supply side of Capacity Building ecosystem, by reviewing, benchmarking and targeted upgradation of the various Civil Service Training Institutes (CSTIs):
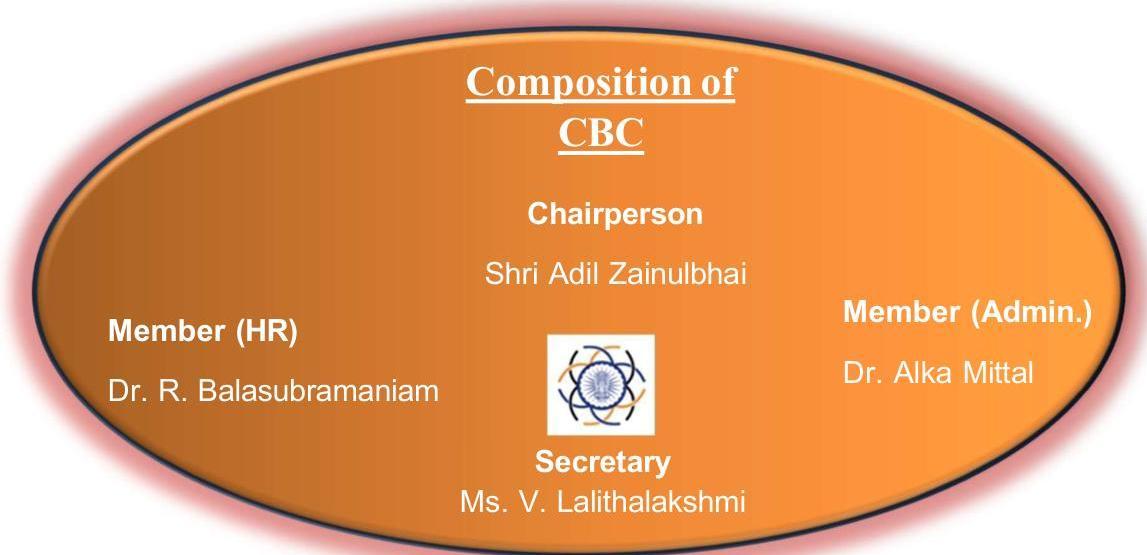
Developments on the iGOT Platform during the year are highlighted below –
7.11 The iGOT platform has shown consistent progress in onboarding users during the year with cumulative learner registrations crossing $\mathbf{7 5 , 0 0 , 0 0 0}$ during the Financial Year 2024-25
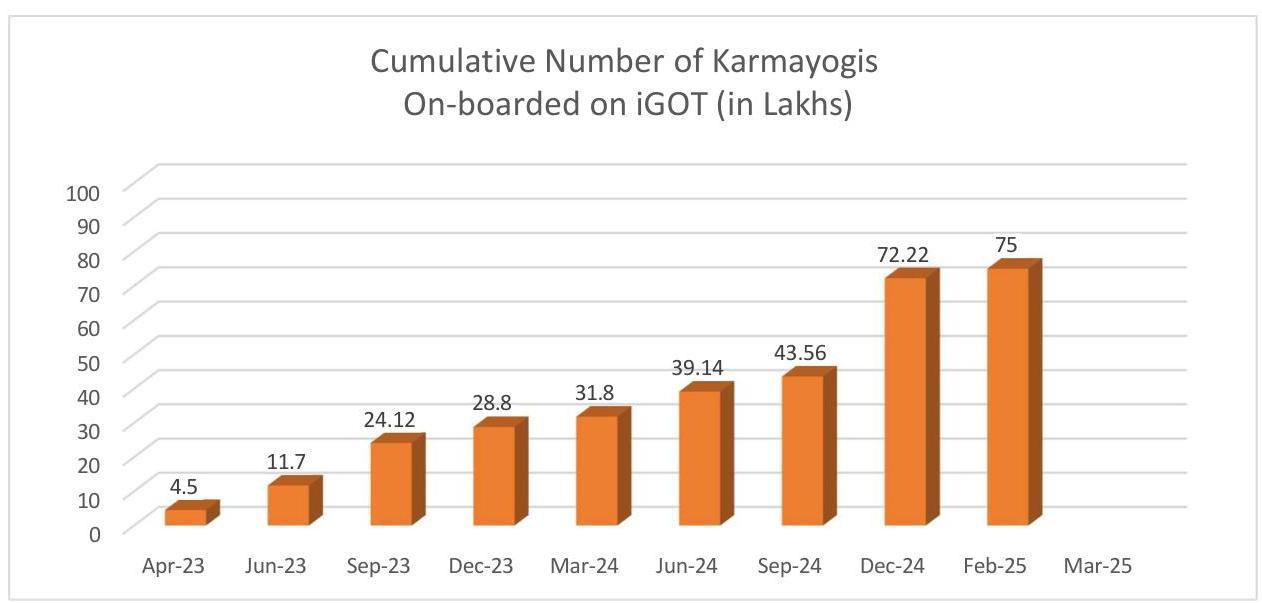
Content Generation and user engagement on the Platform has also shown encouraging progress.
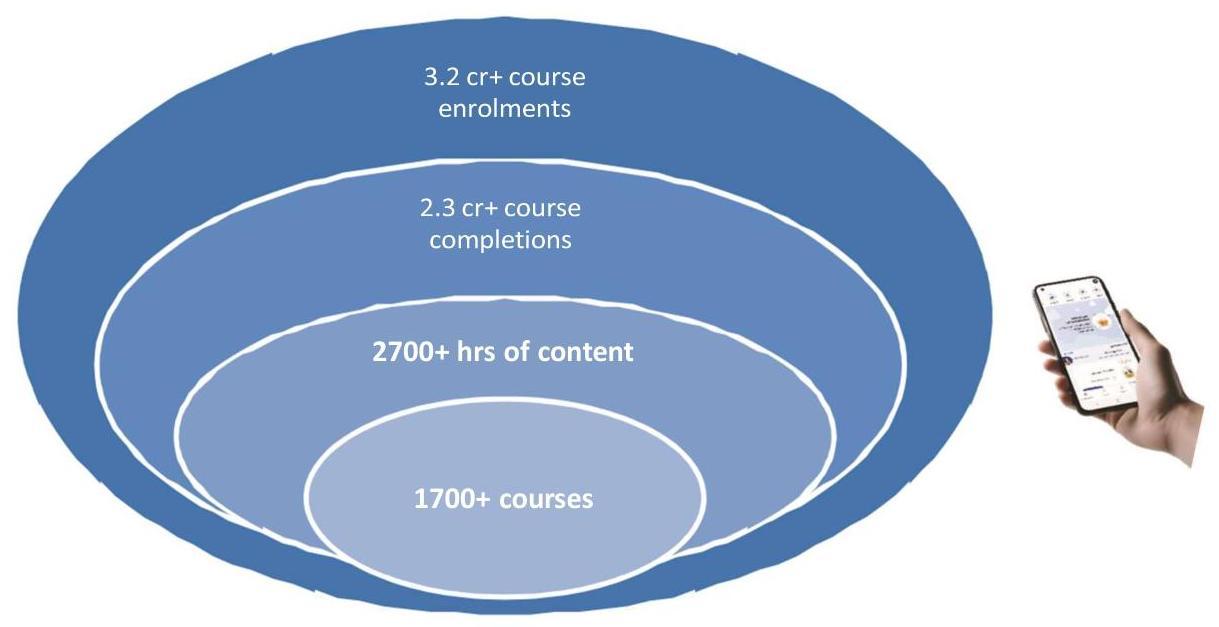
7.12 National Standards for Civil Service Training Institutions (NSCSTI)
a. Accreditation of CSTIs: CBC is closely collaborating with the Civil Services Training Institutions (CSTIs) for standardization of training and capacity building, pedagogy and methodology. This initiative caters to the supply side of the capacity building ecosystem. More than 336 Institutes have registered so far and 166 Institutes have been given accreditation, after the launch ‘National Standards for Civil Service Training Institutions’ portal by Hon’ble MoS (PP) Dr. Jitendra Singh on July 18, 2022.
b. NSCSTI Framework – The NSCSTI framework aims to introduce benchmarks on key parameters for CSTIs as a means for continuous improvement of these Institutions. This portal is aimed at setting common standards of excellence and promote organizational improvement through continuous self-assessment of Training Institutes. This would also institutionalize a forum to highlight best-practices and facilitate collaborative learning, and give direction for long-term strategic planning.

Initiatives under the Mission Karmayogi during F.Y, 2024-25
7.13 The major activities during the financial year 2024-25 under Mission Karmayogi are highlighted below:
Monitoring and Evaluation framework
7.14 The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework have been prepared and circulated to all the stakeholders. The key stakeholders of the M&E for Mission Karmayogi are the DoPT, CBC, SPV-KB, MDOs, and CSTIs. DoPT is the nodal agency that will oversee the monitoring and evaluation of Mission Karmayogi at the national level.
The performance of all users of the iGOT – Karmayogi platform will be monitored and evaluated on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). This will include the individual learner, the supervisor, the organisation, the peer group, the content provider, the content creator, and the technology service providers etc. The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework (M\&E Framework) aims to provide a structured approach to the monitoring and evaluation activities necessary for such a large and significant program.
Scoring System to incentivize the Ministries /Departments
7.15 Guidelines for execution of scoring system and provisional ranking to incentivize Ministries /Departments to uptake the usage of iGOT platform have been circulated. This system has been introduced to ensure that through their respective Capacity Building Units, the Ministries/Departments focus their efforts on the organizational KPIs.
The scoring system will play a crucial role in recognition of the top performing M/Ds which will further catalyze the adoption of the iGOT Karmayogi platform. This will quantify efforts and measures the success of Ministries/Departments in implementing capacity-building initiatives.
It focuses on four broad areas including, user onboarding, availability of KYM on iGOT, course completion, and implementation of Annual Capacity Building Plan (ACBP). The score will capture information across these parameters. Indicators across the parameters will have weights assigned to them,
and score for each M/D shall be the weighted sum of their performance on these criteria. The scores would be published on the iGOT portal.
Ministries /Departments shall be ranked based on their total. Top $5 \mathrm{M} / \mathrm{Ds}$ shall be recognized on the Civil Services Day for their outstanding performance in capacity building.
Initiatives of CBC
7.16.1 CBC has initiated the activities for creation of Annual Capacity Building Plans (ACBPs); CBU formed at 106 MDOs; draft ACBP approved in 103 MDOs, ACBP live on iGOT in 81 MDO and 14 Ministries /Departments have published courses on iGOT Platform on KYM. The ACBP for the 7 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) (viz. Ahmadabad, Bhubaneswar, Mysore, Rajkot, Pune, Nagpur and New Delhi) has been approved.
CBC undertook perception survey of $400+$ officers and their supervisors (of civil servants in their first posting) to understand their preparedness and performance of the young officers in their first postings. Innovations in Public Administration’ programme received 247 entries pan India (centre, state and local governments and group A, B and C).
Large Scale Citizen Centric Training for frontline workers at $(\sim 93,000)$ Ministry of Railways, $(\sim 1440)$ UT Police Forces and $(\sim 100)$ NYKS volunteers, were also planned and executed; Master trainers have been developed to institutionalize the process going forward.
Course launch on iGOT for Science & Technology Leaders and Emerging Technology organized. NonOfficial Director (NOD) summit was organized jointly with DPE and IICA for the training and orientation of $300+$ NODs of CPSEs. Drafted note on ‘Succession Planning \& Leadership Development for Maharatnas’. Numerous stakeholder workshops were conducted for the benefit of MoEFCC, ISRO /S\&T, IIPA, LBSNAA etc.
CBC has signed 32 MoUs and Sols with knowledge partners such as IIMs, IITs, ISB, QCI, ASCI, and NITI Aayog etc.
Amrit Gyaan Kosh:
7.16.2 Under its horizontal interventions, CBC has launched Amrit Gyaan Kosh, a comprehensive Knowledge Bank designed to serve as a repository of case studies, teaching notes, and supplementary learning resources in audio and digital formats. It curates best practices in the form of case studies to support the training and development of civil servants across the nation. In collaboration with Harvard Business School and the Stanford Leadership Academy for Development, CBC has trained faculty from CTIs and ATIs to develop high-impact case studies that enhance governance learning and decisionmaking. So far, 30 case studies have been onboarded on iGOT, with 60 more in progress, ensuring the creation of shared learning resources within the Capacity Building ecosystem.
Working with the states:
7.16.3 Recognizing the diverse governance challenges across different levels of administration, Mission Karmayogi has expanded its focus beyond central ministries to target 2.2 crore state-level civil servants and 50 lakh personnel across Urban Local Bodies, Zilla Parishads, and Panchayats. The iGOT platform plays a pivotal role in this transformation, equipping state and municipal officials with digital learning solutions tailored to their needs.
Tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoUs) between CBC, KB – iGOT and the states have been signed with 17 States/UTs for implementation of Mission Karmayogi. These states/UTs are Andhra
Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Meghalaya, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Uttarakhand, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Bihar, Odisha, Ladakh, Punjab, Puducherry, Haryana, Karnataka, and Assam.
CBC along with Integrated Government Online Training (IGOT) portal are also channelizing their efforts in capacity building of Urban Local Bodies under the aegis of National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB). CBC’s mission is to create optimal learning opportunities for each public functionary with the objective to build an agile and future-ready municipal civil service. A bottom-up approach is conceived to identify and deliver skill development landscape focusing on functional, domain and behavioural competencies for fulfilling responsibility of each designation under any Urban Local Body.
At the grassroots level, the Viksit Panchayat Initiative has been undertaken by CBC to drive systemic change by empowering 900 Panchayati Raj Institution (PRI) representatives across 60 Panchayats in Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, and Odisha. Leveraging AI-driven tools, real-time dashboards, and competency-based training, this initiative enhances service delivery, community participation, and financial self-sufficiency. With 40 e-learning courses developed on key governance themes, the program is pioneering a data-driven, citizen-centric approach to local governance.
Initiatives of DoPT
7.17 DoPT published guidelines for setting up of Centre of Excellence in certain niche domain areas in CSTIs to be identified in consultation with CBC. The Centre of Excellence (CoE) shall be a one-stop resource center for capacity-building of civil servants and the civil services ecosystem and research, consultancy/ advisory services in the identified domain/specialized area. Central CSTIs satisfying the eligibility conditions will be able to set up Centers of excellence in the specialized domain areas and emerging technology fields. The self-assessment proforma to be filled by the CSTIs and the Evaluation Metrics were issued on 22.10.2024.
DoPT has created 76 hours of e-learning content developed by Karmayogi Digital Learning Lab set up on 27 August, 2021 at ISTM in line with the Civil Service capacity building initiatives of DoPT. It includes 23 hours of e-content for various MDOs and 53 hours for DoPT. The lab covers an area of about 1000 square feet, equipped with server room, video recording facilities, fifteen (15) workstations with state-of-the-art hardware, and software tools.
A Workshop was organized by DoPT on 03/10/2024 at CSOI with Capacity Building Unit (CBU) of all Ministry/Departments with an objective of facilitating and leading the effective roll out of capacity building interventions under Mission Karmayogi. The workshop aims to facilitate knowledge and experience sharing for achieving the goals of Mission Karmayogi.
7.18 Initiatives of SPV- Karmayogi Bharat
Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, Hon’ble Minister for Railways, Communications, Electronics \& IT, launched iGOT AI – an advanced AI-powered learning system designed to enhance capacity-building for government officials. It will give personal and unique course recommendations for civil servants when they $\log$ in on the platform.

The Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar became the first State/UT in the nation to launch a State Learning Week (SLW).
Launched by Chief Secretary Dr Chandra Bhushan Kumar, IAS, Andaman & Nicobar Administration, and Adil Zainulbhai, Chairman, Capacity Building Commission, this initiative emphasizes a strong commitment to capacity building and governance excellence.
Scheduled from 18th to 23rd March, SLW aims to inspire officials across the UT to actively engage in structured learning, driving professional growth and strengthening public service delivery.
As part of this initiative, all officials are encouraged to dedicate at least four hours to learning through iGOT courses and webinars during the week.
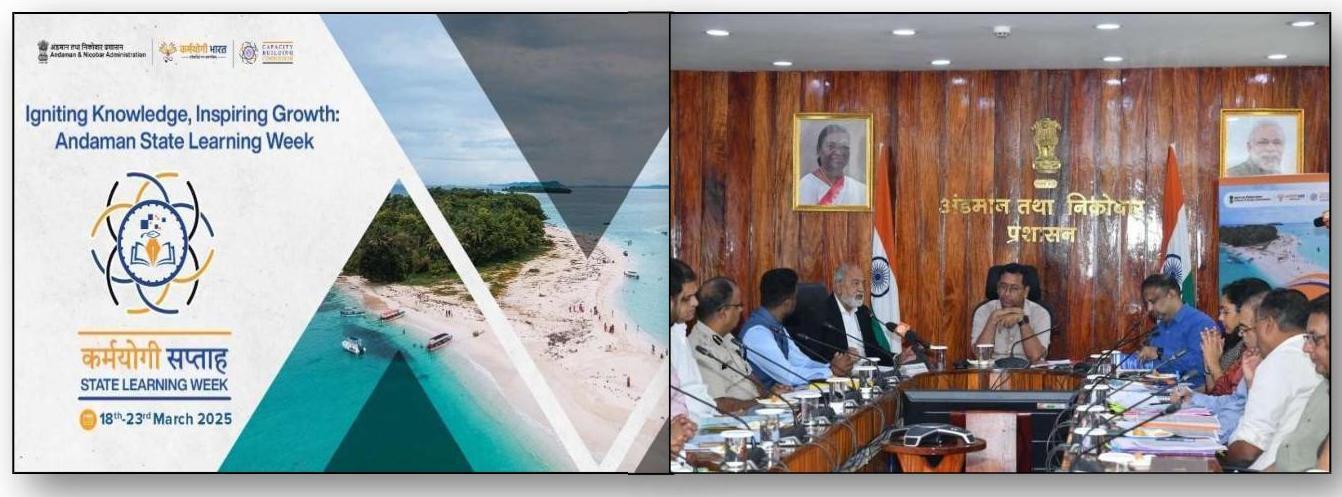

7.19 Central Sector Scheme – “Training for All”
Training Support is given under Training For All (TFA) Scheme through the following components:
a. State Category Training Programme (SCTP)
b. Trainers’ Development Programme (TDP) & Faculty Development Scheme (FDS)
c. Comprehensive Online Modified Modules on Induction Training (COMMIT)
d. Augmentation of Capacity of Training Institutions (ACTI)
7.19.1 “Training for All (TFA)” is a Central Sector Scheme sponsored by the Department of Personnel \& Training. The Scheme has been in operation since 1992. The objective of the Scheme is capacity building of all the Government officials at National and State levels through training interventions to provide training for all viz. developing management skills and knowledge in different areas for officers/officials of State Governments / State Public Sector Undertakings and State Autonomous Bodies; development of a cadre of professional trainers and resource persons in the country; improving functional knowledge, skill and attitudinal orientation of the frontline functionaries; imparting training, including training on soft skills, to the newly recruited officers/officials at cutting edge level functionaries; provide opportunity to trainers / faculty members of various Central and State Training Institutes to undergo short-term training programmes in the institutions of excellence within the country; augment the existing training mechanisms with online module-based training, coupled with certification to government servants; and provide financial support to the State Administrative Training Institutes (ATIs) for augmenting infrastructure.
7.19.2 State Category Training Programme (SCTP): Under this component, support is provided to State / Union Territory (UT) ATIs by way of sponsoring training programmes in the areas accorded priority by the Central Government. The programmes are designed for officers/ officials of State / UT Governments / State Public Sector Undertakings and State Autonomous Bodies to sensitize about new and important issues facing the society. The courses cover a wide range of subjects under broad thematic groups such as Audit \& budget: Resource mobilization and management, Child protection and welfare, Citizen centric services and community engagement, Emergency Healthcare, Drug abuse free India and Nasha Mukt Bharat, Local Govt. and Panchayati Raj, Social cohesion and Conflict Resolution, Visioin of Viksit Bharat, e-office, handling of course cases, use of AI tools in Governance, Ethics in Administration, Disaster Management, Right to Information, Gender Issues, Decentralized Planning, Role \& Responsibilities of DDOs, Financial Management, Environment \& Climate Change, e-Governance, Cyber Security, Leadership \& Team Building, Public Private Partnership, etc.
During the year 2024-25, this Department has sponsored 1189 SCTP courses to various State / UT ATIs on several thematic subjects.
7.19.3 Trainers’ Development Programme (TDP) \& Faculty Development Scheme (FDS): Recognizing the importance of trainers in the capacity building ecosystem, the Trainer Development Programme (TDP) was started in the mid-eighties and institutionalized in 1990s. Over a period of time, indigenous mechanisms were evolved for developing a cadre of professional trainers and resource persons in the country to create a cascading and multiplier effect by developing the Central / State / UT employees as Master Trainers (MTs) and Recognized Trainers (RTs) of various “Training of Trainers (ToT)” packages. The programme has gone a long way in embedding the Systematic Approach to Training (SAT) into the process of designing and imparting effective training to government officials. Under the component, financial assistance is provided to State / UT ATIs \& selected Central Training Institutes (CTIs) to develop a cadre of professional trainers and resource persons in various ToT packages.
The following ToT programmes sponsored under the TDP component are conducted by various training institutions across the country:
- Training Needs Analysis (TNA)
- Design of Training (DOT)
- Direct Trainer Skills (DTS)
- Evaluation of Training (EoT)
- Management of Training (MoT)
- Experiential Learning Tools (ELT)
- Mentoring Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Introduction to SAT courses
- National Training Policy (NTP)
During the year 2024-25, this Department has sponsored 179 TDP courses in various Central / State Training Institutions.
DoP&T has been implementing the FDS with a view to broadening and honing the knowledge and skill base of the trainers/faculty members working in the training institutes. All MTs/RTs developed by this Department under TDP, faculty members working in Central Training Institutions (CTIs) and State ATIs for conducting domestic trainings are eligible for support under the Scheme. The trainers / faculty are sponsored to undergo training in domestic short duration programmes / correspondence courses conducted by premier Institutions.
7.19.4 Comprehensive Online Modified Modules on Induction Training (COMMIT): A Blended Training Programme was conceptualized and launched in 2017 in the backdrop of the mandate of the National Training Policy (NTP), which stipulates that all civil servants from lowest level to the highest level will be provided training at the time of their entry into civil service and that priority will be given to the training of front-line staff, including training on soft skills, so as to improve customer orientation as well as quality service delivery to the citizen.
The blended course allows officers and faculty to take advantage of flexibility and convenience of an online course while retaining the benefits of the face-to-face classroom experience. The mission of COMMIT is to develop skills and attitude towards improving service delivery keeping the citizen at the centre. The advantage of such a blended programme is requirement of limited classroom space; to create new opportunities for officers who have had limited or no training to build the requisite skills, knowledge and attitude; and offer the convenience of online learning combined with the social and instructional interaction (e.g. motivational talk, understanding of the vision and proctoring assessments).
The COMMIT programme comprises of 15 e-courses ( 12 Generic and 3 Domain specific) of 28 hours duration. The COMMIT component has been aligned with the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) – Mission Karmayogi for hosting the programme on iGoT Karmayogi platform from FY 2023-24. Some financial support was given for registration and 8 hours orientation-cum-registration session during 2024-25. However, since then, no financial support is being given to Training Institutes for COMMIT programme as the programme is being implemented fully in online mode through iGOT Karmayogi platform.
7.19.5 Augmentation of Capacity of Training Institutes (ACTI): Earlier, the objective of this initiative was to provide support to State / UT ATIs for augmenting infrastructure in the form of hardware, software and courseware, networking of training institutions and consolidating the training ware; and developing case studies, e-learning packages, training films, organizing workshops, special programmes, seminars etc. Now, ACTI component has been reviewed and aligned with the objective of Mission Karmayogi to setting up of Digital Learning Lab/ Digital Studio for enabling ATIs to create e-content on identified competencies in local languages as also for the wider circulation /dissemination including that of Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) etc.. The maximum quantum of assistance to an ATI for a list of permissible items and HR cost for two persons for initial one year of setting up of Digital Labs/studio, under ACTI component is Rs. 74 Lakh (Approx.) in a financial year.
$90 %$ of the actual cost is to be borne by DoP&T and the remaining $10 \%$ cost as matching contribution shall be borne by the concerned ATI. Revised modalities highlighting all aspects of setting up of Digital Lab/studio by ATIs have been issued on 27.01.2025. The DoP\&T is further in the process of simplification of these modalities.
Long-Term Domestic Post Graduate programmes in Public Policy and Management
7.20 The courses sponsored by Department of Personnel \& Training under Long Term Domestic Program Scheme are as under: –
(i) Post Graduate Program in Public Policy and Management (PGPPM) at the Centre for Public Policy, Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore;
(ii) One-year Diploma Program in Public Policy and Sustainable Development (PP \& SD) or Two year M.A. (Public Policy and Sustainable Development) Degree Program at the TERI School of Advance Studies, New Delhi;
(iii) Post Graduate Diploma Program in Public Policy and Management (PGDM-PPM) at Management Development Institute, Gurugram;
(iv) One-year Advanced Management Program in Public Policy (AMPPP) at Indian School of Business, Hyderabad/ Mohali;
These programs have been envisaged to enhance the competence of Mid-Career Civil Servants in Public Policy and Management by –
(i) Broadening awareness of the latest trends in policy approaches,
(ii) Developing technical, analytical and leadership skills for public policy,
(iii) Providing opportunity in specialization and
(iv) Exposing them to alternative systems of public management in other countries.
During 2024-25, $9^{\text {th }}$ Batch of One year Advanced Management Program in Public Policy (AMPPP) commenced on $07^{\text {th }}$ July, 2024 at Indian School of Business- Hyderabad/ Mohali, which is being attended by 28 participants. $16^{\text {th }}$ Batch of Program in Public Policy \& Sustainable Development (PP \& SD) commenced on $20^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024 at TERI School of Advance Studies- New Delhi, which is being attended by 1 participant. $17^{\text {th }}$ Batch of Post Graduate Diploma in Management-Public Policy and Management (PGDM-PPM) commenced on $11^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024 and is being attended by 16 participants. $21^{\text {st }}$ Batch of Post Graduate Diploma in Management-Public Policy and Management (PGDM-PPM) commenced on $27^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024 and is being attended by 16 participants.
A workshop to review/revamp LTDP scheme with all the stakeholders was conducted on 23.10.2024 at Civil Services Officers’ Institute (CSOI), K.G. Marg, New Delhi.
Mid-Career Interaction between Armed Forces and Civil Services Officers
7.21 Mid-Career interactions programme (MCIP) between Armed Forces and Civil Services Officers are being organized at the Central Training Institutes/State Administrative Training Institutes and Defence Institutions in various parts of the country with the objective to benefit both the Armed Forces and Civil Services Officers by way of mutual learning from each other’s strength and also by imbibing the best points of each other’s work culture, ethos and customs. This, in the long run, is expected to help the participating officers to combat future challenges to national security in a better manner.
During the current financial year 2024-25, 4 programs have been planned- one by DoP\&T and three by M/o Defence i.e. each by Army, Navy \& Airforce. The MCIP were conducted at Signal Training Centre (Army), Jabalpur, Maritime Warfare Centre- Kochi (NAVY), Dr. MCR HRDI Telangana and College of Air Warfare- Secunderabad (Air-Force) on the themes ‘Enhancement of Border area infra to INCL vibrant village PGME for promoting border area tourism’, ‘Atmanirbhar Marching together towards amrit Kaal’,
‘Citizen Centric Governance, and ‘Space as a new frontier for national security and development’. Out of these, three programs have already been conducted and the fourth MCIP at College of Air WarfareSecunderabad (Air-Force) is scheduled from $17^{\text {th }}$ to $19^{\text {th }}$ February, 2025.
Overseas Training Programmes
7.2217 Officers were nominated for programmes supported by foreign agencies under bilateral programmes viz., Knowledge Co-Creation Program of Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) held in Japan under the Technical Cooperation Program of the Government of Japan and 6 officers were nominated for one year Masters Degree Course in “School of Government”, “School of Local Governance” and “Law” under Young Leaders Program (YLP) offered by Embassy of Japan held at the National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies, (GRIPS) Tokyo, Japan and the Kyushu University, Graduate School of Law, Japan
One-week In-Service Training (IST) Programme for Officers of All India Services, those working under Central Staffing Scheme and Officers of Central Secretariat Service (CSS) and Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS).
7.23 The Training Wing sponsors ‘In-Service Training Programme’ of ‘one-week duration’ in various ATIs/CTIs/ Premier Training Institutes in the country by inviting proposals from them on relevant themes. During the year (2024-25), 30 programmes (Physical/Offline mode) are being offered at 18 training institutions and 2 programs (Online mode) are being offered at 2 training institutions. These programmes provide middle and senior management level officers an opportunity to update their skills in areas of their choice-in sectors they are currently working in, or in areas they are expected to work in the near future, or in areas they want to specialize in. These programs also provide a valuable platform for horizontal and vertical knowledge sharing.
The primary objective of the IST program is to sensitize the participants to national concerns and the values enshrined in the Constitution; to provide for exchange of experience and adequate discussions on issues of values, ethics and attitudes; to make the participants more confident to face problems in their work areas and attempt solutions; and to train the participants to look at problems in an integrated manner and develop a systematic approach.
In the past, these programs have been offered in diverse and broad thematic areas: such as Environment & Natural Resource (management), Environmental Impact Assessment (development projects), Climate Change (preparedness), Green Mobility, Data driven decision making using data analytics, Cybercrimes and Cybersecurity, Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Education (Reforms \& challenges), Administrative Law, Competition Law, Corporate law, Dispute resolution, Agricultural \& Rural Development, Land Acquisition (rehabilitation \& resettlement), Supply Chain efficiency, Ethics in Public Governance and Administration, Fiscal Policy Management, Infrastructure Financing, Financial Markets Regulation, Procurement (procedures \& contract management), Project Analysis/Appraisal (risk analysis/management), Social Sector (financing/marketing), Digital Governance and Innovation, Egovernance (opportunities \& challenges), Leadership, Innovations in public service, Public Policy (Citizen-centric formulation/implementation), Public Private Partnerships, Smart Cities for Urban transformation, Managing Negotiations, Stress Management, Team Management and Development, etc.
Advanced Professional Programme in Public Administration (APPPA) At Indian Institute of Public Administration, New Delhi
7.24 The Training Wing has been sponsoring a ten-month Advanced Professional Programme in Public Administration (APPPA) at the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), New Delhi every year since 1975-76.
The objectives of this programme are to prepare the participants to make greater contribution to better governance, develop attitudes that focus on citizen services and also to strengthen leadership qualities in the civil service. It provides an opportunity to the participants to analyze major contemporary issues in Governance, learn about recent developments in the social sciences and their application in administration; review their experiences by making a critical analysis of environmental and other factors, apply relevant concepts, skills and techniques relating to policy, behavioral and administrative sciences and to demonstrate their creative and analytical abilities individually and in groups. It also seeks to develop interpersonal skills and sensitiveness to the needs of the people with a view to making administration more responsive and result oriented.
An officer with at least 10 years of Group ‘A’ (class-I) service and at least of the rank of Director/Deputy Secretary in the Government of India or holding an equivalent post is eligible for APPPA course. The Programme is also open for senior officers (Group ‘A’) from State Services.
This 10-month programme includes three semesters, rural and urban field visits in India. The $50^{\text {th }}$ APPPA course in this series commenced from July 1, 2024 and is scheduled to end on April 30, 2025 and 24 officers are attending for the said course.
7.25 Indian Institute of Public Administration
Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), New Delhi is an Autonomous Research and Training Institute of Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT), Government of India. IIPA was established on 29th March 1954 for promotion of Public Administration in post-colonial era and changing the colonial mindset of the Civil Services.
Presently, the Hon’ble Vice President of India Shri Jagdeep Dhankhar, is the President of IIPA and Hon’ble Union Minister of State, Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, Dr. Jitendra Singh is the Chairman of IIPA Executive Council. Shri Surendra Nath Tripathi, IAS (R), Former Secretary, Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs, Government of India is the present Director General of IIPA. IIPA Executive Council includes, among others, the CEO, NITI Aayog, Secretary (P), DoPT, Secretary (Expenditure) and Director, LBSNAA, Mussoorie.
The activities of IIPA include research, training, publication and dissemination of information in the field of Public Administration \& Governance. Every year IIPA conducts around 20-30 Research Studies which consists of evaluation of government schemes, policy advisory and policy analysis for different Ministries / Departments of Government of India, State Governments and International Organizations. IIPA Applied Research Wing gained a qualitative upswing with specific governance areas of concern. IIPA faculty completed around 15 Research Studies for various Central Ministries and State Governments till December 2024.
IIPA conducts over 137 training programmes last year for officers of Government of India, State Governments, PSUs, Defence Forces and Foreign Governments. IIPA has been conducting training for Chief Information Security Officers’ Deep Dive Training on Cyber security (Under Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative) (Sponsored by NeGD, MeitY, (Govt. Of India), Induction Training Programme on Public Administration and Governance cum Exposures visits for the Odisha Administrative Services Officers Trainees (Sponsored by Gopabandhu Academy of Administration Government of Odisha) Training Programme cum Exposure Visit For Gujarat Administrative Service (Sponsored by Sardar Patel Institute of Public Administration), International Capacity Building Programme on Innovations in Organizational Management, Foundation Training Programme of Department of Science \& Technology, Mid-Career Training Programme (MCTP) on Higher Management for IES Group A Officers Superintendening Engineers (Civil \& E/M) National CPWD Academy Central Public Works Department, Training cum Study Tour programme officers of State Council Of Educational Research \& Training (SCERT officers Patna), Training Programme for Assistant Audit Officer of Finance and Prosecution of BIPARD, IIPA has conducted 116 training programmes till December 2024.
Advanced Professional Programme in Public Administration (APPPA) is a 10-month long programme for Mid-Senior Civil Servants and Defence Forces Officers is the flagship programme of IIPA under the aegis of Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), Government of India. The $50^{\text {th }}$ APPPA commenced on $1^{\text {st }}$ July 2024. Hon’ble Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh interacted with the participants on $2^{\text {nd }}$ July 2024. Total Twenty-Four (24) participants are participating, majority of them being from all tri- services of armed forces, Indian Coast Guard and others from ITS, Indian Postal Services.
The Institute disseminates information, analyses viewpoints and knowledge related to public administration, governance, policy and public administration, governance, policy and development through its regular publications viz., monthly digital edition of IIPA Newsletter, quarterly editions of Indian Journal of Public Administration (IJPA) in association with Sage Publications, quarterly editions of Nagarlok, Documentation in Public Administration (DPA), biannual editions of Lok Prashashan (Hindi Journal) and quarterly editions of IIPA Digest. IJPA, Nagarlok and Lok Prakashan, all three are also listed in the UGC- Care List of Journals.
IIPA has prepared commendable Digital Infrastructure and it has now VC equipped eight Lecture Halls for conducting both online/offline programmes. In fact, IIPA has prepared all the Digital Material for APPPA and other Online Programmes.
IIPA receives grant-in aid from DoPT, Govt. of India under Salary, General and Capital heads. For BE 2024-25, IIPA has been allocated Rs. 10.00 crore under Salary, Rs. 2.50 crore under General and Rs.2.50 crore under Capital i.e. total of Rs. 15.00 crore.
7.26 Assistant Secretary Training Programme in Union Ministries
The Department of Personnel and Training is entrusted with the implementation of Assistant Secretary Training Programme to provide exposure to the young IAS officers to Government of India functioning at early stage(s) in their career after their District training and before they proceed for Phase II to LBSNAA.
This Programme started in 2015 as per the vision of Hon’ble Prime Minister when 2013 batch officers were posted as Assistant Secretary in Ministries/Departments. Starting with the 2021 Batch, the programme was made an integral part of induction training. So far, 1400 IAS officers have undergone the Assistant Secretary Programme since its inception. This programme is a crucial part of the 2-year induction training of IAS officers and has been meticulously designed to offer them a comprehensive understanding of the Government of India’s functioning, and to equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary to become effective leaders and change agents.
The objectives of this programme are to familiarize young officer trainees with the structure and functioning of the Central Government and to provide them with a national perspective on policy formulation and implementation. The hands-on training and exposure to flagship schemes, coupled with the practical experience gained through desk attachments and the preparation of policy analysis papers, are integral parts of the programme.
The Assistant Secretaries are attached with various Ministries/Departments of Government of India, handling flagship schemes/programmes/missions. They are given pre-joining reading material as part of their learning related to the concerned Ministries/Departments through “Gyan” portal of LBSNAA and iGOT platform which includes annual reports of last financial year(s), Acts administered and flagship schemes/important programme details of the concerned Ministries/Departments.
The emphasis in this programme is laid more on hands on learning by assigning them independent charge in the respective Ministries/Departments as Desk Officer/Under Secretary in the respective Ministries/Departments. They also get an opportunity for formal interaction with dignitaries like Hon’ble
President, Hon’ble Vice President, Hon’ble Prime Minister, Hon’ble MoS(PP) and heads of national agencies and organizations.
During this period, they worked exclusively as Desk Officer in the respective Ministries/Departments. The following activities were undertaken in the Assistant Secretaries Programme-2024 when 181 IAS Officer Trainees of 2022 batch were attached with 46 identified Ministries/Departments:
(i) The Inaugural Session chaired by Principal Secretary to Prime Minister – 20.05.2024.
(ii) The Inaugural Session was followed by Orientation Session for Assistant Secretaries 20.05.2024.
(iii) A visit to the New Parliament House on 30.05.2024
(iv) Call on with the Hon’ble Vice President of India – 03.06.2024.
(v) All Assistant Secretaries visited Rajghat on 08.06.2024.
(vi) All Assistant Secretaries visited Pradhan Mantri Sanghrahlaya on 15.06.2024.
(vii) A peer learning exercise was held where the Assistant Secretaries exchanged their knowledge about their Ministry/Department with their colleagues in sector wise groups – 15.06.2024 and 10.07.2024
(viii) All Assistant Secretaries visited NIA Headquarters (in groups) on 08.06.2024 and 22.06.2024
(ix) Interaction with Hon’ble MoS (PP) on 27.06.2024
(x) Half day attachment with Intelligence Bureau on 29.06.2024
(xi) Call on with the Hon’ble President of India – 01.07.2024
(xii) A cricket match was held between Cabinet Secretary XI and Assistant Secretary XI on 06.07.2024 at Siri Fort, DDA Sport Complex, New Delhi
(xiii) Half day Attachment with Ministry of External Affairs on 08.07.2024
(xiv) Half day attachment with IIPA on 10.07.2024 along with inter-sectoral peer learning.
(xv) Hon’ble Prime Minister interaction with the Assistant Secretaries on 11.07.2024 at Sushma Swaraj Bhawan, New Delhi.
(xvi) Valediction session on 12.07.2024 – the last day of Assistant Secretary Programme under chairmanship of the Cabinet Secretary
The Assistant Secretary Programme 2024 has prepared the officers to take on greater responsibilities and challenges in their cadre states. They are now equipped with a broader macro perspective and the ability to implement policies effectively, ensuring better inter-sectoral coordination and de-siloisation.
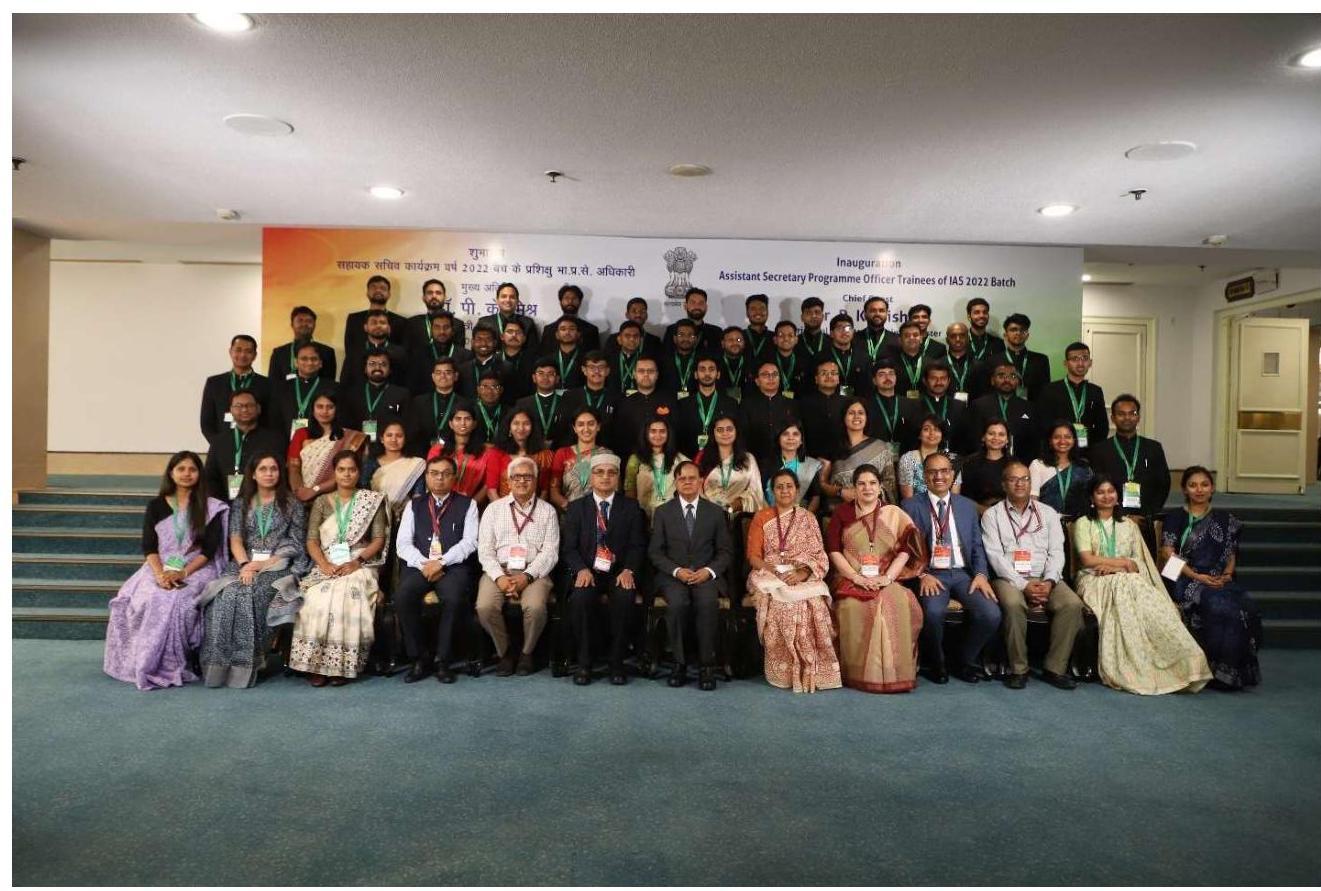

The Inaugural Session chaired by Principal Secretary to Prime Minister – 20.05.2024
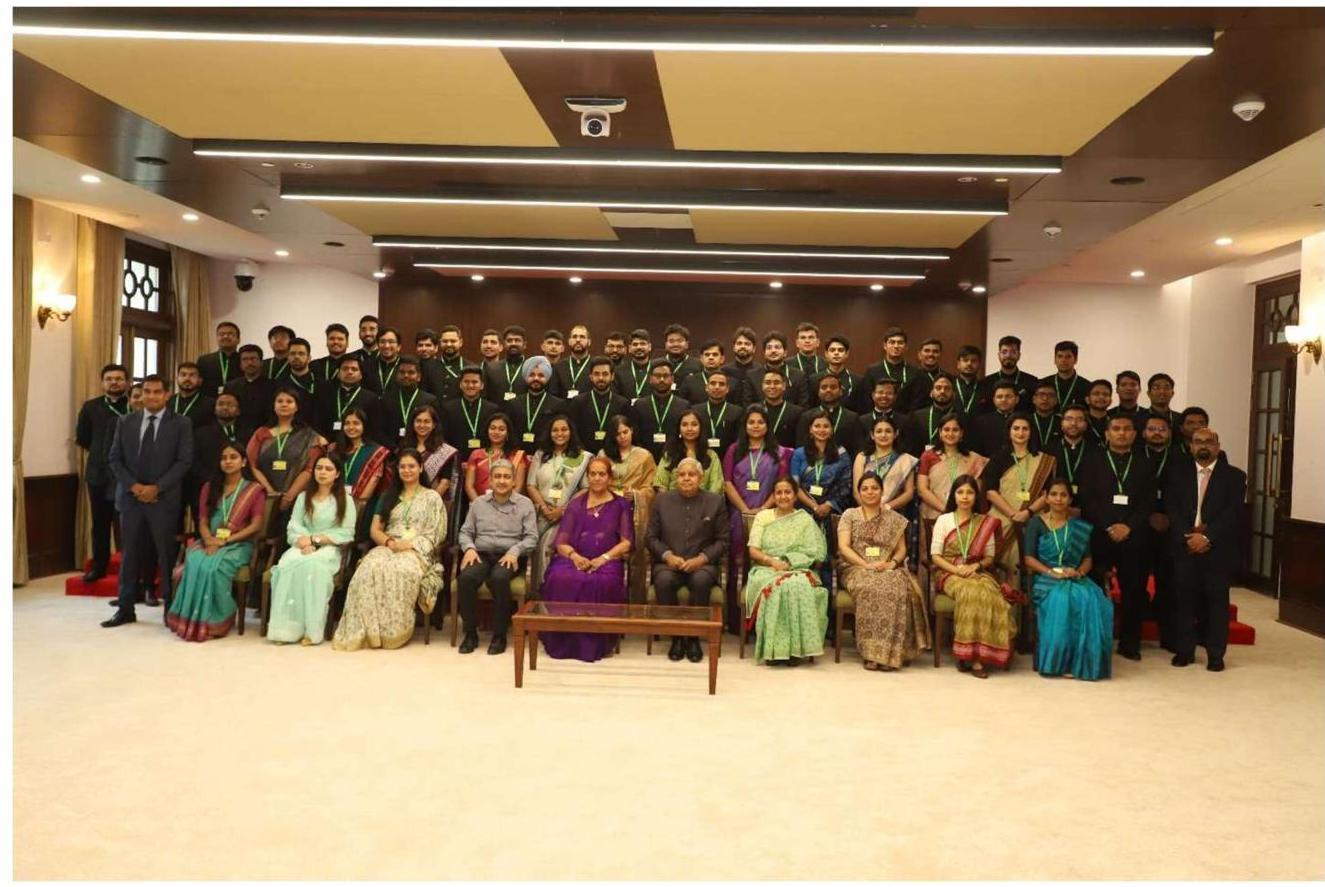

Call on with the Hon’ble Vice President of India – 03.06.2024
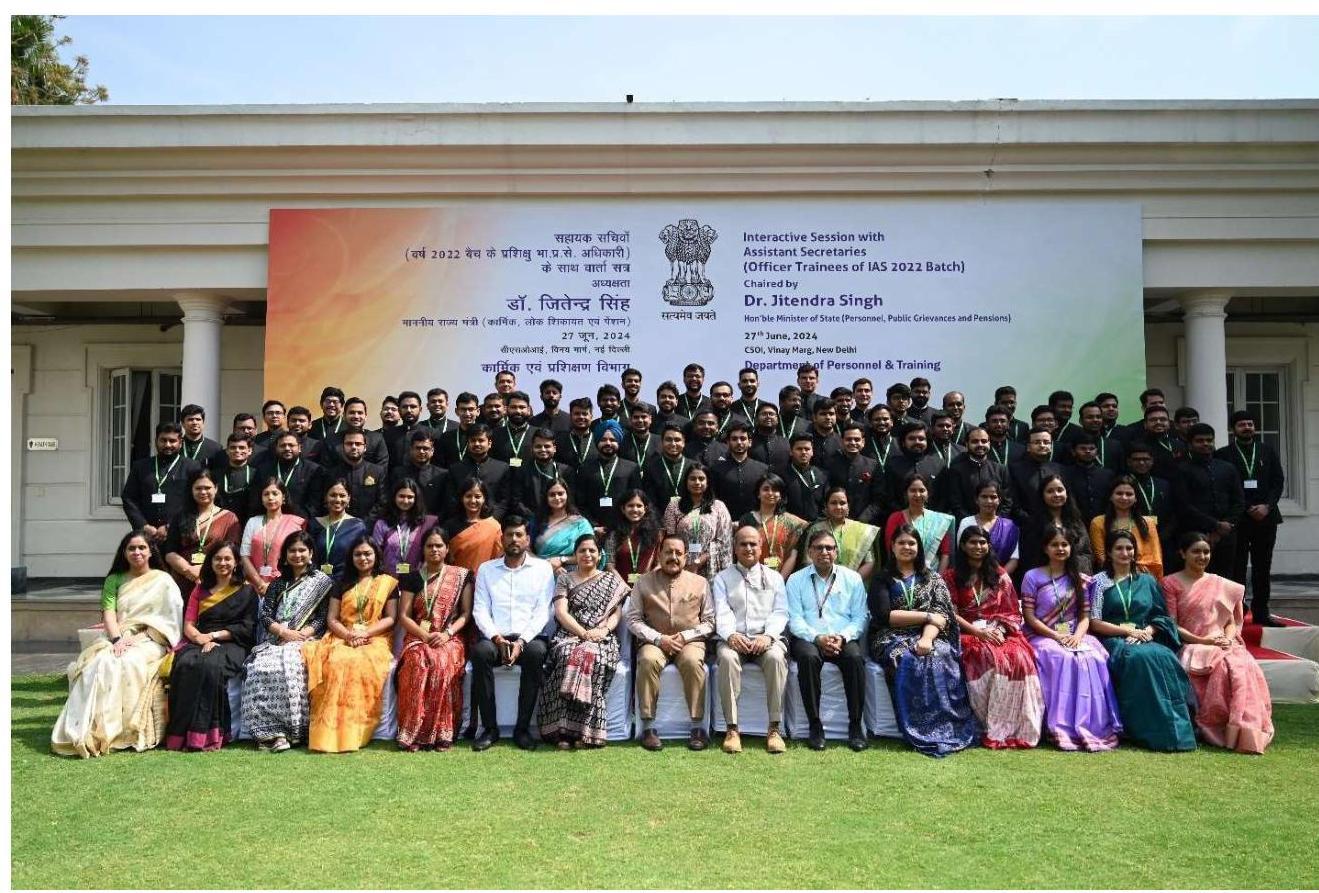

Interaction with Hon’ble MoS (PP) on 27.06.2024

Call on with the Hon’ble President of India – 01.07.2024
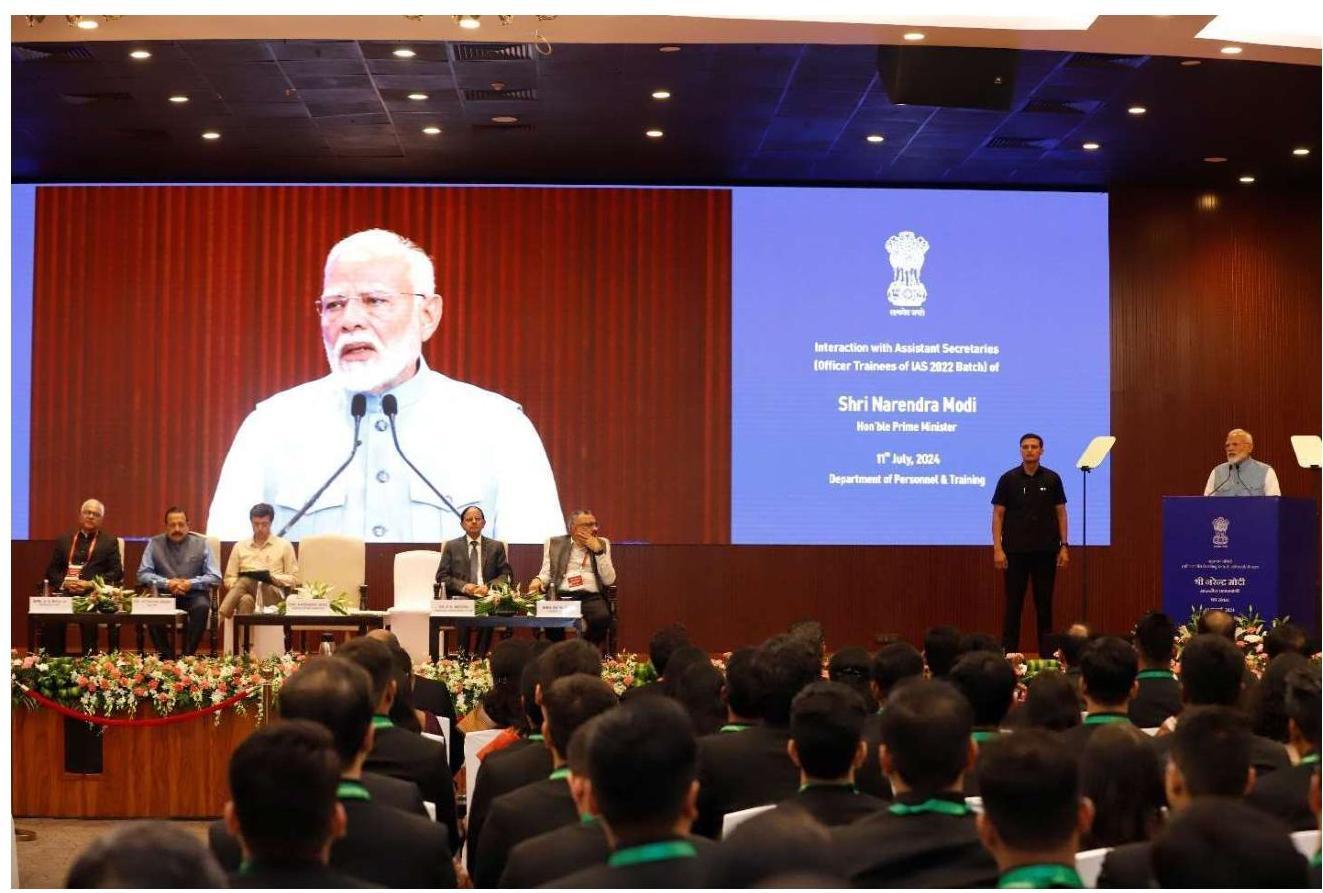

Hon’ble Prime Minister interaction with the Assistant Secretaries on 11.07.2024 at Sushma Swaraj Bhawan, New Delhi

Valediction session on 12.07.2024 – the last day of Assistant Secretary Programme under chairmanship of the Cabinet Secretary
CHAPTER 8
TRAINING INSTITUTIONS
LAL BAHADUR SHASTRI NATIONAL ACADEMY OF ADMINISTRATION, MUSSOORIE (UTTARAKHAND)
8.1.1 Introduction
The Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussoorie, is Government of India’s premier institution for the training of higher civil services in the country.
8.1.2 History of the Academy
On April 15, 1958, the then Union Home Minister Pandit Govind Ballabh Pant announced in the Lok Sabha, that the Government would set up a National Academy of Administration, where training would be given to all the recruits of the Civil Services. The Ministry of Home Affairs also decided to amalgamate the IAS Training School, Delhi and the IAS Staff College, Shimla to form a National Academy of Administration to be setup in Mussoorie’s Charleville Estate. On the first day of September, 1959 curtains were drawn on the training in Metcalfe House. Union Home Minister Pandit Govind Ballabh Pant was instrumental in effecting this shift to Mussoorie.
The Charleville Hotel was built in 1854 by General Wilkinson on the grounds of Chajauli Estate, a part of the abutting Chajauli Patti. The grounds of Happy Valley were acquired in 1904 by the brewer V.A. Mackinnon.
The main building of the erstwhile Charleville complex was destroyed in a fire in 1984. However, its old architecture can still be seen in some of the buildings inside the main campus of the Academy. The Ladies’ Block and the G.B. Pant Block were damaged in earthquake of 1991 and on these two sites, the two new buildings viz. ‘Dhruvshila’ and ‘Kalindi Guest House’ came up. A part of the “Happy Valley Club” extending right below the Charleville Hotel, now belongs to the Academy. This has the horse-riding ground, the shooting range and the sports club. The racecourse and polo ground, that was carved out of a hillside in 1904, were leased by the Uttar Pradesh government to the Academy. It is used, for housing the horse-riding establishment and conducting various sports events.
In October 1972, the name of the Academy was changed to “Lal Bahadur Shastri Academy of Administration” and in July 1973 the word “National” was added to it. The Academy is now known as the “Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration” (LBSNAA). There have been subsequent expansions and several new buildings have been constructed and others acquired over the years
8.1.3 Academy Mission
Mission
“We seek to promote good governance by providing quality training towards building a professional and responsive civil service in a caring, ethical and transparent framework.”
Serve the Underprivileged
“Be humane in your approach while dealing with people; be the voice of the underprivileged and be proactive in addressing any injustice against them. You can achieve success in this Specialize if you act with integrity, respect, professionalism and collaboration”.
Integrity
“Be consistent in your thoughts, words and actions which will make you trustworthy. Have courage of conviction and always speak the truth to even the most powerful, without fear. Never ever tolerate any degree of corruption, be it in cash, kind or intellectual honesty”.
Respect
“Embrace diversity of caste, religion, colour, gender, age, language, region, ideology and socio-economic status. Reach out to all with humility and empathy. Be emotionally stable; grow with confidence and without arrogance”.
Professionalism
“Be judicious and apolitical in your approach; be professional and completely committed to your job with a bias for action and results; and continuously pursue improvement and excellence”.
Collaboration
“Collaborate in thoughts and actions by engaging deeply with all to evolve consensus. Encourage others, promote team spirit and be open to learning from others. Take initiative and own responsibility”
8.1.4 Financial Statement of LBSNAA
Budget allocation of LBSNAA is made under “Demand no. 074 – Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pension”. The provision includes establishment related expenditure under Non-Scheme (Revenue). The budget allocation is made for various core activities of the Academy that include training programmes such as the Foundation Course, Mid-Career Training Programmes etc. Infrastructure related expenditure is provided under Scheme (Revenue) and Scheme (Capital) under the Scheme Improvement of Infrastructure and Upgradation of Essential Facilities at LBSNAA.
The details of actual expenditure for FY 2020-21, 2021-22, 2022-23, 2023-24, 2024-25 and allocation for financial year 2025-26 are as under:
(Figures in ₹ Thousands)
| $\begin{gathered} \text { S. } \ \text { No. } \end{gathered}$ | Non-Scheme (Revenue) / Establishment | Actual Expenditure | Budget Allocation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | 2023-24 | 2024-25 | 2025-26 | ||
| 1 | Salaries | 1,62,877 | 1,62,235 | 1,81,500 | 1,19,649 | 98,959 | 1,30,000 |
| 2 | Wages | 33,495 | 36,498 | 42,500 | 71,067 | 55,217 | 1,00,000 |
| 3 | Rewards | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,646 | 1,002 | 1,000 |
| 4 | Medical | 4,480 | 5,145 | 7,000 | 6,779 | 5,296 | 6,600 |
| 5 | Allowances | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67,192 | 68,095 | 90,000 |
| 6 | LTC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,560 | 1,569 | 2,500 |
| 7 | Training Expenses | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,246 | 16 | 200 |
| 8 | Domestic TA | 5,996 | 5,725 | 5,400 | 5,770 | 5,443 | 7,000 |
| 9 | Foreign TA | 84 | 0 | 233 | 0 | 290 | 500 |
| 10 | Office Expenses |
88,950 | 85,528 | 1,08,845 | 87,491 | 1,06,732 | 1,20,000 |
| 11 | Rent, Rates & Taxes | 1,998 | 1,964 | 1,998 | 2,980 | 1201 | 3,500 |
| 12 | Printing \& Publications | 350 | 636 | 644 | 633 | 412 | 1,000 |
| 13 | Rent for others | 0 | 0 | 0 | 716 | 123 | 1,000 |
| Other Admin Expenses | 200 | 199 | 290 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 14 | Digital Equipment |
0 | 0 | 0 | 1,817 | 367 | 1,500 |
| 15 | Fuel and Lubricants | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9,616 | 3,734 | 5,000 |
| 16 | Minor Civil \& Electric Works | 1,500 | 1,500 | 2,500 | 2,729 | 0 | 2,200 |
| 17 | Professional Services | 1,22,500 | 1,48,796 | 2,49,664 | 2,64,343 | 79,182 | 10,000 |
| 18 | Repair \& Maintenance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2,667 | 697 | 750 |
| 19 | Grants-inAid | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 0 | 500 |
| 20 | Bank Agency Charges | 0 | 0 | 0 | 521 | 0 | 500 |
| 21 | Other Revenue Expenditure |
5,200 | 3,999 | 3,767 | 4,960 | 4,223 | 5,500 |
| 22 | Salaries Canteen |
1,660 | 3,506 | 2,847 | 125 | 0 | 2,800 |
| 23 | Medical Canteen | 31 | 134 | 199 | 117 | 96 | 300 |
| S. No. |
Non-Scheme (Revenue)/ Establishment |
Actual Expenditure | Budget Allocation |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | 2023-24 | 2024-25 | 2025-26 | ||
| 24 | Allowance Canteen |
0 | 0 | 0 | 73 | 0 | 1,100 |
| 2020-21 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | 2023-24 | 2024-25 | 2025-26 | ||
| 25 | LTC Canteen | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 50 |
| 26 | Professional Services MCTP |
9,000 | 59,999 | 59,994 | $1,14,488$ | 62,656 | 80,000 |
| 27 | Professional Services ITP |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60,922 | $1,20,000$ |
| 28 | Professional Services DSTP |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4,036 | 30,000 |
| 29 | Swachhta Action Plan |
597 | 593 | 451 | 728 | 0 | 800 |
| 30 | Other Charges IT |
597 | 596 | 598 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 4,40,015 | 5,17,553 | 6,68,930 | 7,69,422 | 5,60,280 | 7,24,300 | |
| 31 | Scheme (Revenue) |
1,10,000 | 1,14,000 | 1,72,680 | 1,79,278 | 1,19,402 | 2,05,000 |
| 32 | Scheme (Capital) |
2,84,400 | 2,45,000 | 3,74,814 | 1,72,487 | 8,01,326 | 6,73,300 |
| 33 | Non-Scheme (Capital) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30,027 | 24,269 | 51,000 |
| Grand Total | 8,34,415 | 8,76,553 | 12,16,424 | 11,51,214 | 14,88,312 | 16,53,600 |
8.1.5 In Service Training Programmes
The Professional Orientation Training-IST Section has played an important role in enhancing the capacity, knowledge, and professional competencies of All India Service (AIS) (IAS, IPS and IFoS) Officers with minimum 4 years of service as on April 1, 2024 (upto 2019 batch) and up to the rank of Secretary to the Government of India/Chief Secretary and equivalent, Group ‘A’ Officers working under the Central Staffing Scheme in the Government of India and Officers of Central Secretariat Service (CSS)/Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS) (Of the level of DS/Sr. PPS and above) through well-structured In-Service Training (IST) programs. These programs have been instrumental in equipping participants with the tools and techniques to address evolving governance challenges while fostering gender equity, innovation, and sustainability.
8.1.6 Overview of In-Service Training Programme:
The IST Section successfully organized a series of impactful training programs during FY 2024-2025, catering to diverse areas of governance and administration. A total of 12 training programs were conducted, witnessing enthusiastic participation from officials across different Ministries/ Departments and various State Governments. The details of In-Service Training Programme are given below:
| $\begin{gathered} \text { Sr } \ \text { No. } \end{gathered}$ | Name of Course in IST Section | Course Date | No of Female Particip ants | No of Male Partici pants | Total Particip ants | Course CC/ACC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Five- Day Capacity Building and Sensitization Programme on Criminal Law Reforms | 24th – 28th June, 2024 | 10 | 38 | 48 | Dr. Anju Choudhary |
| 2 | One Week In-Service Training Programme on Rural Development: Saturation Approach of Government Programmes |
$\begin{aligned} & \text { 01-05 July, } \ & 2024 \end{aligned}$ | 14 | 40 | 54 | Dr. Bagadi Gautham |
| 3 | In-service Training Programme on “Delivering Good Governance in Himalayan & North-East States/UTs” | 15th to 19th July, 2024 | 3 | 33 | 36 | Shri Abhiram G Sankar |
| 4 | One Week Capacity Building In- Service Training Programme on Fostering Gender Responsive Governance |
22nd – 26th July, 2024 | 30 | 18 | 48 | Ms. Sanmuga Priya Mishra |
| 5 | In-Service Training Programme on Municipal Finance for Urban Administrators | 23rd to 27th September, 2024 | 27 | 32 | Dr. Bagadi Gautham | |
| 6 | Workshop on Roadmap for the Vision Document for Viksit Bharat (ii: 2047for Governance Sector (SgoS – 09) | 07th-08th November 2024 |
6 | 24 | 30 | Shri Ganesh Sankar Mishra |
| 7 | In-Service Training Programme on Transportation, Logistics and Multimodal Integration | 18th to 22nd November, 2024 | 10 | 39 | 49 | Shri Rajesh Meena Ms. Ankita Dhanda |
| 8 | Trainers Development Programme on “Mentoring” | 11th to 13th November, 2024 | 5 | 4 | 9 | Dr. Anupam Talwar |
| 9 | Yielding Demographic Dividend through Skill Mission IST- 12 | (2nd – 6th December, 2024) |
13 | 26 | 39 | Shri Shelesh Nawal |
| 10 | Building Infrastructure for Viksit Bharat | 16th to 20th Decemb er, 2024) | 10 | 37 | 47 | Shri Rajesh Meena Ms. Ankita Dhanda |
| 11 | Administration Challenges and Opportunities in Electricity Distribution Companies | 06th to 10th January, 2025) | 3 | 39 | 42 | Ms. Ankita Dhanda Shri Gautam Thapliyal |
Total Participants: 434 (104 Female, 330 Male)
Focus Areas: Capacity building, gender-responsive governance, criminal law reforms, rural development, municipal finance, and infrastructure development.
Special Emphasis: Promoting inclusive governance and sustainable development in critical sectors, including rural development, urban administration, transportation, and electricity distribution.
The IST Section continues to strengthen the skillsets and awareness of officials, contributing significantly to the national vision of “Viksit Bharat @ 2047.” With an unwavering commitment to excellence, the LBSNAA, Mussoorie aims to design and deliver even more comprehensive programs in the coming financial year.
8.1.7 $18^{\text {th }}$ Round of IAS Phase- IV (MCTP)
| Name of Course | $18^{\text {th }}$ Round of Phase-IV (MCTP) | |
|---|---|---|
| Duration (Specify Dates) | $18^{\text {th }}$ June $-13^{\text {th }}$ July, 2024 | |
| Name of Course Coordinator | Ms. Sowjanya | |
| Names of other members of Course team | Nand Kumarum, Shanmuga Mishra, and Abhiram G. Sankar | |
| Number of participants | Total $\quad$ Male $\quad$ Female 83 62 21 |
|
| Batches which participated | Officers of 2000, 2001, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009 Batches | |
| Course inaugurated by | Shri Sriram Taranikanti, Director, LBSNAA | |
| Valedictory Address by | Shri Sriram Taranikanti, Director, LBSNAA |
Aim
To equip officers who have completed 14 to 16 years of service effective transition to policy formulation and better implementation.
Course Objectives
- To equip officers who have completed 14-16 years in service with skills to enable them to be effective policy makers, align their work in lines with Mission Karmayogi.
- To promote an understanding of the aspirations of the people and to achieve it through Jan Bhagidhari, to move towards a developed nation (Viksit Bharat)
- To understand the evolving nature of governance given the technological advances and to bring about its diffusion and adoption in all their efforts in their respective departments by providing resilient leadership.
Week-wise design of the Course
$\square$ Inputs based on
$\diamond$ Last three years’ End of Course Reports, and
$\checkmark$ Session wise feedback of last three courses
$\square$ Aimed at leveraging on participants experience and knowledge and peer to peer learning
$\square$ Interactive and participative
$\square$ Attempt to provide strategic and global perspective.
Mix of speakers- academicians, senior officers, grassroots practitioners, industry: National and International.
8.1.8 $15^{\text {th }}$ Round of Phase-V (MCTP)
| Name of Course | $15^{\text {th }}$ Round of Phase-V (MCTP) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (Specify Dates) | $08^{\text {th }}-26^{\text {th }}$ April, 2024 | ||
| Name of Course Coordinator | Ms. Sowjanya | ||
| Names of other members of Course team | Shri Abhiram G. Sankar and Shri Romeo Vincent Tete | ||
| Number of participants | Total Male Female 53 38 15 |
||
| Batches which participated | Officers of 1991, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996 and 1997 Batches | ||
| Course inaugurated by | Ms. S. Radha Chauhan, Secretary, Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), Government of India | ||
| Valedictory Address by | Shri Ajay Kumar Bhalla, Union Home Secretary |
Aim
- To equip officers who have completed 26 to 28 years in service with skills to enable them to handle senior leadership positions and change management in lines with Mission Karmayogi.
- To promote an understanding of the impending challenges in governance, given the rapid changes in technology along with required piloting of organizational transformation in order to suit the vision of the country.
- To give an overall perspective of different sectors of economy and the strategic changes and roadmap needed for taking the country to the status of a developed economy.
Course Objectives
- Develop a sound appreciation of strategic management in government to cope with future challenges;
- Understand the nuances of public policy, ethics and regulation relevant for policy formulation and implementation;
- Appreciate the policy challenges and ecosystem facing the government in key sectors and their inter-relationship;
- Acquire better understanding of leadership and negotiation skills
- To Analyse and formulate policy and programs in a selected area/sector and to bring a transformatory change needed for comprehensive development.
- Have deeper understanding of thematic issues in the context of infrastructure, regulation, human resource development and economy,
- Broadening perspectives for high positions.
8.1.9 $21^{\text {st }}$ Round of MCTP Phase-III
| Duration | December $02^{\text {nd }}$ to December $27^{\text {th }} 2024$ |
|---|---|
| Name of Course Coordinator | Ms. Shanmuga Priya Mishra |
| Names of other members of Course team | Mr. Rajesh Meena Bujeta, Mr. Prem Kumar V.R, Mr. Gautam Thapliyal and Ms. Ankita Dhanda |
| Number of Participants | Total 155 |
| Male 34 Female 121 |
|
|---|---|
| Batches represented | $2009,2010,2011,2012,2013,2014,2015$ 2016 Batches |
| Course Inaugurated by | Shri Sriram Taranikanti, Director, Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration |
| Valedictory Address by | Smt. Radha S. Raturi, Chief Secretary of Government of Uttarakhand |
Aim
To equip officers with necessary skill – sets to serve at middle management for effective transition from District Administration to Head of Department with focus on Excellence in implementation and Citizen Centricity, to move towards a developed nation.
Course Objectives
- Opportunity to develop core strength in various sectors of governance and bridge the knowledge gaps in usage of technology in their respective domains.
- To strive for efficient service delivery and learning from experiences across the country.
- To strengthen communication, interpersonal and team building skills and appreciate the centrality of values in governance.
Week-wise design of the Course (should provide a schematic overview of main academic inputs)
Course Design
Week 1 Public Policy perspectives, Data of Decision Making, Education, Life of HODS and inter agency coordination
Week 2 PPP Projects, Revenue Generation, Urban Infrastructure, Ethical Dilemmas, Land & Agriculture, Skills \& MSME and Welfare Perspectives
Week 3 Health, Stress Management, Project Management, HR Management, Transport \& Logistics, Judiciary Interface, Group work and Interaction with Phase-I
Week 4 Personal Finance, Leadership \& Emotional Intelligence, Negotiation
8.1.10 Conference of Central Training Institutions (CTIs)
CTIs Conference – November 25, 2024
99th Foundation Course
Record of Discussion with Representatives from CTIs
Dated: $25^{\text {th }}$ November 2024
Venue: Sardar Patel Hall, Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussoorie
Conference Coordinator: Dr. Anupam Talwar, Deputy Director
Number of Participants: 16 Nos.
A Conference with representatives of CTIs was chaired by the Director, LBSNAA, Shri Sriram Taranikanti during the 99th Foundation Course on 25th November, 2024 at LBSNAA, Mussoorie.
The purpose of the Conference was, inter alia, to:-
i). Inform the respective CTIs about the inputs and focus areas of the 99th Foundation Course so that this information may help in curation of Phase I/ equivalent training courses for the Officer Trainees in their respective CTIs.
ii). Debrief and interaction by Officer Trainees with representatives of CTIs
iii). Ideas exchange and inputs on Capacity Building and Training of Civil Servants
List of participants from CTIs:
| Sr. No. | Name of Delegate (Shri/ Ms) | Central Training Institute |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Archana Gopinath, Course Director | Rafi Ahmad Kidwai National Postal Academy (RAKNPA), Ghaziabad |
| 2. | Sameer Mehta, Course Director | National Institute of Audit & Accounts (NAAA), Shimla |
| 3. | Shreyas Patel, Joint Director | National Institute of Defence Estates Management (NIDEM), New Delhi |
| 4. | Padamsing Patil, Joint Director | Institute of Government Accounts & Finance (INGAF), New Delhi |
| 5. | Anil Yadav, Deputy Director & Course Coordinator | Indian Corporate Law Service Academy, (ICLSA) Manesar |
| 6. | Satish Gurumurthy, Joint Director (OT Cell) | National Academy of Customs Excise & Narcotics (NACIN), Palasamudram |
| 7. | Kunal Angrish, Associate Professor & Course Director | Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy (IGNFA), Dehradun |
| 8 . | E. Sai Charan Tejaswi, Assistant Director (IS-I) |
Sardar Vallabh bhai Patel National Police Academy (SVPNPA), Hyderabad |
|---|---|---|
| 9 . | Abhay Deware, Deputy Director & ACD-1of $78^{\text {th }}$ Batch of IRS | National Academy of Direct Tax (NADT), Nagpur |
| 10 | Asheesh Pandey, Professor \& Head of Research Division | Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT), New Delhi |
| 11 | Anantha Sivaguru S., Sr. Accounts Officer (Training) \& Course Coordinator | National Academy of Defence Financial Management \& Regional Training Centre (NADFM), Pune |
| 12 | Rashmi Roja Thushara Nair, Course Director |
Indian Institute of Mass Communication (IIMC), New Delhi |
| 13 | Sathish Balakrishnan, Under Secretary | Sushma Swaraj Institute of Foreign Service, Ministry of External Affairs (SSIFS), New Delhi |
| 14 | Senthil Kumaresan, Sr. Security Commissioner- Training |
Sri Jagjivan Ram Railway Protection Force Academy (JRRPFA), Lucknow |
| 15 | Swadesh Kumar Singh, Sr. Professor (Transport Management \& IT) |
Indian Railways Institute of Transport Management (IRITM), Lucknow |
| 16 | Ashok Kumar, Jt. Director/Professor |
Arun Jaitley National Institute of Financial Management (AJNIFM), Faridabad |
INSTITUTE OF SECRETARIAT TRAINING AND MANAGEMENT
8.2 About ISTM
Established in 1948, Institute of Secretariat Training \& Management (ISTM) has the mandate to implement cadre training programmes of Central Secretariat Service (CSS) and Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS) and other Organized Services of the Central Secretariat. Further, the Institute is entrusted with the task of providing orientation training to the officers joining the Central Government under the Central Staffing Scheme for the first time as Deputy Secretary and Director and conducting DAKSHTA Programmes of CBC in phygital mode. The Institute also imparts training to the officers of the Central \& State Governments, PSUs, Autonomous Bodies, and the UT Administrations. ISTM has also forayed into online and hybrid training which not only increased its outreach but also resulted into more focused and efficient training. Further, in line with the Karmayogi Guidelines-2023, ISTM is constantly curating and updating e-learning contents for different functional and behavioural competencies. ISTM is certified as ‘Tate’ (UTAKRISHT)’ by CBC.
8.2.1 Campus
The Institute is located in the Old JNU Campus, and is housed in four different blocks, viz. Administrative Block, Seminar Hall Complex, Library Building, and Hostel Block. At present ISTM has thirteen lecture halls, two Auditoria and two Conference Halls. In addition, ISTM is having four ICT Labs with 137 desktop computers and video conferencing facility. The ISTM has well-furnished hostel facilities with 80 rooms, 4 well-furnished guest rooms with modern facilities and three dining halls with modern kitchen facility. Hostel Cyber Room has sevencomputer set along with printer internet and Wi-Fi facility.
8.2 Human Resources
As of December 31, 2024, ISTM has a sanctioned staff strength of 95 , with 70 in position, including 24 of 28 sanctioned faculty members, primarily experienced officers from Central Services. Additional expertise is sourced from administrators, professors, and trainers from other institutions.
8.3.1 Training Programmes
ISTM conducts various categories of training programme (Annexure-III), which includes:
(i) Foundational and ‘in-service’ Courses as per CSS and CSSS Cadre Training Plan
(ii) Induction Training component for Officers of Group ‘A’ services of ICoAS, Director General Civil Aviation (DGCA) and CVOs of CVC etc.
(iii) Induction Training component for various Group ‘A’ organized service like IAS, IFS, IRS, ISS, IES, ITS, ICLS, IDES, IIS & IRTS probationers.
(iv) Office Management, Financial Management, Management Services, Behavioural Training
(v) Training of Trainers, Trainers Development Programmes and State Category Development Programmes (SCTP) sponsored by DOPT
(vi) Peripatetic Training Programmes
(vii) Training on Right to Information, Handling Parliamentary Matters, Basic Economics
(viii) Workshop on Prevention, Protection, Prohibition \& Redressal of Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
(ix) Organization Specific Programmes/ Cadre Specific Programmes
8.3.2 Details of Courses conducted during 2024 – 2025 (April, 2024 to January, 2024).
| Courses | No of Course Conducted |
Participants | No of training days |
No of Training weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTP-CSS | 42 | 1803 | 1367 | 273 weeks/4 Days |
| CTP-CSSS | 23 | 1008 | 579 | 116 Week 3 Days |
| Calendar Courses 2024-25 |
119 | 4035 | 492 | 98 Weeks 4 Days |
| TDP Courses | 5 | 86 | 25 | 5 Weeks |
| OSP (46) \& PT Programs (7) |
53 | 1505 | 279 | 56 Weeks 3 Days |
| ToT-CBSE | 254 | 8360 | 516 | 103 Weeks 2 Days |
| Total | $\mathbf{4 9 6}$ | $\mathbf{1 6 7 9 7}$ | $\mathbf{3 2 5 8}$ | $\mathbf{6 5 4}$ Weeks 2 Days |
8.3.3 Major Highlights
(i) MoU singed byISTM: –
ISTM has signed 4 Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) with the following Institutes/organizations to facilitate the sharing of resources, expertise, and best practices for capacity building and training:
a. CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education)
b. NSSTA (National Statistical Systems Training Academy)
c. AJNIFM (Arun Jaitley National Institute of Financial Management)
d. SPIPA (Sardar Patel Institute of Public Administration)
These MoUs aim to foster inter-institutional cooperation, optimize resource utilization, and improve the quality of training programs
(ii) Training of Trainers for Central Board of Secondary Education (ToT-CBSE)
As per terms of the MoU with CBSE, ISTM is conducting Training of Trainer (ToT) courses for around 15000 trainees, mainly principals, vice-principals, PGTs & TGTs belonging to CBSE affiliated schools. (TOT) courses are meant to fill a crucial gap between teaching and training and are part of mandatory requirement as per National Education Policy, 2020.
(iii) Certificate of Appreciation from Hon’ble MoS (PP)
ISTM has been honoured with a Certificate of Appreciation from the Hon’ble Minister of State (PP) during the Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week valedictory ceremony. This recognition was awarded for ISTM’s exceptional performance in hosting courses that were most widely consumed by Government officials during the Karmayogi Saptah which included Team Building, Prevention of Sexual Harassment for Women at Workplaces and Conduct of Conduct for Government Employees.

8.4.1 Foundation Training Programme for ASO Probationers
ISTM conducts the Foundation Training Programme of Direct Recruit ASOs which is of 90 weeks duration in blended mode. The broad components of ASO (FTP) are as follows:
| S. No. | Modules | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pre-Foundation Course (online on Karmayogi i-GOT Platform) | 06 |
| 2. | ISTM Phase – 01 | 09 |
| 3. | On-the-Job Training | 73 |
| 4. | ISTM Phase – 02 | 02 |
| TOTAL | $\mathbf{9 0}$ |
This includes training on behavioural, domain and functional competencies identified by the Government as essential for efficient and effective functioning in the Central Secretariat, ‘Experiential Learning’ through “Bharat Darshan”, “NGO Attachment”, and “Village Attachment”.
Emphasis is given on Institutional collaborations with identified Institutions of Excellence such as Parliamentary Research and Training Institute for Democracies (PRIDE) for handling of Parliamentary work, National Archives of India (NAI) for Record Management, Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA) for imparting specialized training on selected competencies etc.
8.4.2 FTP for DR-Steno Grade D in the Central Secretariat focuses on domain knowledge (office procedures, departmental security), functional skills (noting, drafting, IT tools, communication), and behavioural modules (ethics, values, teamwork). Classroom training has been restructured from 8 weeks to 5 weeks for enhanced efficiency and focused learning.
8.4.3 In addition, various extracurricular activities like ‘Essay & Precis writing’, ‘Blood Donation Camp’, ‘Cultural event/ programme’, ‘Extempore/Quiz Competition’ ‘Yoga Sessions” ‘Sports Meet’ etc. are organized to inculcate team working skills and grooming leadership skills.
8.5 Celebration of Hindi Diwas and Hindi Fortnight, 2024
For promoting the use of Hindi in official works by using motivation and incentives, the institute has celebrated Hindi Diwas on 14th September 2024 and Hindi Fortnight has been organized from 14th September, 2024 to 28th September, 2024. Various competitions; such as Essay Writing, Noting \& Drafting, Translation, Official Language Policy, Extempore, Dictation, Poetry Recitation etc.; were conducted to celebrate and propagate the simplicity, flexibility and uniqueness of Official Language-Hindi.
8.6 Karmayogi Digital Learning Lab (KDLL) at ISTM
ISTM houses a unique of its kind “Karmayogi Digital Learning Lab (KDLL)” at its premises. This facility is developed by the DoPT under the Technical Assistance Grant from the Asian Bank. Through this facility and otherwise, ISTM contributed total 184 courses of e-Learning material on i-GOT Karmayogi portal. 53 courses have been developed and made live during this year.
8.7 Integrated Training Complex: “Karmayogi Bhavan”
On 12th February 2024, the Hon’ble Prime Minister laid the foundation stone of Phase I of the Integrated Training Complex “Karmayogi Bhavan” at Old JNU Campus, New Delhi. It is proposed to develop `Centres for Excellence’ for various themes as part of new infrastructure and digital labs in line with emerging technologies.
In Phase I, an Integrated Building for ISTM and DoPT (Training Wing) will be constructed on 6.09 acres with an overall cost (including the land cost) of approximately Rs. 240 crores. The whole project is being executed by CPWD in Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) Mode. The construction work has been awarded to M/S PNSC Infrastructure Pvt. Ltd. by CPWD. The building will be constructed keeping in view the principles of Green Building and Energy Conservation. It will be solar panelled with rainwater harvesting provisions and four-to-five-star rating under GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) point system.
Excavation and PCC work has been completed in the 6000 sqm area out of total site area -8000 sqm . The RCC for raft of auditorium portion has been completed. The RCC for raft of available space and column casting is in process.
8.8 ISTM Library
8.8.1 The ISTM Library is a valuable resource for both staff members and trainees. With a collection of 20,432 volumes spanning various categories, including a notable reference section and special manuscripts from trainees, the library operates in a semi-automated, digital manner. Noteworthy publications by the library include daily infographics, monthly information bulletins, quarterly newsletters, ISTM LIB-DEX and Monthly Digest.
8.8.2 Important Activities of ISTM Library in this year
i. Celebration of National Librarian’s Day from 13th to 14th August 2024 with the theme “Old is Gold,”
ii. Visit of Secretary(P) at ISTM Library and Launch of $1^{\text {st }}$ issue of ISTM Monthly Digest and Unveiling of the modified version of ISTM Journal of Training Research and Governance on October 14, 2024.
iii. Celebration of National Library Week commencing with an inauguration on Nov 14, 2024.

CHAPTER 9
e-Human Resource Management System 2.0 (e-HRMS 2.0)
- Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) introduced the Electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS) with effect from 25.12.2017 to digitize the service records of Central Government employees and for providing certain HR processes in a digital working environment. e-HRMS is one of the six key pillars of Mission Karmayogi.
- e-HRMS2.0, launched on 25.12.2022 by the Hon’ble Minister of State for Personnel, Pensions and Public Grievances, is a completely revamped version of e-HRMS that envisions to cover the entire life cycle of an employee’s service and offers AI enabled dashboards for insights/suggestions for transparent and efficient decision-making in-service matters.
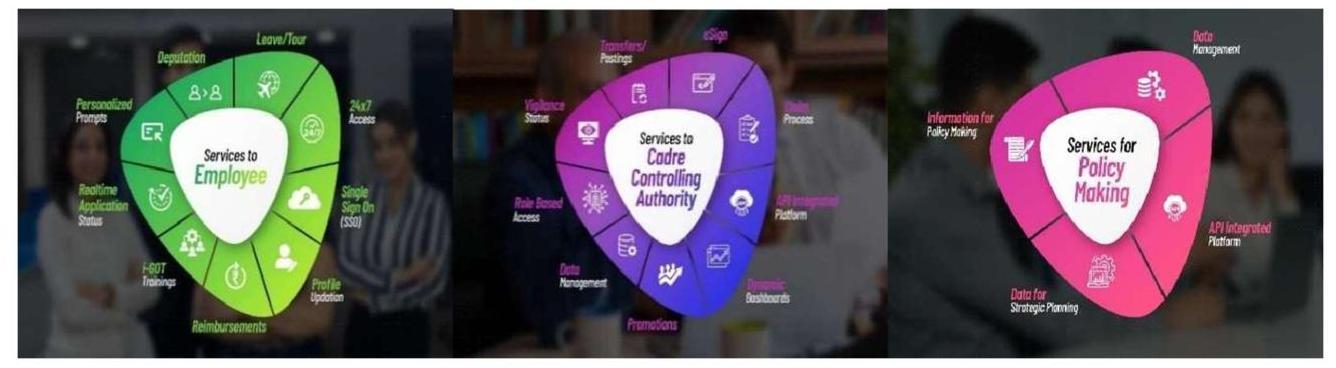
Services on eHRMS 2.0
3. e-HRMS 2.0 has been modelled to provide all major employee related HR Services like training, promotion, deputation, transfer, superannuation, resignation, integrating various related platforms such as i-GOT, SPARROW, PFMS, Bhavishya, Probity etc. and facilitating the uptake of entitlements & benefits like various kinds of Reimbursements, Claims, Advances and Leaves by the employee in an easy and transparent manner.
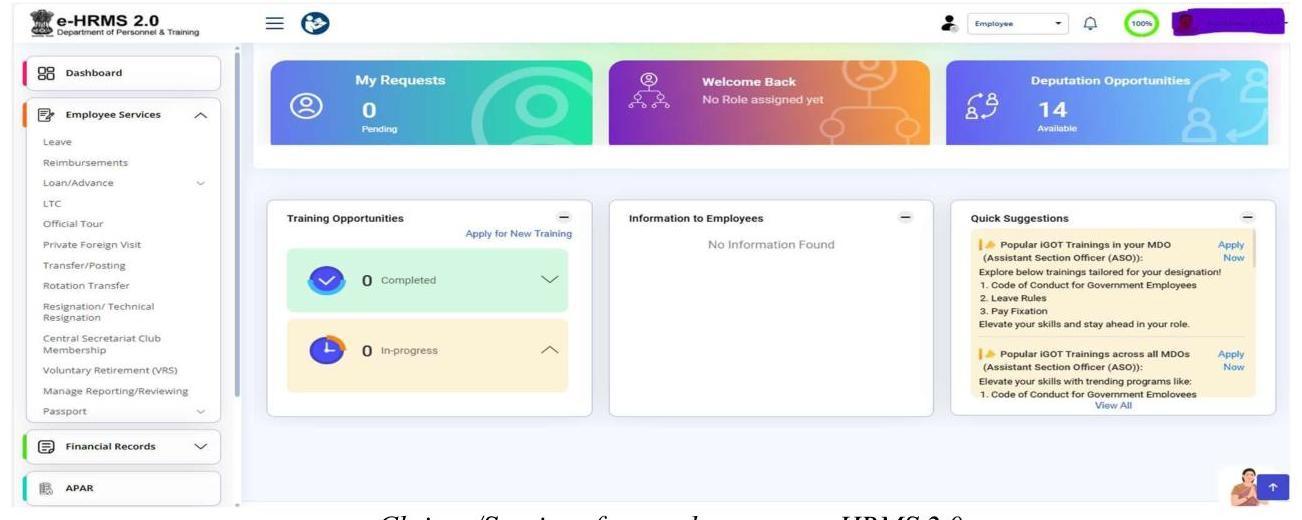
Claims/Services for employees on e-HRMS.2.0
4. e-HRMS provides analytics to the Senior Administration in Policy formulation and implementation. e-HRMS has built in tools and capabilities to bring together dispersed data to generate automated clearances and suggestions in its modules.
Salient Features of e-HRMS
| 1. | Single source of authentic employee data | 6. | 24X7 access and availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2. | Common document repository of employees | 7. | Ease of sharing information among stakeholders |
| 3. | MIS reports analytics | 8. | e-Sign facility |
| 4. | Standardization of master data | 9. | Alerts/notification functionality |
| 5. | Minimizes manual entry of data | 10. | Integrated with other applications like i-GoT Karmayogi, SPARROW PFMS, Probity etc. |
Achievements:
a. As per e-HRMS Dashboard report, more than 4.60+ lakh employees of 193 Ministries /Departments/ Organizations (MDOs) including 04 UTs and 03 State Govt have been on-boarded onto the e-HRMS platform.
b. Training, Deputation, IPR, APAR, Vigilance Clearance, Leave, Reimbursement are in use by various MDOs now.
c. Financial Sanctions for Claims & Reimbursements have been integrated with PFMS, Leave Module enhanced with new leave engine and new features of configurable work calendars and leave account and new functionality for NOC/Intimation for Passport, LTC Claim rolled out. Modules for TA/DA, pension benefits, NOC for Higher Studies, Briefcase allowance, Medical reimbursement (Non-CGHS) etc. have been developed and roll out is in process.
d. Akin to the citizen’s charter, timelines for Service Delivery through e-HRMS 2.0 portal has been issued vide DoPT ‘s OM No. 3/1/2024-e-HRMSv2.0 dated 29.02.2024. Deemed approval of various types of leaves has been implemented.
e. e-Service Record is LIVE now. Integration with Bhavishya portal in progress. Post integration, eHRMS will be a one-stop shop for onboarded employees to apply for retirement benefits like pension, CGHS card and NOC for Govt Accommodation, requirement of physical service book shall be done away with and the process will be completely paperless and trackable.
f. AI enabled analytical dashboard for various roles (Nodal/MDO/CCA/AVD/Super-admin etc.) have been developed providing various analytics to senior administration for decision and policy making. It is envisaged that e-HRMS shall serve as a comprehensive directory for all central government employees, also making available real time data on competencies gained by them through capacity building courses on i-GOT and enabling critical decision-making for deployments leading to more productive and efficient workforce. Functionality for creation of dynamic queries for suggestive result sets for right person for right job is in progress.
Other key highlights:
Integration Status: For Vigilance Clearance, APAR, Training, Salary Slips, Retirement module, the eHRMS2.0 portal integrates with Probity, SPARROW, i-GOT, PFMS.
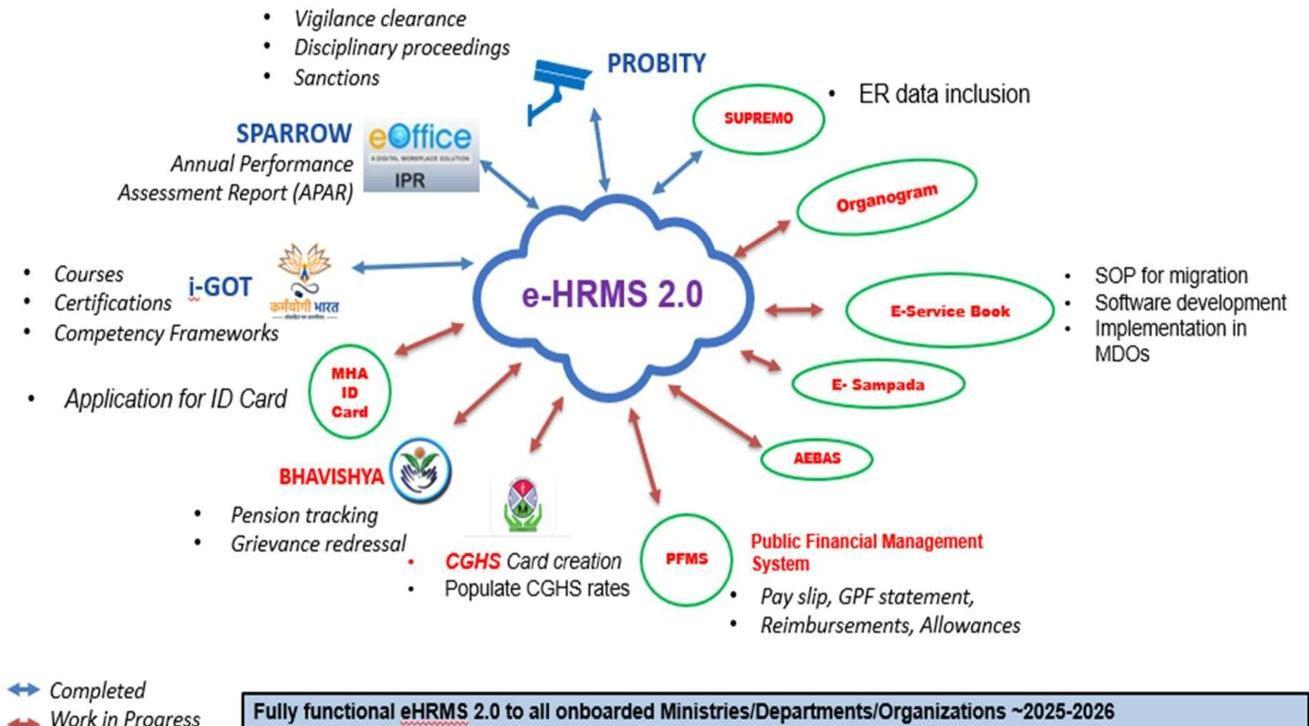
b. Deputation module leverages AI based features to alert employees about the opportunities available to them according to their qualification/experience. The platform allows application for these deputation opportunities by interested and eligible employees and provides a transparent and trackable mechanism for subsequent processing of the applications, relieving and joining.
c. e-HRMS 2.0 has also developed linkages with iGOT-Karmayogi platform to offer training programs, store competency history of officers and download of certificates for successfully completed trainings from the portal itself. It leverages the power of AI to automatically suggest suitable training opportunities for individual officers, based on their assigned role and preferred career path and nudges the employee to gain further competency by broadcast of information of most popular trainings and trainings being done by others at his level or in her MDO.
d. Successful paperless DPCs have been conducted via e-HRMS 2.0 portal. This has saved transaction time and costs and increased transparency.
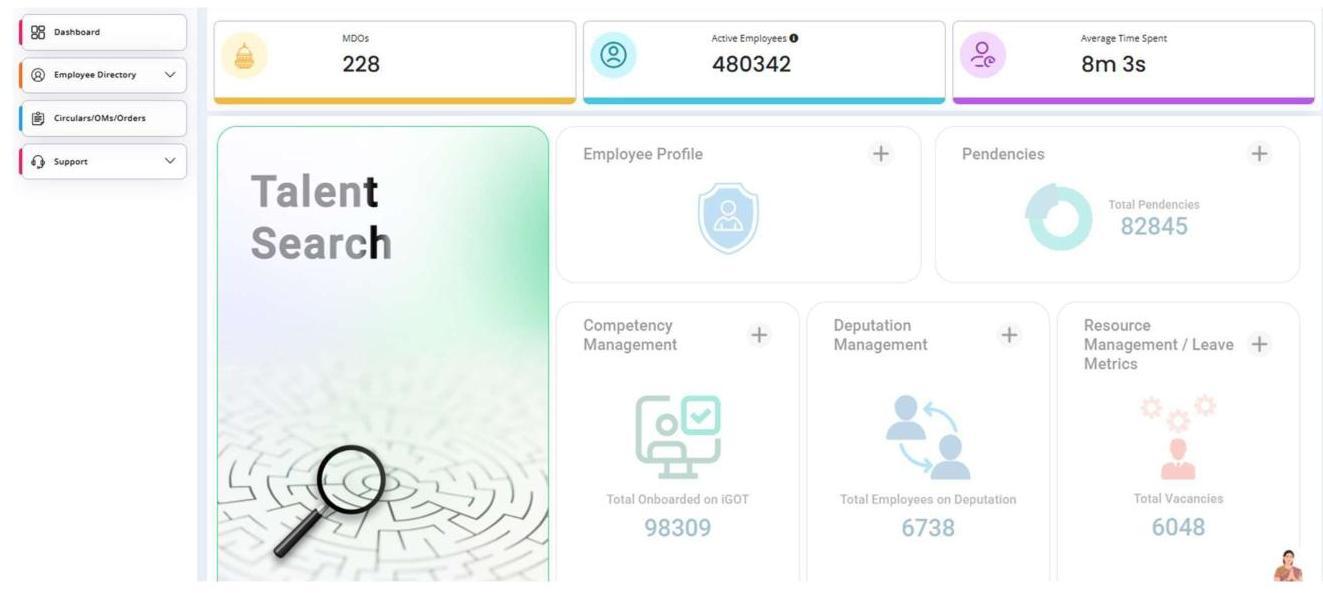
e-HRMS Super Admin Dashboard
CHAPTER 10
ADMINISTRATIVE VIGILANCE DIVISION
10.1 Administrative Vigilance Division-I is responsible for examination of disciplinary cases and vigilance matters in respect of Indian Administrative Service officers working under the Central Government and State Governments under the All India Services (Discipline and Appeal) Rules 1969 and All India Services (Death-Cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958. Administrative Vigilance Division-I is also responsible for examination of disciplinary cases received from the Ministries / Departments in respect of Group ‘A’ officers of the Central Secretariat Service (CSS) and Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS) for initiation of disciplinary proceedings under Rule 14, Rule 16, Rule 19 of CCS (CCA) Rules, 1965 and under Rule 9 of CCS (Pension) Rules 1972.
Administrative Vigilance Division-III is responsible for Complaints of corruption relating to Central /States /UT Administration and Public Sector Undertakings; Suggestions for eradication of corruption and publicity thereon; Complaints of corruption relating to commercial firms; All matters concerning the CVC; Disagreement cases with the advice of CVC from other Ministries / Departments; Annual Report of the CVC; Parliament Questions pertaining to anti-corruption activities of Government; Reference relating OECD matters; Allegations / complaints / enquiries against Chief Ministers and Ministers of State Governments; Setting up of Commissions of Inquiry relating to corruption charges and matters relating thereto
10.2 The Division processes cases referred by the State Governments and Ministries / Departments under Government of India on the following issues:
- Proposals from the State Governments seeking to impose major penalty of dismissal / removal / compulsory retirement on members of IAS.
- Proposals from the State Governments seeking permission under the AIS (DCRB), 1958 Rules to initiate action against retired members of IAS.
- Proposals from the State Governments for imposing penalty of cut in pension against retired IAS officers.
- Proposals to initiate disciplinary proceedings / suspension of IAS officers working under the Government of India.
- Appeal against suspension submitted by IAS officers serving in the States.
- Memorial submitted by IAS officers against the orders passed by the Central Government or the State Governments in disciplinary proceedings in which the officer is aggrieved.
- Requests for sanction for prosecution against IAS officers under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- Requests for sanction for prosecution under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 against Group ‘A’ officers of the Central Secretariat Service (CSS) and Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS) cadres.
- Handling of Privilege Notices from the Members of Parliament received from the Lok Sabha / Rajya Sabha Secretariat as well as complaints against IAS Officers.
- Examination of vigilance status of IAS officers for purposes of empanelment/ training/ posting on deputation and other purposes as per extant guidelines. To facilitate this function, a Computerized Vigilance Information System is in operation with a central data base which can be accessed by the requisitioning Divisions concerned of this Department.
- Examination of vigilance status of all Group ‘A’ officers of the Central Secretariat Service (CSS) and Central Secretariat Stenographers Service (CSSS) cadres for various purposes viz. promotion, empanelment, deputation, VRS, etc as per extant guidelines.
- Advice / clarification to the State Governments / Central Ministries/ Departments on the procedural aspects of disciplinary proceedings.
10.3 Disciplinary Proceedings:
- During the period 01.04.2024 to 20.01.2025, nine final orders in five disciplinary cases against Group ‘A’ officers of CSS was issued. In one case, charge sheet was issued against Group ‘A’ officers of CSS cadre.
- During the period 01.04 .2024 to 31.01 .2025 , four final orders were issued in disciplinary proceedings against IAS officers.
- During the period 01.04 .2024 to 31.01 .2025 , twenty-four disciplinary proceedings cases against the IAS officers were handled at different stages and 11 court cases were examined/processed.
- In one case, suspension against Group ‘A’ officer of CSS cadre was revoked and in one case, suspension against Group ‘A’ officers of CSS cadre was accorded against Group A officers of CSS cadre.
- In five cases, suspension cases against IAS officers serving in the State Governments were reviewed by the Central Ministry’s Review Committee and suspension period in these cases was extended.
- In five cases, suspension of IAS officers while serving in State Governments were confirmed and further extension in suspension period beyond thirty days was approved.
- One appeal received under Single Window System was examined and processed for advice of UPSC. One appeal was disposed of and in one appeal, advice tendered by UPSC was sent to State Government for seeking representation of Charged Officer.
10.4 Sanction for Prosecution and Monitoring of Proposals of Sanction for Prosecution under provisions of Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988:
- Sanction for prosecution have been granted in 22 cases against 22 IAS Officers under Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 (as amended in 2018) for the period from 01.04.2023 to 13.03.2025. Out of these said prosecution sanction orders, one order has been issued by withdrawing the earlier order issued. Also, in one case, sanction for prosecution against 01 IAS Officers was granted under section 6 of PC Act, 2006 (1949 A.D.) (Act. No-III of Samvat 2006).
- Sanction for prosecution was accorded against 00 (NIL) Group ‘A’ officer of CSS cadre, under Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 in respect of Group ‘A’ officers of CSS cadre.
10.5 Privilege Notices from Members of Parliament and Complaints against IAS officers:
- During the period 01.04.2024 to 06.03 .2025 , 6 Privilege notices against officials of Districts Administration for protocol violation were received from the Lok Sabha/Rajya Sabha Secretariat and processed during the period. 5 Privilege notices were finally disposed of.
- During the period 01.04 .2024 to 06.03 .2025 , two complaint was received from Hon’ble Members of Parliament against IAS officers.
- During the period 01.04 .2024 to 06.03 .2025 , 1272 complaints against IAS officers were received, 1213 complaints processed, and 1213 complaints were finally disposed of.
- During the period 01.04 .2024 to 20.01 .2025 , 48 complaints against Group ‘ A ‘ officers of CSS/CSSS cadres were received and processed.
Disagreement cases in Disciplinary matters:
10.6 In order to bring about greater uniformity in examining on behalf of the President the advice tendered by the CVC and taking decisions thereon, it has been decided that this Department should be consulted before the Ministries/Departments finally decide to differ from/not to accept any recommendation of the Central Vigilance Commission in those cases which relate to Gazetted Officers for whom the appointing authority is the President, the matter is to be referred to this Department for resolving the disagreement. This Division has disposed of no such cases between 01.04.2024 and 31.01.2025.
Disagreement in the matter of Prosecution Sanction cases:
10.7 Similarly, the cases of disagreement between the CVC/ CBI and Sanctioning/Disciplinary Authority in the matter of Prosecution Sanction cases are required to be referred to DoP&T for a final decision in terms of this Department’s OMs dated 01.03.2019 and 18.07.2019. As per these OMs, before taking a final decision for grant or denial of sanction for prosecution, the Competent Authorities shall obtain views of DoP\&T, in cases where they decide to differ with CVC’s advice. Accordingly, the views of DoP\&T may be taken into account while passing final speaking order.
This Division has disposed of 5 such cases between 01.04.2024 and 31.01.2025.
Appointment of Central Vigilance Commissioner and Vigilance Commissioner:
10.8 In terms of Section 5(2) of the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003, consequent upon attaining the age of 65 years, the then Vigilance Commissioner Shri Arvinda Kumar had demitted the office of the Vigilance Commissioner on 29.09.2024. The process of filling up the vacant post has already been initiated in this Department.
Central Vigilance Commission
Introduction
10.9 The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) is the apex integrity institution mandated to combat corruption and ensure integrity in public life. It is a statutory body vested with superintendence over vigilance administration of various Ministries of the Central Government or corporations established by or under any Central Act, Government companies, societies and local authorities owned or controlled by that Government.
With its outreach measures, CVC also endeavours to create awareness for achieving transparency, accountability, probity and corruption free system of administration.
Statutory Provisions
10.10 CVC was set up by the Government of India through Resolution No. 24/7/64 dated 11.02.1964. Later on, it was accorded statutory status through the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003 (No. 45 of 2003) passed by the Parliament.
10.11 The role and functions of CVC include exercising superintendence over the functioning of DSPE (CBI) and monitoring progress of cases registered for investigation by DSPE under PC Act, 1988.
10.12 CVC also reviews the progress of cases pending with the competent authorities for grant of sanction for prosecution of employees of the organizations covered under its advisory jurisdiction, especially those in which sanction has been delayed.
10.13 CVC can inquire or cause inquiry into complaints/offences alleged to have been committed under the PC Act 1988 by employees as specified in Section 8 of the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003 (45 of 2003).
10.14 As part of superintendence over vigilance administration of organizations covered under its jurisdiction, CVC tenders advice in disciplinary matters having vigilance angle, involving officers covered under its advisory jurisdictions.
10.15 CVC is the designated agency to receive and act on complaints or disclosure on any allegation of corruption or misuse of office from whistle blowers under the “Public Interest Disclosure and Protection of Informers’ Resolution” (PIDPI), 2004.CVC, as the designated agency under PIDPI Resolution is empowered to take appropriate steps if the complaint is found to be motivated or vexatious.
10.16 Each organization covered under the advisory jurisdiction of the CVC has a vigilance unit headed by the Chief Vigilance Officer (CVO). The CVOs act as extended arms of the CVC and are responsible for timely action on advice tendered by the Commission, apart from ensuring proper implementation of the guidelines issued by CVC. One of the important functions of CVOs is to advise the authorities in the organizations for establishing effective systems and procedures and to periodically monitor compliance of the same to minimize systemic failures/loopholes, which provide opportunities for malpractices/irregularities.
10.17 As per Section 14 of the CVC Act, 2003, CVC submits an Annual Report of its activities to the President within six months of the close of the year under report. On receipt of such report, the President shall cause the same to be laid before each House of Parliament.
Multi-Pronged Strategy to combat Corruption
10.18 CVC has adopted a multi-pronged strategy to fight and eliminate corruption, which stresses not only on punitive vigilance but also on preventive mechanism and participative measures.
Punitive Vigilance
10.19 The Commission is of the firm view that time-bound and effective punitive action resulting in award of exemplary and adequate punishment acts as a deterrent to committing willful misconduct. The Commission on its part tenders appropriate advice in respect of cases referred to it by various organizations. It reviews the progress of departmental actions periodically, through the mechanism of review meetings. The Commission seeks investigation report from the organizations concerned, in respect of those complaints where specific issues with perceptible vigilance angle is found.
10.20 The advisory role of Commission extends to the specified categories of employees of the Central Government, corporations established by or under any Central Act, Government companies, societies and local authorities owned or controlled by the Central Government and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto. Commission’s advisory role consist of a two-stage mechanism i.e. First Stage Advice (FSA), after completion of investigation but before initiating disciplinary action and Second Stage Advice (SSA), i.e. after issuance of charge sheet to delinquent employee on completion of the inquiry proceedings, if the competent authority holds a view, which is different from Commission’s FSA, the Commission is to be approached for obtaining its SSA.
Preventive Vigilance
10.21 Central Vigilance Commission, the apex institution for vigilance administration in the country uses various tools for effective vigilance administration. Preventive Vigilance measures are amongst the most important tools to eliminate corruption as it improves upon existing systems, procedures and establishes
in-built checks within the system to bring about standardization, transparency, accountability and probity in Public Administration. Effective Vigilance Administration fosters a culture of integrity and trust, which is essential for smooth functioning of any institution. The Commission has compiled a booklet titled “Preventive Vigilance Initiatives”. The booklet elucidates initiatives undertaken by various organizations to promote preventive vigilance. By disseminating best practices and success stories, this book aims to inspire other organizations to adopt similar measures to create an ecosystem to foster a culture of integrity across all sectors and organizations, thus promoting good governance.
10.22 In an era where digital transformation is reshaping various sectors, the importance of leveraging technology to enhance service delivery, ensuring transparency and preventing fraud has never been more critical. Commission has organized two significant conferences in August 2024. The first conference was organized at Scope Convention Centre, New Delhi in collaboration with Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (IOCL) on the topic of “Leveraging Technology for Increasing Transparency in Governance”. This conference aimed to share and present best practices on leveraging technology for vigilance administration and project monitoring. The second conference was organized on the topic “Digital Initiatives to Prevent Banking, Financial Services and Insurance Frauds” at Punjab National Bank, Corporate Office, New Delhi. This conference highlighted the pressing need for financial institutions to adopt advanced technologies to combat the increasingly sophisticated tactics of cybercriminals. Industry leaders discussed the implementation of multi-layered strategies involving technology, data, artificial intelligence, and human expertise to create robust defenses against fraud. A special edition, bringing out the salient learnings from these conferences have been compiled in the booklet titled “VIGEYE VANI” Special Issue on Leveraging Digital and Technological Initiatives for Transparency and Cyber Fraud Prevention.
10.23 Public procurement constitutes a substantial part of Government expenditure and impacts economic activities in the country. Therefore, it is imperative that decisions taken in relation to the public procurement are not only transparent and fair, but also facilitate quality – oriented delivery in a timely manner. However, there are certain challenges being faced in the field of public procurement, which dent the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the public procurement regime. Prominent among these challenges are quality compromises, delay in completion of the procurement activities and large number of contractual disputes. Public Private Partnership (PPP) and Engineering, Procurement & Construction (EPC) modes of procurement, which were brought in to accelerate the pace of infrastructure development are also experiencing certain challenges. With a view to analyses the causative factors giving rise to these challenges and to suggest possible mitigation measures, the Commission brought out a booklet titled “Public Procurement: Challenges and Way Forward (2024 Edition)”. About one hundred case studies have been included in this booklet which can be a useful reference tool for all officials dealing with Procurement.
Participative Vigilance
10.24 Commission endeavors to promote integrity in everyday functions of citizens and elicits participation of all stakeholders in the fight against corruption. The Participative Vigilance strategy involves making people aware of the ill effects of corruption and the need to fight it. The observance of Vigilance Awareness Week (VAW) is a step in this direction. The Commission observes Vigilance Awareness Week in the week in which the birthday of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel falls.
10.25 Vigilance Awareness Week (VAW) was observed from $28^{\text {th }}$ October 2024 to $03^{\text {rd }}$ November 2024, during the year with the theme “Culture of Integrity for Nation’s Prosperity”: “साि्ान” की सं”दित से रू की समृि5″.
10.26 Since last couple of years, the Commission has been running a three-month campaign leading upto the Vigilance Awareness Week. This year, the campaign associated with the Vigilance Awareness Week was undertaken from $16^{\text {th }}$ August 2024 to $15^{\text {th }}$ November 2024. The Commission has advised to all the organizations that during the three-month campaign ( $16^{\text {th }}$ August 2024 – $15^{\text {th }}$ November 2024) associated with the Vigilance Awareness Week, they may undertake following action in five focus areas:
(i) Capacity Building Programs;
(ii) Identification and Implementation of Systemic Improvement Measures;
(iii) Updation of Circulars / Guidelines / Manuals;
(iv) Disposal of Complaints; and
(v) Dynamic Digital Presence.
10.27 The observance of Vigilance Awareness Week 2024 commenced with the taking of the pledge by public servants in the Ministries/ Departments/ Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs)/ Public Sector Banks (PSBs) and all other organizations, on $28^{\text {th }}$ October 2024.
10.28 The Hon’ble President of India, Smt. Droupadi Murmu graced a function which was organized on the occasion of the Vigilance Awareness Week at Vigyan Bhawan on $08^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024. The function was attended by previous Central Vigilance Commissioners and Vigilance Commissioners, and other senior officials of Government of India, Public Sector Undertaking, Public Sector Banks, etc.
10.29 On the occasion, the first copy of the following three booklets were presented to the Hon’ble President by the Central Vigilance Commissioner:
(i) Booklet on Preventive Vigilance
(ii) Vigeye Vani Special Issue on Leveraging Digital and Technological Initiatives for Transparency and Cyber Fraud Prevention
(iii) Booklet on Public Procurement: Challenges and Way Forward
10.30 A Special Cover prepared by the Department of Posts on the occasion of Vigilance Awareness Week 2024 was released and presented to the Hon’ble President by the Central Vigilance Commissioner during the function.
Training and Capacity Building
Training of Inquiry Officers (IOs) and Presenting Officers (POs)
10.31 With a view to reduce the time taken in finalization of Departmental Inquiries, Commission has initiated a 3-day uniform Training Programme for Inquiry Officers (IO) and Presenting Officers (PO) of the Government organizations including PSUs and PSBs. The training programme is conducted through six Training Institutions namely Institute of Secretariat Training & Management (ISTM), HPCL Academy, CBI Academy, Central Academy for Police Training (CAPT), Indian Institute of Bank Management (IIBM) and National Productivity Council (NPC).
10.32 Since the launch of the 3-day IO/PO training in August 2021, Commission has successfully organized training of 97 batches of IO/PO covering over 3238 officers. During the year 2024, Commission organized 17 batches of IO/PO training in offline mode and trained 448 officers. The focus of Commission is to train adequate potential IO and PO across the country.
Induction Training for CVOs
10.33 The Commission has undertaken an initiative of holding 2 days’ Induction Training on a quarterly basis, for newly appointed CVOs. This training is generally conducted in the last month of each quarter. Three such training programs were held in the year 2024. A total of 39 newly appointed CVOs were given training during the year 2024.
Advanced Training on Vigilance Investigation
10.34 The Commission has organized an advance training on “Vigilance Investigation” from $26^{\text {th }}$ February to $28^{\text {th }}$ February 2024 at Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel National Police Academy (SVPNPA), Hyderabad. 26 full time CVOs were trained covering areas like challenges in the field of Procurement, Current Global Trends in Economic Offence and Forensic Audit, Vigilance in Financial Sector, Critical Examination for Prosecution Sanction, Digital Forensic, Digital Evidence & Evidence Appreciation, Conduct of Departmental Inquiries, monitoring expeditious finalization and improving quality of report, Interaction between CBI \& CVOs \& Investigation of Corporate fraud, Examination of Audit Inspection reports etc. from Vigilance Angle and challenges to Cyber Security.
Training on Preventive Forensics
10.35 The Commission has considered the utility of Forensic Science in investigation of vigilance cases and designed a training programme to suit to all the CVOs/ Vigilance Officers across all the organizations for orienting them on preventive side of Forensics. From April 2022, Commission is regularly organizing 3-day offline training on “Preventive Forensics” at National Forensic Sciences University, Gandhinagar. Total 243 participants from Government Departments, CPSEs and Public Sector Banks etc. have participated in these training programs during the year 2024.
Training on Public Procurement
10.36 Department of Expenditure in consultation with the Commission has released Manuals for Procurement of Goods, Works, Consultancy and other services. Considering the importance of understanding the procurement procedure, the Commission has formulated a 3-day training module on public procurement, in consultation with Arun Jaitley National Institute of Financial Management (AJNIFM), Faridabad. Based on this module, trainings were conducted at AJNIFM and IIM, Vishakhapatnam for officers of the Government Organizations under the jurisdiction of the Commission. During the year 2024, 10 such training programs were organized wherein 450 officers participated.
Regional Conference /Training Programs by the Commission
10.37 As part of the outreach programme, various regional conferences / training programs for CVOs and other vigilance functionaries have also been organized by the Commission, across different geographical regions. The details of such conferences / training programs organized by the Commission during the year 2024 are as under: –
| S. No | Date | Description | Location | No. of Participants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $\begin{aligned} & 07^{\text {th }} \text { June, } \ & 2024 \end{aligned}$ | One Day Training Programme for CVOs under Ministry of Education, Department of Higher Education. | Delhi | 37 |
| 2 | $\begin{aligned} & 02^{\text {nd }} \ & \text { August, } \ & 2024 \end{aligned}$ | One Day Workshop on Best Practices on Leveraging Technology for Increasing Transparency in Governance. | Delhi | 345 Physically \& 249 participated Through video conferencing |
| 3 | $\begin{aligned} & 22^{\text {nd }} \text { to } \ & 23^{\text {rd }} \ & \text { Aug, } 2024 \end{aligned}$ | Conference on Digital Initiatives in Preventing Frauds in Banking, Financial Services and Insurance. | Delhi | 187 |
| 4 | $\begin{aligned} & 30^{\text {th }} \text { Aug, } \ & 2024 \end{aligned}$ | One day Workshop for Part- Time CVOs of Education Department. | Chennai | 32 |
| 5 | $\begin{aligned} & 13^{\text {th }} \text { to } 14^{\text {th }} \ & \text { Dec, } \ & 2024 \end{aligned}$ | Capacity Building and Training Programme on various aspects of Vigilance Administration, including Disciplinary Processes and training | Kolkata | 93 |
| of $\mathrm{IOs} / \mathrm{POs}$ organized by UCO Bank. |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | $20^{\text {th }} \quad$ Dec, 2024 |
Workshop conducted by CVC on “Best Practices on Leveraging Technology for increasing transparency in governance” organized by HAL at Bengaluru. |
Bangalore | 100 |
Lokpal & Lokayuktas Act, 2013 (No. 1 of 2014) \& related matters
10.38 In order to establish a more effective mechanism to deal with complaints relating to allegations of corruption against public servants, the Government of India enacted Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, which came into force with effect from 16.01.2014. Further, the Lokpal and Lokayuktas (Amendment) Act, 2016 has been brought into force w.e.f. 16.01.2014.
The institution of Lokpal was operationalized with the appointment of its Chairperson and Members in March, 2019.
Appointment of Chairperson and Members of Lokpal
10.39 The president, on the recommendation of the Selection Committee constituted under sub-section (1) of section 4 of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, has appointed Justice Shri Ajay Manikrao Khanwilkar as Chairperson, Lokpal with effect from, 10.03.2024 (afternoon).
Further, the President, on the recommendation of the Selection Committee constituted under sub-section (1) of section 4 of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013, has also appointed, Justice Shri L Narayana Swamy, Justice Shri Sanjay Yadav and Shri Sushil Chandra as Members, Lokpal with effect from 12.03.2024 (forenoon) and Justice Shri Ritu Raj Awasthi, Shri Pankaj Kumar and Shri Ajay Tirkey as Members, Lokpal with effect from 27.03.2024 (forenoon).
Rules made under the Act
10.40 The rules which are necessary for effective and efficient functioning of the Lokpal have already been framed and notified. The exercise to frame other Rules will be taken up as and when the need arises.
CHAPTER 11
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION
11.1 Brief: The International Cooperation Division deals with the matters pertaining to implementation of the review of United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC), G20 Anti-Corruption Working Group (G20 ACWG) and BRICS Anti-Corruption Working Group (BRICS ACWG). The primary tasks of this Division emanate from the follow up to the ratification of the United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) and the other consequential international collaborative efforts on global platforms. This Division acts in conjunction with specialized agencies like the Central Vigilance Commission, Central Bureau of Investigation, Enforcement Directorate and other line Ministries entrusted with the specific tasks within their respective administrative domain, viz. combating corruption, extradition matters, prevention of money laundering, mutual legal assistance treaties, etc.
11.2 UNCAC: The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) is a universally binding international legal Instrument to fight corruption at both domestic and global level and was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in October 2003. The convention aims to bring in rationalization and uniformity in legal frameworks and in the approaches in the fight against corruption. The provisions contain both mandatory and non-mandatory obligations. India signed the Convention in December 2005 and ratified the same in May 2011, after being satisfied of substantial compliance status of its domestic laws with the tenets of the Convention.
11.3 The Convention provides for a detailed mechanism for peer review of the status of implementation of its provisions by the Member States. This Department, in coordination with Ministry of Home Affairs, Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Ministry of External Affairs, Department of Legal Affairs; Constitutional bodies like CVC and UPSC; and other organizations like Central Bureau of Investigation, Enforcement Directorate, finalized the Executive Summary of $1^{\text {st }}$ cycle review on Chapter III (Criminalization and Law Enforcement) and Chapter IV (International Cooperation) of UNCAC in 2020. The second cycle review of implementation of Chapter-II (Preventive measures) and Chapter-V (Asset Recovery) of UNCAC has been initiated in November 2015.
11.4 Details of interactions held on various global platforms specific to UNCAC related issues during the period from April 2024 to December 2024 are indicated below:
| S. No. | Description | Period | Organized by | Venue/Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | $15^{\text {th }}$ Session of the Implementation Review Group | $\begin{aligned} & 10.06 .2024- \ & 14.06 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
| 2. | $18^{\text {th }}$ session of the Working Group on Asset Recovery | $\begin{aligned} & 10.06 .2024- \ & 14.06 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
| 3. | $13^{\text {th }} \quad$ open-ended intergovernmental expert meeting to enhance international cooperation under the Convention | $\begin{aligned} & 10.06 .2024- \ & 14.06 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
| 4. | First resumed $15^{\text {th }}$ Session of the Implementation Review Group | $\begin{aligned} & 28.08 .2024- \ & 06.09 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
| 5. | $15^{\text {th }}$ session of the Working Group on the Prevention of Corruption | $\begin{aligned} & 28.08 .2024- \ & 06.09 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
| 6. | Second resumed $15^{\text {th }}$ session of the Implementation Review Group | $\begin{aligned} & 04.11 .2024- \ & 08.11 .2024 \end{aligned}$ | UNODC | Vienna |
11.5 G20 ACWG: India is also a Member of G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group (ACWG). The focus of this Group is towards the global financial system, particularly from the point of view of denial of entry or visa to corrupt officials, providing measures to protect whistle blowers, promote effective functioning of anti-corruption bodies and association of private and business sector in combating corruption. Three G 20 ACWG meetings are held every year. Every year, the group prepares deliverables, usually in the form of high-level principles, compendia of good practices and country-specific guidance. In addition, the group is obliged to report annually on its progress and regularly publishes monitoring or accountability reports. In the year 2023, India chaired the G20 ACWG with Italy being the Co-Chair
11.6 India kept its focus on the topic of Fugitive Economic Offenders in continuation to the efforts on the same from previous years in G20 ACWG meetings of 2023. The basic objective behind this was to place the concern of India and other developing countries on the issue of Asset Recovery and the need for deliberation in the anti-corruption group for enhanced international cooperation. International Cooperation division coordinated the finalization of following G20 ACWG deliverables in 2023:
- G20 High-Level Principles on Strengthening Law Enforcement related International Cooperation and Information Sharing for Combatting Corruption,
- G20 High-Level Principles on Strengthening Asset Recovery Mechanisms for Combatting Corruption,
- G20 High-Level Principles on Promoting Integrity and Effectiveness of Public Bodies and Authorities Responsible for Preventing and Combatting Corruption,
- Compendium of Good Practices on enhancing the role of auditing in tackling corruption,
- G20 ACWG Accountability Report on Mutual Legal Assistance
- G20 Anti-Corruption Ministerial Meeting Outcome Document and Chair’s Summary,
- India’s initiative of updating four guides related to Asset recovery and Mutual Legal Assistance on G20 ACWG platform.
India was a member of G20 Troika (group of past, present and future presidencies) in 2024. In consultation with relevant stakeholders viz. Ministry of External Affairs, Department of Revenue, Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Central Bureau of Investigation, Central Vigilance Commission, Enforcement Directorate etc., International Cooperation Division has been working towards taking forward India’s anti-corruption priorities in G20 ACWG forum. India participated in the following meetings of G20 ACWG under Brazilian Presidency.
| S. No. | Description | Period | Venue/Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st G20 ACWG meeting 2024 | $24.03 .2024-$ 26.03 .2024 |
Brasilia, Brazil |
| 2. | $2^{\text {nd }} \text { G20 ACWG of } 2024$ | $25.06 .2024-$ 27.06 .2024 |
Paris, France |
| 3. | $3^{\text {rd }} \text { G20 ACWG of } 2024 \text { along with }$ side event |
$21.10 .2024-$ 23.10 .2024 |
Natal, /Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil |
| 4. | G20 Anti-Corruption Ministerial Meeting |
24.10 .2024 | Natal/Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil |
On $1^{\text {st }}$ December, 2024, South Africa assumed the presidency of G20. India is preparing to collaborate its anti-corruption priorities, with South Africa, centered on Enhancing International Cooperation to deal with Fugitive Economic Offenders and Recovery of Assets.
11.7 BRICS ACWG: Initially, BRICS Anti-Corruption Working Group (ACWG) held its meeting on the margins of G20 ACWG meetings. After the induction of Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran and United Arab Emirates (UAE) in BRICS in 2024, under Russian Presidency, the BRICS ACWG initiated to hold its
meeting in a separate track. Three BRICS ACWG Meetings were held under the Russian Presidency and India participated in all these meetings. The details of the said meetings are as follows:
| S. No. | Description | Period | Venue/Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st BRICS ACWG Meeting | 17.04.2024-18.04.2024 | Moscow, Russia |
| 2. | 2nd BRICS ACWG Meeting | 06.06.2024-07.06.2024 | Vienna, Austria |
| 3. | 3rd BRICS ACWG Meeting | 26.08.2024-27.08.2024 | Vienna, Austria |
11.8 Pillar-IV-Fair Economy, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework: India signed the said Pillar of the agreement on 21 September 2024. International Cooperation division of DOPT coordinated the negotiations and is the nodal for anti-corruption matters of the Pillar-IV.
11.9 Other miscellaneous activities: Apart from the direct participations by the Department of Personnel and Training, the concerned Ministries/Departments/Organizations are representing the Government of India in respect of specialized areas. The role of DoPT in such cases is towards providing overarching support and inputs on global platforms include participation in FATF, SAARC, Stolen Asset Recovery (StAR) initiative etc. Further, International Cooperation division coordinates India’s anticorruption matters pertaining to other departments/concerned authorities, for e.g. UNHRC, MoUs, FTAs, other arrangements/agreements etc.
CHAPTER 12
CENTRAL BUREAU OF INVESTIGATION
CONSTITUTION, ORGANIZATION AND EVOLUTION OF CBI
A SETTING-UP OF SPECIAL POLICE ESTABLISHMENT
12.1 During the early stages of World War-II, the organization known as the Special Police Establishment (S.P.E.) was created by the Government of India in 1941, by an Executive Order to investigate cases of bribery and corruption in transactions with which the War and Supply Department of the Government of India was concerned. It was further extended to include cases of corruption in the Railways also, presumably, because the Railways were strategically concerned with the movement and supply of war material.
12.2 An Ordinance No. XXII of 1943 was issued by the Government of India, by which a Special Police Force for the investigation of certain offences committed in connection with departments of the Central Government and with powers to investigate such offences, wherever committed in British India, was constituted. This Ordinance lapsed on $30^{\text {th }}$ September 1946 and was replaced by the Delhi Special Police Establishment Ordinance No. 22 of 1946, which was subsequently replaced by the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946 (Act XXV of 1946).
B ESTABLISHMENT AND EVOLUTION OF CBI
12.3 The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was established vide Resolution No.4/31/61-T dated 1st April, 1963 of the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. CBI has evolved out of the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) with an enlarged Charter of functions.
C Enlarging Role for Preventive VIGILANCE
12.4 To ensure probity, integrity, fairness and transparency in public life, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was entrusted with several Anti-Corruption and Preventive Vigilance functions in respect of the Central Government Departments, Central Public Sector Undertakings etc.
D EXPANDING ROLE AND RESTRUCTURING
12.5 The Economic Offences Division (EOD) in CBI was to cover various economic offences mainly pertaining to serious frauds in Banks, Stock Exchanges, Financial institutions, Joint Stock Companies, Public Limited Companies, misappropriation of public funds, misallocation of national natural resources like Coal, criminal breach of trust, cheating of small investors through Ponzi Scheme and Chit fund Scams, Cyber Crime, IMPEX Laws, counterfeiting of currency, narcotics, drug trafficking, offences related to antiques, arts & treasures, piracy, forgery of travel documents/ identity papers, fraud in overseas job rackets, Wildlife crimes etc.
E. INTERFACE WITH CVC
12.6 In pursuance of the directions of the Hon’ble Supreme Court in the Vineet Narain case, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) was accorded statutory status by enactment of the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003. The Commission was vested with superintendence over DSPE, in terms of Section 4 of the DSPE Act as far as it relates to the investigation of cases under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
12.7 The function and powers of the Commission, laid down in Section 8 of CVC Act, 2003. CVC exercises superintendence over the functioning of the DSPE in respect of investigation of offences under the PC Act. Issues discussed /reviewed during the Director, CBI and CVC Monthly Review Meetings
F. THE LOKPAL AND LOKAYUKTAS ACT, 2013
12.8 With the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013 (Act No. 1 of year 2014), the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946 has been amended providing for selection of Director, CBI on the recommendation of a Committee consisting of the Prime Minister- Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition recognized as such in the House of the People or where there is no such Leader of Opposition, then, the Leader of the single largest Opposition party in that House – Member and the Chief Justice of India or Judge of the Supreme Court nominated by him – Member.
12.9 The Act of 2013 further provides for a Directorate of Prosecution in CBI headed by a Director who shall be an officer not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India, for conducting prosecution of cases under this Act.
12.10 As per the Act, the Lokpal on receipt of a complaint, alleging commission of an offence punishable under PC Act, 1988 by a Public Servant, may order :-
(a) preliminary inquiry against any public servant by the DSPE (CBI) to ascertain whether there exists a prima facie case for proceeding in the matter; or
(b) investigation by DSPE (CBI) when there exists a prima facie case.
12.11 The Lokpal shall, notwithstanding anything contained in section 4 of the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946 and section 8 of the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003, have the powers of superintendence over, and to give direction to the Delhi Special Police Establishment in respect of the matters referred by the Lokpal for preliminary inquiry or investigation to the Delhi Special Police Establishment under this Act. Provided that while exercising powers of superintendence or giving directions as above, the Lokpal shall not exercise powers in such a manner so as to require the Delhi Special Police Establishment to investigate or dispose of any case in a particular manner.
G. CBI AS National Central Bureau (NCB)- NODAL POINT FOR INTERPOL IN INDIA
12.12 CBI has been the representative of the Country, since 1966, with International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO), popularly known as INTERPOL. Director, CBI is the ex-officio Head of National Central Bureau of India (NCB-India).
4.2 International Police Cooperation Unit (IPCU), CBI holds Conferences acting as the nodal point for law enforcement agencies in the country. It coordinates with States, primarily, through Interpol Liaison Officers (ILOs) in pending matters of Extradition, Letters Rogatory (LRs), Mutual Legal Assistance / Requests in Criminal Matters, issuance of Notices and guidance for International aspect of Investigation.
H. SPECIALISED UNITS WITHIN CBI
12.13 Realizing the ominous trend of exponential growth of Cyber Crimes early, the Cyber Crime Investigation Cell was setup in CBI in 1999.
12.14 Cyber & Hi-Tech Crime Investigation \& Training (CHCIT) Centre has been set up at CBI Academy in June 2010 by Ministry of Information Technology, Government of India for capacity building in the areas of investigation of cyber-crime, through training and providing tools and technology. The Centre aims to upgrade Cyber/Hi-Tech Crime investigation capabilities of CBI and also to provide worldclass training to the investigators of CBI, State Police and Law Enforcement Agencies of
I. CYBER CRIME INVESTIGATION
12.15 CBI is the designated nodal agency of the Government of India entrusted with the investigation of computer crimes. Meeting the evolving challenges of cybercrimes head-on, CBI has successfully elevated its capabilities in cybercrime investigation. Engaging in a multitude of critical functions and fostering collaborations both nationally and internationally, CBI is committed to effectively combating cybercrime.
12.16 This Division has won the faith of the Hon’ble Supreme Court of India in solving the NEET case on a war footing. The branch has again established its credibility, capability and professional skills in successfully solving the NEET cases that have been transferred by various State Governments. The NEET cases involve various modus operandi by several localized groups. The group from Hazaribagh specialized in leaking the question paper from the center of exam in connivance with the controlling authorities of the exam center and facilitating their candidates in lieu of huge sums of money. The group from Godhra wanted to mark the correct answers OMR sheets of the favored candidates before the same were sealed and sent to National Testing Agency [NTA].
12.17 The most common method was the use of dummy candidates who appeared in the exam in place of the actual candidate. The enormous demand and limited opportunities for getting admission to the MBSS was the driving factor which was used by the fraudsters to lure the candidates and their parents to spend lakhs of rupees. It was a tussle between money and merit, but law of the land prevailed in restoring the faith of the other meritorious and hard-working candidates.
12.18 The entire nation was focused on the outcome of the case that was transferred by the Govt. of Bihar. The accused persons had hatched a criminal conspiracy to commit the theft of the question paper of NEET UG 2024 examination and distribute the solved questions among the chosen candidates in lieu of huge amount of money.
12.19 The Hon’ble Supreme Court again exhibited its confidence on the CBI by transferring 18 cases related to a multi-level marketing (MLM) scheme that was floated in 2016-2017 involving crypto currency. The group of cases commonly known as ‘Gain Bitcoin’ are spread across Maharashtra, West Bengal, Delhi, Chandigarh, Punjab, Karnataka, Gujarat, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir. The accused persons collected money from the general public by using the multi-level marketing scheme that offered Bitcoin mining contracts. Under these contracts, people were promised a $10 %$ monthly return on every investment for 18 months, and the payout would be done in Bitcoins. Initially the investors were given returns but after a few months when the increase in members dwindled the payments stopped. It has been alleged that the accused persons purchased Bitcoins from the money collected from the investors and has refused to divulge the details. Three cases involving 18 police cases have been taken over.
12.20 There has been a surge of cases relating to ‘Digital Arrest’. Numerous complaints have been received regarding an elaborate cyber fraud network operating across India, particularly targeting residents of Delhi. The modus operandi involves impersonation, intimidation, and digital surveillance to extort significant sums of money from victims. The fraudsters present themselves as officials from courier companies, law enforcement agencies, or government authorities, accusing the victims of involvement in illegal activities such as drug trafficking, money laundering, or human trafficking. To deal with this new menace and taken down the cyber crime network two Cases of Digital Arrest of victims from Delhi and Rajasthan have been registered and are being investigated.
J. INTERNAL VIGILANCE
12.21 Members of Central Bureau of Investigation, the premier investigating agency fighting corruption, are required to maintain the highest standards of probity. As public, Constitutional courts and the Government repose so much faith in the CBI, it jealously guards its standards of integrity.
K. FUNCTIONING OF CBI
12.22 Legally, CBI derives its power to investigate from DSPE Act, 1946. Section 2 of the Act vests DSPE with jurisdiction to investigate offences notified under section 3 of the Act in the Union Territories only. However, the jurisdiction of the DSPE Act can be extended by the Central Government to other areas, including Railway areas and States under Section 5(1) of the Act, provided a State Government accords consent under Section 6 of the Act. The Executive Officers of CBI of the rank of Sub-Inspector and above exercise all powers of a Station Officer-in-charge of the Police Station for the concerned area for the purpose of investigation. As per Section 3 of the Act, Special Police Establishment is authorized to investigate under those sections of law, which are notified by the Central Government from time to time. The Hon’ble Supreme Court of India and the Hon’ble High Courts also entrust matters for Investigation or Enquiry to CBI. These may be new cases or cases which are already registered by the State Police or other investigating agencies. In the cases entrusted to CBI by the Hon’ble Supreme Court or the Hon’ble High Courts, there is no requirement for any notification under section 5 or 6 of the DSPE Act, 1946.
12.23 The Director, CBI, heads the organization and is assisted by Special Director(s) and Additional Director (s). The organization is divided into Zones, each headed by a Joint Director. The Zones may be classified into Investigating Zones and Support Zones/ Divisions.
12.24 CBI has 16 investigative Zones and 58 investigative Branches spread across India. The Investigating Zones, comprise of Branches, which are headed by DIG/SP/ASP and report to Joint Directors, who report to Director, CBI through a Special Director/ Additional Director. Some of these Zones have Ranges under them, which are headed by DIG. They supervise the branches falling within their jurisdiction.
12.25 During the period of April 2024 to March, 2025, the Central Bureau of Investigation has emerged as a Premier Investigating Agency of the country, which enjoys the trust of the people, Parliament, Judiciary and the Government. The organization has evolved from an Anti-Corruption Agency to a Multifaceted, Multi-Disciplinary Police Investigative Agency with capability, credibility and legal mandate to investigate and prosecute offences. As on date, offences under existing 110 Central Acts, 54 State Acts and 290 offences under the Indian Penal Code ( 213 offences under the BNS 2023) have been notified under section 3 of the DSPE Act, 1946.
L. HUMAN RESOURCE AND INFRASTRUCTURE UPGRADATION
12.26 The total sanctioned strength of CBI as on 31.03 .2025 was 7300 against which 5705 officers were in position and 1595 posts were vacant. The vacancies existed in the ranks of Joint Director (04), Deputy Inspector-General of Police (03), Senior Superintendent of Police (09), Superintendent of Police (45), Additional Superintendent of Police (20), Deputy Superintendent of Police (29), Inspector (382), SubInspector (188), Assistant Sub-Inspector (34), Head Constable (48), Constable (196). The posts of Law Officers (47), Technical Officers (57), Ministerial Staff (526) and Canteen staff (07) at various levels were lying vacant.
12.27 INDUCTION
During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, total 535 Officers/Officials were inducted on deputation in CBI in different ranks comprising of Additional Director (01), Joint Director (01), Deputy Inspector General of Police (03), Superintendent of Police (12), Deputy Superintendent of Police (06), Deputy Adviser [Engg. /Civil] (03), Deputy Advisor [Eng./Electronics, Electrical] (01), Inspector (57], Assistant Sub-Inspector (02), Head Constable (08) and Constable (441).
12.28 DIRECT RECRUITMENT
During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 63 Officers/Officials were recruited in different ranks under direct recruitment quota comprising of Public Prosecutor (43), Assistant Public Prosecutor (07), Lower Division Clerk (12) and MTS (01).
12.29 COMPASSIONATE APPOINTMENT
During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 10 Officials were recruited in different ranks under direct recruitment quota comprising of Lower Division Clerk (07) and MTS (03).
12.30 DEPARTMENTAL PROMOTION COMMITTEE
During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 49 meetings of DPCs/Review for Promotions of Executive and Ministerial Staff were held and 461 officers/ officials (including LDCE) were promoted in different ranks comprising of Joint Director (01), DIG (05), Sr. SP (05), SP (09), ASP (04), DSP (31), Inspector (39), Sub-Inspector (14), ASI (16), Head Constable (61), ALA (04), DLA (10), Sr. PP (15), PP (04), AO(01), OS (08), CA (06), UDC (53), LDC (04), PPS (01), Sr.PS (02), Asstt. Halwai cum Cook (01), and Tea Coffee Maker (01).
M. CRIME STATISTICS REGISTRATION
12.31 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 852 Regular Cases/Preliminary Enquiries [RCs724, PEs-128] were registered. Out of 852 cases, 103 cases were taken up on the directions of the Constitutional Courts and 64 cases on the requests of the State Governments/Union Territories. Other than these, 38 references of Lokpal were taken up.
N. DISPOSAL FROM INVESTIGATION/ENQUIRY
12.32 The Investigation in cases were expedited during the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025 and as a result, investigation were completed in 1039 cases comprising of 896 Regular Cases (RCs) and 143 Preliminary Enquiries (PEs). Other than this, Inquiry/Status Report were sent in 37 Lokpal references.
12.33 MODE OF DISPOSAL
12.33.1 Mode of disposal of RCs
Out of 896 Regular Cases [RCs], Prosecution, Prosecution & RDA was recommended in 766 cases, while only RDA were recommended in 4 cases. The break-up of the disposal of 896 RCs from investigation, is depicted as under: –
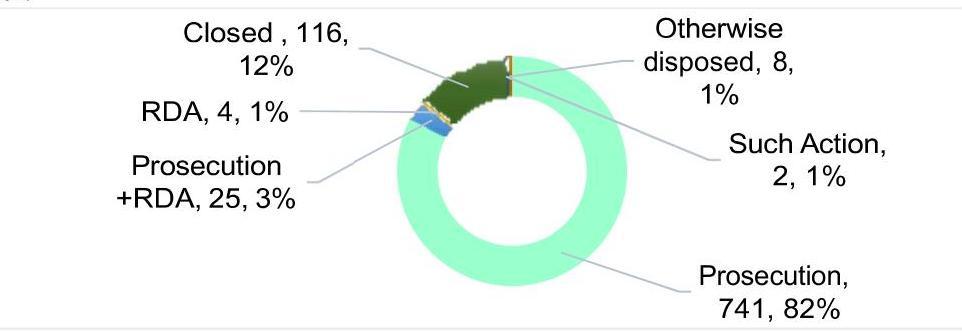
12.33.2 Mode of disposal of PEs
Out of 143 PEs, 44 PEs were converted into Regular Cases (RCs) and RDA was recommended in 4 PEs. The break-up of the disposal of 143 Preliminary Enquiries (PEs), is depicted as under: –
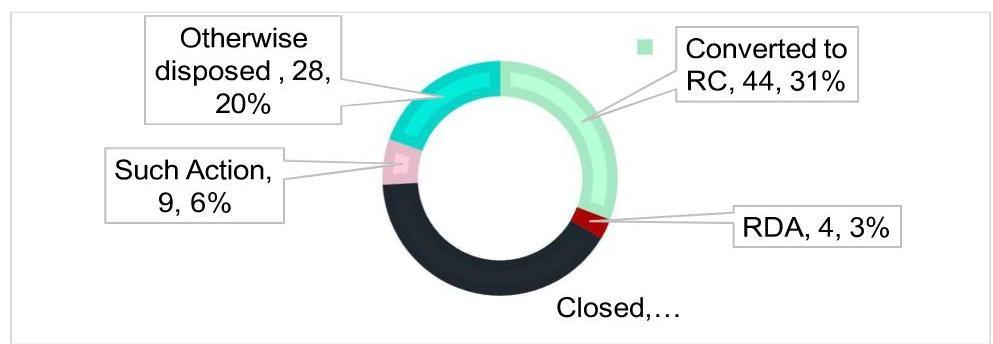
12.34 CASES PENDING UNDER INVESTIGATION/ENQUIRY
A total number of 907 cases (RCs 827 , PEs 80 ) were pending under investigation/ enquiry at the end of March, 2025. Other than this, 8 Lokpal References were pending at the end of March, 2025. Out of 827 RCs, 427 RCs were pending under investigation for more than one year. Similarly, out of 80 PEs, 42 PEs were pending under enquiry for more than three months.
12.35 TRIAL
During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, Courts delivered Judgements in 702 Court Cases of CBI. Out of these, 423 cases resulted in Conviction, 170 in Acquittal, 25 in Discharge and 84 cases were disposed of for other reasons. The conviction rate was $\mathbf{6 8 . 4 4 %}$.
A total number of 11351 Court Cases were pending under trial in various Courts as on 31.03.2025.
O. COORDINATION
12.36 Coordination with Law Enforcement /State/Union Territory
$19^{\text {TH }}$ HEADS OF NCB CONFERENCE
12.37 $19^{\text {th }}$ Heads of NCB Conference was held from $23^{\text {rd }}-25^{\text {th }}$ April 2024 at Lyon, France.
VISIT OF DIRECTOR OF BRAZILIAN FEDERAL POLICE
12.38 A high-level delegation led by Mr. Valdecy Urquiza, Director of Brazilian Federal Police visited CBI Headquarters on $3^{\text {rd }}$ April, 2024 and met with Shri Praveen Sood, The meeting involved exchange of insights in addressing a wide range of criminal activities and strengthening police cooperation for combating trans-national crimes.
VISIT OF MR STEPHEN KAVANAGH, EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR POLICE SERVICES, INTERPOL
12.39 A high level delegation from the UK visited CBI headquarters on $15^{\text {th }}$ April, 2024. Both sides shared commitment to addressing global crime threats in a coordinated and effective manner including via INTERPOL channels.
VISIT OF AMBASSADOR OF THE REPUBLIC OF CHILE
12.40 H.E. Mr. Juan Angulo Ambassador, Embassy of the Republic of Chile in India visited CBI Headquarters, New Delhi on $20^{\text {th }}$ May, 2024.
VISIT OF MEXICAN DELEGATION
12.41 A Mexican delegation led by Admiral José Luis Vergara Ibarra, Naval Attaché; visited CBI Head Quarters, New Delhi on $6^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024. Discussions were held related to enhancing information sharing on drug trafficking which is within responsibilities of Mexican Navy.
$10^{\text {th }}$ INTERPOL LIAISON OFFICERS CONFERENCE
12.42 The INTERPOL Liaison Officers Conference [ILOs], organized by CBI, was inaugurated by Shri Govind Mohan, Union Home Secretary of India at the CBI Headquarters, New Delhi on $5^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024.
SIGNING OF MOU BETWEEN CBI AND ANTI-CORRUPTION COMMISSION (ACC), MALDIVES
12.43 The CBI and Anti-Corruption Commission, Maldives signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to exchange technical assistance in investigating and prosecuting corruption offences. The MoU was formally exchanged on 9th October, 2024 during a ceremony held as part of Maldives President Dr. Mohamed Muizzu’s visit to India. On behalf of CBI, Shri Praveen Sood, Director, CBI and on behalf of ACC, Maldives Uz. Adam Shamil, President, Anti-Corruption Commission, Maldives signed the MoU.
SIGNING OF MOU BETWEEN CBI AND FINANCIAL CRIME COMMISSION (FCC), MAURITIUS
12.44 An amended/modified Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and the Financial Crimes Commission of Mauritius (formerly known as the Independent Commission Against Corruption (ICAC)) was signed on 7th March 2025
LAUNCH OF BHARATPOL 07.01.2025
12.45 Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation, Shri Amit Shah, Inaugurated the Bharatpol Portal Developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) at Bharat Mandapam New Delhi on 7th January 2025. CBI has developed the BHARATPOL online Portal, which is a ground-breaking initiative to bring a multi-dimensional momentum in Indian Policing through Rapid and Real Time International Police Cooperation.
ILO TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR USAGE OF PORTAL ON 07.01.2025 – A/N
12.46 A training Programme for INTERPOL Liaison Officers of all State Police forces and Central Law enforcement agencies on BHARATPOL and its Module wise Operations was organised on 7th January 2025. 110 Officers from State and Central LEAs attended the Training.
LETTERS ROGATORY (OUTGOING)
12.47 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 74 Letter Rogatory (LRs) were sent abroad, out of which 54 LRs pertain to CBI cases and 20 LRs pertains to State Law Enforcement and other Central Law enforcement agencies. It was confirmed by Indian Law Enforcement Agencies including CBI that 47 LRs are fully executed during the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, out of which 42 are of CBI and 5 were of other ILEAs. During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, 29 LRs of States/ Central Agencies, out of which 27 of CBI and 02 of State and Central Law Enforcement Agencies, were disposed as closed/withdrawn on partial execution.
12.48 As on 31.03.2025, a total 533 LRs were pending with other countries, out of which 276 pertain to CBI cases and 257 pertain to State Police and other Central Law Enforcement Agencies.
LETTERS ROGATORY (INCOMING)
12.49 As many as 32 Letters Rogatory (LRs)/Treaty Based Requests were received from various countries requesting to provide assistance in the investigation of criminal matters. Besides these, 06 LRs/MLA requests were received as Addl./ Supplementary requests. Execution Reports in 66 cases were sent to MEA/MHA, after receiving the same from Indian Investigating Agencies, for onward transmission to the law enforcement agencies of the requesting countries. Besides these, 02 LRs/MLA requests were otherwise disposed of as closed or withdrawn. As on 31.03.2025, 71 LRs/MLA Requests are pending for execution.
INTERPOL NOTICES
12.50 Notices are issued for fugitives wanted either for prosecution or to serve a sentence. Brief of the INTERPOL Notices are as under: –
- Red Notice is a request to law enforcement agencies worldwide to locate and provisionally arrest a person pending extradition, surrender, or similar legal action.
- Blue Corner Notice is a request from INTERPOL for information about a person’s identity, location, or activities. It is also known as an enquiry notice.
- Yellow Notice is a global police alert for a missing person. It is published for victims of parental abductions, criminal abductions [Kidnappings] or unexplained disappearances. The Yellow Notice can also be used to help identify a person who is unable to identify himself or herself.
- Black Notice is an INTERPOL Notice that requests information about unidentified bodies. It is used to help member countries identify deceased people and provide closure to their families.
- Green Notice is a warning issued by INTERPOL to alert member countries about people who are considered a potential threat to public safety.
12.51 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025 Notices that got published by NCB- India on request of Indian LEA’s are as follows:
Red Notices published by NCB -India -126
Blue Notices published by NCB -India -89
Yellow Notices published by NCB -India -24
Black Notices published by NCB-India -07
Green Notices published by NCB-India -01
EXTRADITION / DEPORTATION’
12.52 CBI via its Global Operations Centre (GOC) geo-locates wanted criminals and fugitives in cooperation with foreign law enforcement agencies via INTERPOL channels and through issue of INTERPOL notices. On ascertaining location of wanted subjects, CBI coordinates with concerned law enforcement agencies, INTERPOL National Central Bureaux of concerned countries, Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of External Affairs, for return of wanted subject from abroad. NCB-New Delhi also tracks persons wanted by foreign countries in criminal matters via INTERPOL notices: –
| Wanted Persons/Fugitives wanted by India, located abroad | 71 |
|---|---|
| Wanted Persons/Fugitives wanted by other countries, detected/ located in India | 203 |
| Wanted Persons/Fugitives returned to India, from abroad in 2024-2025 | 27 |
INTERPOL STOLEN AND LOST TRAVEL DOCUMENTS (SLTD) DATABASE
12.53 NCB, India has uploaded data relating to lost/stolen/revoked Indian passports into the INTERPOL SLTD Database being maintained by International Police Cooperation Unit [IPCU] Branch. Till 31.03.2025, data of 191031 Stolen / Lost/ Revoked Indian Passports has been uploaded in the SLTD Database. Upto 31.03.2025, 30 cases regarding use of STLD recorded Indian passports have been reported/detected by various other NCBs.
INTERPOL GLOBAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [IGCS] MESSAGES RECEIVED DURING THE PERIOD OF APRIL, 2024 TO MARCH, 2025
12.54 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, NCB New Delhi processed total of 17170 messages for assistance exchanged through INTERPOL Global Communication System with the INTERPOL General Secretariat and the NCBs of other member countries for assistance in police related matters.
INTERPOL OPERATIONS
12.55 INTERPOL runs various targeted operations every year. During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, NCB-New Delhi has participated in INTERPOL run Operations Thunder 2024, HAECHI V, Operation Pangea XVII, Operation Liberterra-II and Operation Secure.
PROCESSING OF APPLICATION FOR RENUNCIATION OF INDIAN CITIZENSHIP
12.56 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, CBI [IPCU] processed and gave comments on more than 22200 applications for renunciation of Indian Citizenship on IVFRT portal of MHA.
P. CAPACITY BUILDING
12.57 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, CBI Academy and the three Regional Training Centers (functioning at Kolkata, Mumbai, and Chennai) conducted a total of 177 courses and trained 9087 Officers/Officials.
Q. AWARDS AND ACCOLADES TO CBI OFFICERS DURING THE PERIOD OF APRIL, 2024 TO MARCH, 2025 PRESIDENT’S MEDAL FOR DISTINGUISHED SERVICE & MEDAL FOR MERITORIOUS SERVICE
12.58 During the period of April, 2024 to March, 2025, twelve (12) officers of Central Bureau of Investigation have been awarded President’s Medals (PSM) for Distinguished Service and thirty-seven (37) officers of Central Bureau of Investigation were awarded Medal for Meritorious Service (MSM) on the occasions of the Independence Day, 2024 and Republic Day, 2025.
R. FUTURE ROADMAP
12.59 Bureau as the designated nodal agency of the Government of India, is entrusted with the investigation of computer crimes. Demonstrating its commitment to tackling the evolving challenges of cybercrimes, Bureau has consistently enhanced its capabilities in cybercrime investigation.
12.60 Besides, considering the dynamism of the field of crime and criminality, the Bureau is making strenuous efforts to keep pace with technological advancements, complexities of criminal act, and evolving legal and social landscapes. Over a period of time, Bureau significantly fortified its capabilities in cyber-crime investigation.
12.61 In order to enhance coordination between law enforcement agencies and INTERPOL named ‘BHARATPOL’ was launched by the Hon’ble Home Minister of India. The platform will significantly advance the India’s law enforcement infrastructure, facilitating seamless, reliable, faster, smoother data sharing on real time basis between the law enforcement agencies and INTERPOL, which would help in combating national and transnational crimes and enhancing national security, as well.
CHAPTER 13
JOINT CONSULTATIVE MACHINERY
13.1 The Scheme for Joint Consultative and Compulsory Arbitration for the Central Government Employees was introduced in the year 1966 on the lines of the Whitely Councils in the U.K. The scheme provides a platform for constructive dialogue & discussion between the representatives of the staff side and the official side for peaceful resolution of all disputes between the Government as employer and the employees. The scheme was introduced with the objectives of promoting harmonious relations and securing the greatest measure of cooperation between the Central Government as the employer and the employees in matters of common concern and further increasing the efficiency of the public service combined with the well-being of those employed.
13.2 The JCM Scheme provides for three-tier machinery:
i. The National Council as the apex body; (chaired by the Cabinet Secretary);
ii. Departmental Councils at the level of individual Ministries / Departments including their attached and subordinate offices and (chaired by respective Secretaries); and
iii. Regional / Office Councils to deal with mainly the local problems at the level of each individual office, depending on its structure. (Chaired by Head of office of respective organizations).
13.3 The scope of the JCM Scheme includes all matters relating to:
conditions of service and work;
the welfare of the employees; and
improvement of efficiency and standards of work,
Provided, however that in regard to recruitment, promotion and discipline, consultation is limited to matters of general principles only and individual cases are not considered.
13.4 National Council (JCM)
The National Council is the apex body under JCM, Chaired by the Cabinet Secretary. It comprises members both from staff side and official side. The official side of the National Council consists of 25 members and the staff side consists of 60 members National Council may have two Standing Committees; i) for the Non- Industrial employees, ii) Industrial employees. So far, 48 meetings of the National Council (JCM) have been held since its inception in 1966.
13.5 Standing Committee Meeting of the National Council (JCM):
The Standing Committee, Chaired by the Secretary (DOPT). So far, 62 meetings of the Standing Committee have been held.
Departmental Council
13.6 Functioning of the Departmental Council which is a vital part of the Joint Consultative Machinery formed with the very important purpose of promotion of harmonious relations and ensuring cooperation between Government and its employees.
13.7 This division is concerned with the recognition of Service Associations formed by employees of different services working in Central Secretariat. At present, process of recognition of Service Associations is in under consideration.
13.8 ARBITRATION
An important feature of the JCM Scheme is the provision for arbitration in cases where there is no agreement between the Official Side and the Staff Side on matters relating to: –
pay and allowances;
weekly hours of work; and
leave, for a class or grade of employees.
13.9 BOARD OF ARBITRATION (BOA)
A Board of Arbitration (BOA) comprising three Members; a Chairman (an independent person) and two Members, nominated, (one each by Staff Side and Official Side), functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Labor & Employment. Award of the Board of Arbitration is binding on both sides, subject to the over-riding authority of Parliament to modify or reject the Award.
CHAPTER 14
ADMINISTRATIVE TRIBUNALS
14.1 The Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985 owes its origin to Article 323-A of the Constitution of India which empowers Central Government to set up Administrative Tribunals by an Act of Parliament for adjudication of grievances and disputes arising out of the conditions of service of an employee appointed to the public services and posts in connection with the affairs of the Union and the States. In pursuance of the provisions contained in the Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985, the Administrative Tribunals, set up under it, exercise original jurisdiction in respect of service matters of employees covered by the Act. As a result of the Supreme Court’s judgment dated 18.03.1997 in the case of L. Chandra Kumar $&$ Others Vs UOI, the appeals against the orders of an Administrative Tribunal shall lie before the Division Bench of the concerned High Court.
14.2 The Administrative Tribunals are distinguishable from the ordinary courts with regard to their jurisdiction and procedure. They exercise jurisdiction only in relation to the service matters of the litigants covered by the Act. They are also free from many of the procedural technicalities of the ordinary courts. The procedural simplicity of the Act can be appreciated from the fact that the aggrieved person can also appear before it personally. Government can also present its cases through its departmental officers or legal practitioners. Further, only an affordable and nominal fee of $₹ 50$ is to be paid by the applicants for filing the original application before the Tribunal. Thus, the objective of the Tribunal is to provide speedy and affordable redress to the aggrieved applicants arising out of employment or conditions of service.
14.3 The Central Administrative Tribunal was set up on 01.11.1985. As on date, it has 19 regular Benches, 17 of which operate at the Principal Seats of High Courts and the remaining two at Jaipur and Lucknow. A statement showing the location of Central Administrative Tribunal Benches, the dates of their establishment and the number of courts in each of these Benches along with a list of places where they hold Circuit Sittings is given in Annexure-IV.
14.4 The Tribunal consists of a Chairman and Members. It has also been the constant endeavor of this Ministry to ensure that the posts of Chairman and Members are filled up well in time and no post remains vacant for long time. The Members of Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) and State Administrative Tribunals (SATs) are drawn from judicial as well as administrative streams, so as to give the Tribunal the benefit of domain expertise both in legal and service matters. The sanctioned strength of Members of Central Administrative Tribunal is 70 (including Chairperson, CAT), out of which 35 are Judicial Members and 35 are Administrative Members. As per Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021, the Chairperson can be a Judicial Member or an Administrative Member.
14.5 The appointment of Chairperson / Members in CAT is made on the basis of the recommendations of a Search-cum-Selection Committee (ScSC) chaired by the Hon’ble Chief Justice of India or a sitting Judge of Supreme Court (nominated by the Hon’ble Chief Justice of India). After receipt of recommendations of the ScSC, appointments are made with the approval of Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC).
14.6 State Administrative Tribunals (SATs) have also been approved for the following States:
(i) Karnataka
(ii) Maharashtra
(iii) West Bengal
(iv) Kerala
(v) Haryana (non-functional)
14.7 The appointments to the vacancies in SATs are made on the basis of proposals sent by the State Governments. Thereafter, their appointments undergo the same process as the one in respect of Central Administrative Tribunal.
14.8 Since its inception in 1985 and up to 31.03 .2025 , the Central Administrative Tribunal received $\mathbf{9 , 6 2 , 0 2 5}$ cases for adjudication (including those transferred from High Courts), out of which $\mathbf{8 , 9 2 , 0 8 6}$ cases have been disposed of, leaving a pendency of $\mathbf{6 9 , 9 3 9}$ cases. A statement indicating the institution, disposal and pendency of cases since inception of CAT is at Annexure-V.
14.9 Section 14(2) of the Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985 empowers the Central Government to extend the provisions of the Act to local or other authorities within the territory of India or under the control of Government of India and to Corporations or Societies owned or controlled by Government of India. In exercise of these powers, the Central Government had extended the provisions of the Act to 229 organizations so far.
14.10 In order to familiarize the newly appointed Members of CAT with the functioning of the Tribunal, a short Orientation Programme / Training is held from time to time. So far, five such Orientation Programme / Training have been held.
14.11 Further, for maintaining absolute integrity and promoting fair practices in the professional court dealings and keeping in view the general directions of the Hon’ble Supreme Court, the designated Selection Committee, in its meeting decided that a Judicial Member of CAT, who earlier practiced as Advocate in a Court in that station, should not normally be considered for posting in the CAT Bench of the same station.
14.12 It has been the constant endeavor of the Government to strengthen the infrastructure in all the Benches of CAT for their smooth functioning. For this purpose, allocation of funds for purchase of land and construction of building during the period 2019-20 to 2024-25 is as under.
| Year | Allocation (Rs. crore) |
|---|---|
| $2019-20$ | 9.98 |
| $2020-21$ | 8.00 |
| $2021-22$ | 10.00 |
| $2022-23$ | 4.06 |
| $2023-24$ | 15.00 |
| $2024-25$ | 18.00 |
14.13 Hon’ble Shri Justice Ranjit Vasantrao More is presently the Chairman of CAT. He was appointed as Chairman with effect from 30.07.2022. Before his appointment as the Chairman, CAT, Shri Justice More had been the Chief Justice of Meghalaya High Court.
14.14 Other initiatives/achievements
(a) Development and management of Human Resources of the Government, Administrative Reforms and Pensioner matters:
(i) The project of cloud based Advance Case Information System consist of various phase i.e. Advance Case Information System (E-Filing & Internal Module), Mobile App, design and development of new website of CAT, SMS facility, online payment, video conferencing setup, e-Courts setup etc. It is submitted that the Advance Case Information System (ACIS) has been made operational in all the Benches of CAT and all the judicial work from filing of fresh cases as per the administrative Act, 1985 till judgments uploading are being processed through ACIS (cloud based application).
(ii) Scanning and Digitization of Judicial records: The CAT is in process of scanning, digitization, metadata preparation, bookmarking uploading the judicial records on ACIS server of Judicial record.
(iii) With regard to the status of various modules developed and implemented in ACIS as per ACIS project, are as under:-
a. E-Filing of Cases: The online filing of cases/documents by Registered users and facility to upload scanned documents has also been implemented alongwith the physical copies of cases filed through e-filing.
b. E-Courts/Smart Court: This office is in process to scan the old judicial proceedings/file, so as to ensure that E-Court/Smart Court may be made fully functional during this year.
c. Display Board: LED Display (Digital Display Board) has been installed in the CAT, Principal Bench at different required locations to facilitate the stakeholders to know the current status of their case in different courts.
d. SMS facility: SMS facility has been made functional for informing the parties about their case status, next listing date and proceeding reports is implemented and the stakeholders are getting status on their mobile and email.
e. Online Payment: The e-payment module of CAT for making online payment of the Application Fees/Court fees etc. through the payment gateway Bharat Kosh in the e-filing module of ACIS of CAT has been made operational w.e.f 12.06.2024.
f. Mobile App: The Mobile Application for both the platform for (Android and iOS (iPhone)) for Advanced Case Information System (ACIS) for all the Benches of the Tribunal has been made live and is being used by all the stakeholders.
g. Hybrid VC hearing: The facility of Hybrid hearing has been implemented and is functional in all the Benches of CAT. Link to join in the respective Courts is being provided in the daily Cause list so that the concerned person may join from anywhere for VC.
h. Facility for applying Certified Copy and Inspection of files through online mode is also under testing phase and shortly will be available to all the stakeholders.
(b) Launch of ACIS Module for e-filing
CAT has rolled out the ACIS module for e-filing of fresh cases and e-filing of ancillary applications/documents in the matter. The facility developed for hearing through virtual mode especially act as a boon for differently abled persons since it minimizes the need for them to visit courts for pursuing their matter. Further, provision have also been made for virtual hearing of court cases for parties-in-person and advocates for which a web link is provided in the daily cause list. Although this initiative benefits the petitioners and the counsels at large, it is particularly beneficial for differently abled persons who are pursuing their cases themselves.
(c) Initiatives for Staff Welfare, Capacity Building and e-Governance etc.
i. e-HRMS 2.0 portal has successfully been implemented in all Benches of CAT.
ii. Formulation of proper Transfer Policy and Grievance Redressal mechanism for the staff of CAT is under process.
iii. Pension papers of soon-to-be retiring employees are being submitted online through Bhavishya portal along with forwarding of Hard copy to the Pay and Accounts Office for early settlement of pensionary benefits.
iv. All provisions of the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal Act, 2013 are being observed in all Benches of CAT along with meeting of the Internal Complaints Committee on every quarter.
v. i-GOT Karmayogi portal has successfully been implemented in all Benches of CAT for Capacity Building needs of the employees in various fields.
vi. Draft Annual Capacity Building Plan has been formulated and forwarded to DoP&T (Training Division) for their comments/approval on the same.
vii. All orders pertaining to appointment, transfers, postings, promotions, etc. are being uploaded on the website of CAT for transparency and probity.
viii. Restructuring of different cadres to cater the ever-changing requirements of the organization.
ix. Amendment of Recruitment Rules of different cadres to cater ever-changing qualifications of the candidates.
x. e Office portal has been successfully implemented in all Benches and is presently under testing/trial phase.
CHAPTER 15
STAFF WELFARE
15.1 The Central Government is the largest single employer in the country and bears the major responsibility for looking after the welfare of a large number of employees spread all over the country. Realizing that improvement in the working and living conditions of the employees and their families leads to efficiency and high morale, the Department of Personnel and Training supports various staff welfare measures. A brief account of various welfare measures dealt with by the Welfare Division is given below.
RESIDENTS’ WELFARE ASSOCIATION
15.2 In order to foster a spirit of mutual help and good will among residents of Government colonies and to promote social, cultural and recreational activities, Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) has been encouraging formation of Central Government Employees Residents’ Welfare Associations (CGERWAs). Every CGERWA seeking reorganization and grants-in-aid from Government is required to adopt Model Constitution prescribed by DOPT. The members of the Managing Committee of these Associations are elected every two years under the Provisions of a Model Constitution framed by the Department of Personnel \& Training. This Department Sanctions grants-in-aid only to recognized Associations, subject to a maximum of Rs. 10,000/- per annum for an Association. Grants-in-aid to 10 CGERWAs was released in 2024-25 for the year 2023-24.
AREA WELFARE OFFICERS
15.3 The Area Welfare Officers (AWOs) are nominated in residential colonies having a large number of Central Government employees. The AWOs serve as a link between the Government and residents in matters relating to the welfare of the Government employees living in various colonies. They also work as field officers in coordinating and maintaining liaison with various agencies of Government such as CPWD, CGHS, Police etc. Applications are invited from Gazetted officers working in various Ministries/Departments for being nominated as Area Welfare Officers for a period of two years. Officers desirous of being nominated as AWOs on voluntary and honorary basis are required to apply through their respective Ministries/ Departments. A total of 46 AWOs in Delhi and 9 AWOs in outside Delhi areas were nominated for the year 2025 and 2026.
CENTRAL CIVIL SERVICES CULTURAL \& SPORTS BOARD (CCSCSB)
15.4 The Central Civil Services, Cultural \& Sports Board, a society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 is the Central agency for promotion of Cultural \& Sports activities amongst the Central Government employees in the country. The Board was set up in 1964 as Central Secretariat Club in the Ministry of Home Affairs. Initially, the objective ofthe Board was to promote cultural and sports activities amongst the Central Government Employees located in Delhi only. Subsequently, Regional Sports Boards were set up in various states. Financial grants in-aid is sanctioned every year by the Board to the Regional Boards.
ACTIVITIES OF THE BOARD INTER MINISTRY TOURNAMENTS 2024-25
15.5 The Board organizes Inter-Ministry Tournaments in 20 disciplines of sports. CCSCSB organizes inter ministry tournament in Athletics, Badminton, Basketball, Carrom, Chess, Cricket, Football, Hockey, Kabaddi, Kho-Kho, Music, Dance \& Short Play, Lawn Tennis, Power lifting, Weightlifting, Best Physique Swimming, Shooting Ball, Table Tennis, Volleyball, Wrestling and Yogasana.
All INDIA CIVIL SERVICES TOURNAMENTS HELD DURING THE YEAR 2024-25
15.6 These tournaments, which are open to Central and State Government employees, aim to give an opportunity to the civil servants to meet and interact with each other and compete. AICS Tournaments are being organized in collaboration with different States/UTs.
15.7 NEW ACTIVITIES UNDERTAKEN BY THE BOARD IN 2024-25
15.7(1) Cricket match between Assistant Secretary Team and Cabinet Secretary Team was organized on $6^{\text {th }}$ July, 2024 at Siri Fort.
15.7(2) Third Edition of National Sports Day was organized in the year 2024-25 at Vinay Marg ground on $29^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024 for Central Government Employees.
15.7(3) Swacchta Abhiyan was organized by CCSCSB on $2^{\text {nd }}$ October, 2024 at GKK, Lodhi Road.
15.7(4) Run for Unity for wards of Central Govt. Employees in 2024-25 on $27^{\text {th }}$ October, 2024 and for Central Government Employees on $31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024 at Vinay Marg Ground.
15.7(5) Organized Inter ministry wheel Chair Lawn Tennis Tournament for first time in the year 202425. The event was started from $30^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024 and concluded on $3^{\text {rd }}$ December, 2024 (International day of person with disabilities).
15.7(6) Fourth edition of Women’s meet was organized in the year 2024-25 on $15^{\text {th }}$ January, 2025.
15.7(7) The Board is affiliated to a number of sports associations/federations at the National level. Board’s teams participate in the National Tournaments organized by these Associations/Federations in Kabaddi, Hockey, Football, Carrom, Cricket and Chess.
SPORTS FACILITIES IN DELHI
15.8 The Board has a sports complex at Vinay Marg, New Delhi which has facilities for Football, Hockey, Cricket, Athletics, Lawn Tennis, Basketball, Volleyball and practice pitches for Cricket. The Board also maintains lawn Tennis Courts at Brassy Avenue, Bharti Nagar, Pandara Road and R.K. Puram Sector 13, New Delhi, there is facility for Indoor games such as Table Tennis at Nirman Bhawan, New Delhi. Open Gym facilities are available at Vinay Marg, Bharti Nagar, Pandara Road and R.K Puram Sector 13 .
COACHING FOR CHILDREN DEPENDENTS OF GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEES
15.9 The Board also conducts regular coaching in Cricket, Football and Lawn Tennis for the children/ dependents of Government employees at Vinay Marg Sports Complex, New Delhi. Coaching in Lawn Tennis is also available at Bharti Nagar, Pandara Road and R.K. Puram Sector-13.
15.10 The Board also organizes Summer Coaching camp in Basketball, Cricket, Football, Volleyball, Self-defense and Lawn Tennis for children/dependents of government employees.
GRIH KALYAN KENDRA
15.11 Grih Kalyan Kendra (GKK) is a registered Society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 and functioning under the aegis of Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions.
15.12 The basic objectives of the Kendra in brief are: –
a) To promote social, economic, cultural and educational activities for the welfare of Central Government Employees and their families.
b) To impart technical and vocational training in home crafts and other household arts for useful utilization of leisure time and better and efficient housekeeping.
c) To organize and promote economic activities that may provide opportunities for gainful employment to families of Central Government employees for supplementing the family income.
15.13 The GKK is administered by GKK Board.
The Board, which has the Secretary (P) or his nominated officer as the President, is responsible for the organization and administration of GKK.
15.14 In pursuance of its objectives, GKK has been conducting the following activities:
a) Training classes in cutting, tailoring and embroidery for the housewives and grown-up girls during their leisure hours.
b) Nursery education for children in the age group of 3 to 5 years.
c) Creches or Day Care Centres for children between the age of 90 days to 10 years.
d) Recreational facilities like Health Club/Gym, Badminton and Tennis, etc.
e) Coaching classes in Martial Arts, Yoga, Music, Dance, Computer, Brain Development, Fine Arts etc.
15.15 The welfare activities run by Grih Kalyan Kendra are indicated in the table given below:
| Place | Number Samaj Sadans/ Centres |
Craft Centres |
Nursery Schools |
Creche Centres |
Health Clubs/ Gyms |
Ayurveda Health Centre |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delhi | 28 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| Mumbai | 4 | – | 4 | – | – | – |
| Chennai | 3 | – | 1 | – | – | – |
| Jaipur | 2 | 1 | – | 1 | – | – |
| Dehradun | 2 | – | 2 | – | – | – |
| Nagpur | 2 | – | – | – | 1 | – |
| Bangalore | 3 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Faridabad | 1 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Kolkata | 1 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Ghaziabad | 1 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Total | 47 | 5 | 12 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
- Staff has been provided by GKK to Crech Centre run by Lok Sabha Secretariat, Parliament Annex.
15.16 The Grih Kalyan Kendra has undertaken the following activities during year 2024.
i) During 2023-24 Nursery classes are conducted in Delhi, Chennai, Dehradun and Mumbai and approximately 880 children have been benefitted. Martial Art and Gym/CrossFit activity, Music and Dance, Computer classes, Fine Art, Ayurveda Health Centre & Craft Activity on outsource basis have also been resumed in GKK, Delhi during 2024-25.
ii) DOPT launched a Yoga training scheme w.e.f. 01.04.2015 in association with Morarji Desai National Institute of Yoga, New Delhi for the benefit of Central Government employees and their dependants free of cost. The training sessionsare conducted in 25 locations in Delhi and 11 Samaj Sadans of Grih Kalyan Kendra outside Delhi upto 31.01.2024. Due to some unavoidable circumstances yoga activity in all 36 centre was discontinued w.e.f. 01.02.2024, however yoga activities have been resumed in 7 centres in Delhi out of which 4 centres are being run by GKK and 3 are outsourced to private parties on fee sharing basis. Yoga trainers have been engaged by Grih Kalyan Kendra on contract basis.
KENDRIYA BHANDAR
OBJECTIVES OF THE ORGANISATION
15.17 The Central Government Employees Consumer Cooperative Society Ltd., New Delhi, operating in the name of KENDRIYA BHANDAR was set up in 1963 in pursuance of Cabinet decision as a Welfare Project for the benefit of the Central Government Employees. The society endeavours to serve the Central Government Employees and the general public at large by providing quality goods of daily needs at reasonable prices through its retail stores. The range of items which Kendriya Bhandar provides includes consumer goods, grocery items, stationery and medicines etc.
MULTI-STATE COOPERATIVE SOCIETY
15.18 The Society is registered under MSCS Act 2002, as a Multi-State Co-operative Society and operates in Delhi and other States of the country.
NETWORK
15.19 The Society operates a network of 145 stores/branches in Delhi, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Cochin, Daman, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Assam, Haryana, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab and Chandigarh etc.
15.20 At Delhi, Kendriya Bhandar has a chain of 97 nos. self service grocery consumer retail stores beside the Institutional Sales Unit (ISU) and 05 Pharmacy shops (inclusive of three JAN Aushadhi Generic Drug Shops). In addition, 08 stores are operating in Delhi-NCR under franchisee system. At Grocery/Consumer stores, all items of consumer goods, groceryitems and certain stationery items are being sold. Through its Institutional Sales Unit, Kendriya Bhandar continues to provide goods to institutions like Tihar Jail, JNU/IIT Hostels, Janpath/Samrat Hotel, Hyderabad House, President House, Vigyan Bhawan, Homes of SocialWelfare Department of Govt. of Delhi, Govt. Hospitals etc. In addition, Kendriya Bhandar has exclusive counter at East Block and West Block, R.K. Puram, New Delhi for sale of stationery and other products.
15.21 Furthermore, Kendriya Bhandar is supplying medicines and related items to CGHS Dispensaries and Hospitals in Delhi-NCR through its existing chemist shops. Jan Aushadhi Generic Drug Shops have been opened in GTB Hospital, DDU Hospital and Shastri Bhawan as a part of Jan Aushadhi project of the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Govt. of India.
15.22 Kendriya Bhandar has opened new retail stores at 23 Acres Residential Colony, Delhi Cantt, Delhi Technological University Bawana Road, Delhi and Metro Vihar DMRC Staff Quarters Bahadurgarh.
SHARE CAPITAL
15.23 As on $31^{\text {st }}$ March 2024, Kendriya Bhandar had a paid-up capital of Rs. 100.81 lakhs out of which Rs. 68.18 lakhs have been subscribed by the Central Government and the rest by individual members.
MODERNISATION/AUTOMATION EFFORTS
15.24 Activities such as billing to customers, purchase, inventory etc. of Stationery division of Kendriya Bhandar, located at R.K. Puram East & West Blocks are computerized through Local Area Network. Further, in Head Office, purchases \& stocks of Consumer items, pulses and spices are computerized. All retail stores have already been computerized and also inventory has been computerized.
15.25 Debit/Credit Card swiping machines have been installed in all stores of Kendriya Bhandar for the convenience of customers.
SALES AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
15.26 Kendriya Bhandar has achieved sales of Rs. 5930.57 crores during the financial year 2023-24 against the sale of Rs. 3122.93 crores in Financial year 2022-23 and also achieved a net profit of Rs. 56.01 crores in the F.Y 2023-24 (after making provision of Rs. 4 Crore for wage Revision) against the net profit of Rs. 5.06 crores during the F.Y.2022-23.
Kendriya Bhandar has declared a dividend of $10 %$ for the year 2023-24. There is no financial assistance from Govt. to Kendriya Bhandar. Source of income of Kendriya Bhandar is trading of products, interest on FDRs etc.
BENEFITS TO CUSTOMERS
15.27 The Society has been able to maintain competitive prices for various products sold by it as compared to those prevailing in the market. In fact, selling prices prevailing in Kendriya Bhandar now are deemed as the benchmark in the market.
15.28 For better quality control, full-fledged Quality Control Department is in place for monitoring the product quality and for making improvements on an ongoing basis. Packed grocery items are sold after pre-testing in the laboratory. On the shelf, post-testing is done periodically. The goods sold in the manufacturers packing carry the warranty of the manufacturer. Complaints books are provided in all the stores for the customer to enter their complaints/suggestions which are acted upon from time to time.
15.29 It is pertinent to mention that the Society has been involved in welfare activities and has always assisted the Central Government and the Govt. of NCT of Delhi in arresting the price rise at the time of crisis. In February-March 2023. Kendriya Bhandar sold Bharat Atta @ Rs 27.50 per kg against market price of Rs. $40-45 /-$ per Kg. Kendriya Bhandar has sold Tomato @ Rs. 70/- per kg against the market price of Rs. 200/- per kg. Recently, Kendriya Bhandar has sold Bharat Dal (Chana Dal) @ Rs.60/- per kg, Bharat Atta @ Rs. 27.50 per kg. and Bharat Chawal @ Rs. 29/- per Kg. in Collaboration with Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food \& Public Distribution, Govt. of India. Kendriya Bhandar is still promoting Bharat Dal, Bharat Chawal \& Bharat Atta at a price fixed by Govt. of India for each item. Kendriya Bhandar came to the aid of Delhi Government and other state Governments and supplied items of their need in record time and in huge quantity during Pandemic. Similarly, Kendriya Bhandar supplied relief material to various states hit by flood, from time to time, and more recently material was supplied to Kerala Govt.
15.30 CCTV cameras have been provided in a large number of stores as a preventive measure against shoplifting, theft etc.
The Civil Service Society (Sanskriti School)
Introduction
15.31 The Civil Services Society is a society registered under the Societies Registration Act. The Society was set up in February 1995, by the wives of the officers of the All India and Allied Civil Services. The wife of serving Cabinet Secretary is the Chairperson of the Civil Services Society. The office of the Society is at Dr S Radhakrishnan Marg, Chanakyapuri, New Delhi – 110021.
Aims and Objectives
15.32 The aims and objectives of the society, inter alia, are as under: –
- To establish progressive schools or other educational institutions in Delhi or outside Delhi, open to the children of officers of the All India and Central Services. Depending on the availability of seats, children of officers of the Public sector (Non – government servants) may also be admitted, at the discretion of the Governing Body.
- To impart sound and liberal education to boys and girls during their impressionable years – a type of education that will lay stress on character building, team work, esprit de corps, physical development and will infuse in school children a spirit of adventure, fair play and justice.
- To develop among its students a feeling of pride in Indian culture and to produce citizens who will truly be global and rise above social, communal, religious and provincial prejudices.
15.33 The Society started its first school with the strength of 32 students, the Sanskriti School, in New Delhi, in the year 1998. The Chairperson of the Society is also the Chairperson of the School. Sanskriti School is a recognized integrated co-educational school,affiliated to the CBSE, offering education from Nursery to Class XII.
15.34 The Society believes that every child can and must realize his/her full potential, and towards this end, must be enabled through appropriate means. With this in mind, the School has a Learning Centre with Special Educators and Counselors guiding children who have special needs, through an Individual Education Program (IEP).
15.35 Likewise, for those from the relatively less privileged sections of society, the Society runs a parallel school Umang in the afternoon. Efforts are also made to mainstream some of the children. These children from the economically weaker sections are admitted through the admission process under the Delhi Education Act.
15.36 The Civil Services Society has set up a Centre for Excellence to promote teacher training initiatives. It has instituted the Sanskriti Lecture Series to motivate students by exposing them to the thought processes of eminent persons.
Management
15.37 The general management of the affairs of the Society is vested in its Executive Committee.
15.38 The general management of the affairs of Sanskriti School is also guided by the Managing Committee.
Activities
15.39 Sanskriti School has well stocked libraries, smart classrooms, laboratories, a gymnasium, a football field and a swimming pool. Apart from the prescribed curriculum, Sanskriti School offers its students a choice of sports and games, like cricket, football, basketball, table tennis, swimming and wide ranging co – curricular activities like yoga, chess, theatre, music, dance, quiz, public speaking, paper craft, etc.
Finance
15.40 The Society has no income of its own other than the annual subscription of the members. For Sanskriti School, the source of income is the fees collected from the students.
CIVIL SERVICES OFFICERS INSTITUTE (CSOI)
INTRODUCTION
15.41 The Civil Services Officers’ Institute is a registered society under the Societies Registration Act and was set up in February 1998. CSOI was allotted a building at K.G Marg, M.S. Apartments complex in 1998 which was later re-appropriated by CPWD to provide facilities of an Institute. Subsequently, the land was allotted to CSOI in 2002 at Vinay Marg, Chanakyapuri measuring 4.23 acres by Ministry of Urban Development, GOI. The new building was constructed by NBCC at a cost of Rs. 44.33 crore and it became operational with effect from December 2012. The Governing Council of CSOI decided to run both the Institutes at their respective locations in view of increased membership.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
15.42 The aims and objectives of the CSOI inter alia include: –
(i) To promote the welfare of the officers of the Civil Services and bring them together under one umbrella to secure complete integration of the services and to build a corps of officers imbibed with the spirit of co-operation in all aspects of Civil Services.
(ii) To hold, organize, arrange and conduct seminars, symposiums, talks, debates, workshops, lectures and other means of dispensing education to meet the needs and challenges of modernday civil administration.
(iii) To print and publish journals, periodicals and manuals to keep the civil servants abreast with modern-day development.
(iv) To acquire and promote modern skills of Civil Administration and harmonize between different fields of Civil Administration by disseminating or exchanging knowledge thereof and by providing such other facilities as would lead to their Universal application.
(v) To establish and maintain libraries and information system to facilitate the study of Civil Administration at International level and spreading information in regard thereto.
(vi) To organize and maintain, on no-profit-no loss basis, limited residential accommodation for the members of the Society coming to participate in the activities of the Association and of other bodies with cognate objectives, as well as non-members, invited to participate in the activities of the Association.
MANAGEMENT
15.43 CSOI is managed by a Governing Council headed by Cabinet Secretary, an Executive Committee headed by Secretary (P), DoPT and a Working Committee headed by Additional Secretary (DoPT). Various sub-committees comprising of members to assist the Working Committee in its day to day smooth functioning, viz:
a) Finance subcommittee
b) Food & Beverages subcommittee
c) Arts \& Events subcommittee
d) Building Maintenance subcommittee
e) IT subcommittee
f) Library subcommittee
g) Sports subcommittee.
15.44 Infrastructure upgradation in CSOI during 2024-25:
a) IT Enhancement \& Upgradation
Installation of New Club Management Software for both locations of CSOI. Redesigning of the website and provisioning of mobile application.
b) Swimming Pool Renovation Project
The renovation work of swimming pool was completed in September 2024. The same was inaugurated by Dr Vivek Joshi, the then Secretary (P), DOPT \& President, CSOI on October 12, 2024. Post inauguration, it was decided to open the pool for members w.e.f October 13, 2024. The same was closed on October 31, 2024.
c) Renovation of Squash Court
The renovation work of Squash Court was executed by NBCC Services Ltd as court had undergone major extensive repairs and now opened for all skill levels.
d) Revamping of Gym at CSOI, Vinay Marg and KG Marg
The Gymnasium at CSOI, Vinay Marg and K G Marg have been revamped. The flooring and venetian blinds at Vinay Marg has been changed. 06 Treadmills and 04 Cross have been added to elevate the workout experience at both locations.
15.45 DEPARTMENTAL CANTEENS
15.45.1 As a measure of Staff Welfare, Departmental Canteens/Tiffin Rooms have been set up in the Central Government Offices/Establishments to make available. Beverages, snacks and meals prepared in hygienic conditions, to the employees at reasonable rates. At present, about 700 Departmental Canteens/Tiffin rooms are functioning in various Central Government Offices all over India. It is stated that Canteen Section DoPT is nodal agency for framing policies, guidelines/instructions for canteen staff of Non-Statutory Departmental Canteen functioning from the Central Government Offices.
15.45.2 In order to improve functioning of NSDC in Central Government Offices, DoP\&T grant financial assistance to Ministries/ Departments for modernization of their Departmental Canteens. Under the scheme, one-time grant is given to canteens for modernization work which includes procurement of kitchen equipment, Furniture fixture, electrical and civil works. For the year 2024-25 an amount of Rs. 50 Lakh has been disbursed among four offices under this scheme in current financial year i.e. 2024-25.
Scholarship Scheme for children of employees of Non-Statutory Departmental Canteen was instituted in 1998 out of the funds in the discretionary fund of Director of Canteens. The scheme was introduced to encourage higher studies among the children of the canteen staff. Eligible wards of NonStatutory Departmental Canteen Employees were awarded with the scholarship amount under this scheme for the due academic year.
CHAPTER 16
RIGHT TO INFORMATION
MANDATE
- Administration of the RTI Act, 2005 including examination of matters related to amendments to the Act.
- Framing of Rules under the RTI Act, 2005 and amendment to the existing Rules made under the RTI Act.
- Issue/framing guidelines and orders to remove difficulties arising in giving effect to the provisions of the RTI Act.
- Appointment of Chief Information Commissioner and Information Commissioners in the Central Information Commission.
- Major policy issues relating to Right to Information Act, 2005.
- Laying of Annual Report of Central Information Commission before the Parliament.
- Action on recommendations of the Central Information Commission and Parliamentary Committee.
- Issue of guidelines and clarification on the strengthening and implementation of RTI Act.
- Implementation of the Annual Programme titled ‘Improving Transparency and Accountability in Government through Effective Implementation of RTI Act’.
- Management of RTI Online web portal.
- Administrative matters of Central Information Commission.
SALIENT FEATURES OF THE RIGHT TO INFORMATION ACT, 2005
16.1 To set out a practical regime for securing information by citizens from the Public Authorities and to promote transparency and accountability in the working of all Public Authorities, the Parliament enacted the Right to Information Act in 2005.
16.2 The Act is comprehensive and covers disclosure of information by public authorities on matters of governance. It is applicable to Government at all levels- Union, State and Local and also to the bodies owned, controlled or substantially financed directly or indirectly by the Government. It covers legislative bodies, the judiciary, the executive and Constitutional bodies.
16.3 The Act casts an obligation on public authorities for Suo-moto disclosure/The Act casts an obligation on public authorities for Suo-moto disclosure/publication of information held by them. It also requires the public authorities to supply information called for by any citizen and to permit him to inspect the documents and collect samples of various works. The procedure for seeking information is
very simple. A person seeking information has to make a request to the concerned Public Information Officer indicating the information required. The request may be sent either by post or be submitted in person or online if such facility exists with the public authority. It can be made in Hindi or English or in the official language of the area in which the application is made.
16.4 The Act creates the machinery to ensure supply of information, which consists of Public Information Officers, Assistant Public Information Officers, Departmental Appellate Authorities, independent Central and State Information Commissions etc.
16.5 The Act requires information to be provided in time bound manner. A Public Information Officer is required to send information called for at the specified address within 30 days. In case the information concerns the life or liberty of a person, it has to be provided within forty-eight hours. The Act provides for imposition of stringent penalty on the Public Information Officer, if the information is not provided within the prescribed period which could be Rs.250/- per day of delay subject to a maximum penalty of Rs. $25,000 /-$.
16.6 The Act has created a system of two appeals. On not being provided information within the stipulated period or on not being satisfied with the reply provided, an applicant can make first appeal within 30 days to the departmental appellate authority, who is generally the next superior officer to the Public Information Officer. If not satisfied with the decision of the first appellate authority, the applicant can file a second appeal to the Central Information Commission or the State Information Commission, as the case may be, within 90 days.
16.7 However, certain types of information pertaining to security of the country, scientific or economic interest of the country and information on trade secrets etc. are exempted from disclosure. Certain security or intelligence organizations have been exempted from disclosing any information except that pertaining to allegation of corruption or violation of human rights. Such organizations are required to designate Public Information Officers and First Appellate Authorities to deal with applications and appeals relating to information pertaining to corruption or violation of human rights.
16.8 With a view to create a brand for the Right to Information, a logo as given below had been adopted for the RTI on 28th October 2010. The logo is very simple and iconic. A sheet of paper with information on it, and the authority figure behind it – providing the information. This represents the two key stakeholders in the process of sharing information under the RTI Act.

CENTRAL INFORMATION COMMISSION
16.9 The Government of India has constituted a Central Information Commission. Further, all the 28 States to which the Act applies, have constituted State Information Commissions. These Commissions are high powered independent bodies which, inter-alia, can look into the complaints made to them and decide the appeals. The Commissions have power to impose penalty on the defaulting Public Information Officers. Central Information Commission entertains complaints and appeals in case of offices, financial institutions, public sector undertakings, etc. under the Central Government and the Union Territories while the State Information Commissions entertain appeals pertaining to offices, financial institutions, public sector undertakings, etc. under the concerned State Government.
16.10 The Central Information Commission, when constituted initially, had five Commissioners including the Chief Information Commissioner. With the last appointment of the Chief Information Commissioner and two Information Commissioners on $6^{\text {th }}$ November 2023, the Commission has now Two Information Commissioners apart from the Chief Information Commissioner in position.
RIGHT TO INFORMATION RULES, 2012
16.11 In supersession of the Central Information Commission (Appeal Procedure) Rules, 2005 and the Right to Information (Regulation of Fee and Cost) Rules, 2005, the Right to Information Rules, 2012 have been notified in the Gazette of India on $31^{\text {st }}$ July 2012.
16.12 The Right to Information Rules, 2012 provide inter-alia that a request for obtaining information shall be accompanied by an application fee of rupees ten by way of cash against proper receipt or by demand draft or bankers’ cheque or Indian Postal Order payable to the Account Officer of the public authority. The applicant may have to pay fee in addition to application fee for obtaining documents or for inspecting the documents. The persons below poverty line are not required to pay any fee for seeking information.
16.13 The RTI Rules, 2012 also prescribe the procedure for deciding appeals by the Central Information Commission, covering the following aspects:
(i) Documents to be enclosed with the appeal;
(ii) Return of Appeal
(iii) Process of Appeal
(iv) Procedure for deciding appeals
(v) Presence of the appellant before the Commission
(vi) Presentation by the Public Authority
(vii) Service of notice by Commission
(viii) Order of the Commission
RIGHT TO INFORMATION RULES, 2019 in respect of Terms and Conditions etc. of Services of Information Commission and Chief Information Commissioner
16.14 RTI (Amendment) Bill, 2019, passed by the Lok Sabha on 22.07.2019 and Rajya Sabha on 25.07.2019, received the assent of the President on $1^{\text {st }}$ August 2019.
16.15 The RTI (Amendment) Act, 2019 was notified, by the Legislative Department, in the Gazette of India on $1^{\text {st }}$ August 2019.
16.16 Notification to bring into force the provision of the RTI (Amendment) Act, 2019 has been published in the Gazette of India, Extraordinary under Part II, Section 3, Sub-Section (ii) on 24.10.2019.
16.17 Consequently, ‘The Right to Information (Term of Office, Salaries, Allowances and Other Terms and Conditions of Service of Chief Information Commissioner and Information Commissioners in the Central Information Commission, State Chief Information Commissioner and State Information Commissioners in the State Information Commission) Rules, 2019’ were notified in the Official Gazette of India, Extraordinary under Part II, Section 3, Sub-Section (i) on 24.10.2019.
RTI Websites for Citizen empowerment and Information
16.18 There is a dedicated website on RTI www.rti.gov.in, which contains valuable information including circulars, notifications and Guides on RTI, search facility for locating CPIOs and Appellate Authorities in Central Government etc. It has links with other RTI related sites as well. Further, there is an RTI online web portal whereby Right to Information (RTI) applications can be filed online by Indian
citizens, including those who are living abroad. An Indian citizen can file RTI application online through RTI online web-portal, having urlwww.rtionline.gov.in. The prescribed fee for RTI application can also be paid online through a payment gateway of State Bank of India by way of internet banking of State Bank of India, debit/ credit cards of Master/Visa/RuPay cards and UPI. This facility at present is available for 2720 Public Authorities of Government of India (as on 24.01.2025). Addition of more public authorities in the last few years has truly made this portal truly useful and empowering for citizens as they can get their information online and also make payment of fee online and all the information can be provided by the Public Authorities through this portal.
ANNUAL PROGRAMME ON RIGHT TO INFORMATION
16.19 The Government has launched a Centrally Sponsored Plan Scheme “Improving Transparency and Accountability in Government through Effective Implementation of the Right to Information Act” in August 2010 to undertake activities in the area of awareness generation and capacity building. Under the scheme, the State Administrative Training Institutes and State Information Commissions are supported through release of grants for awareness generation and training programs of all stakeholders. The total outlay of the scheme under XII th Five Year Plan was Rs. 110.36 crores. During the Financial year 202425, an amount of Rs 161.44 lakh has been released and on receiving the Utilisation Certificates in respect of past releases by the States/UTs, more funds will also be released. After the XII th Five Year Plan (201217), this considered as Annual Program which includes annual expenditure on various activities for spreading awareness about the RTI Act and citizen information performed under the specific Object Heads.
TRAINING:
16.20 The above-mentioned Programme on RTI has components of training of Public Information Officers / First Appellate Authorities of Centre as well as States.
AWARENESS GENERATION FOR RTI:
16.21 The component of awareness generation includes Organization of Workshops, RTI Week Celebration, Innovative Awareness Generation Programs and Publication of Guidebooks.
RTI ONLINE PORTAL
16.22 A web portal namely ‘RTI Online’ has been launched to provide the facility for the Indian Citizens to file online RTI applications and first appeals and also to make online payment of RTI fees. The prescribed fee can be paid by the applicant through internet banking of the State Bank of India as well as by Credit/Debit cards of VISA / Master and UPI, through the payment gateway of SBI, which is linked to RTI Online portal.
16.23 The RTI online portal provides for sending online replies to applications and appeals, though reply can be sent by regular post also. For a successful implementation of this facility, extensive training to the CPIOs / FAAs has been provided by DOPT, with the help of NIC. As on 24.01.2025, 2720 Public Authorities have been aligned with this portal.
SUO MOTU / PROACTIVE DISCLOSURE
16.24 Section 4(1)(b) of the RTI Act lays down the information which should be disclosed by Public Authorities on a Suo-moto or proactive basis. Sections 4(2) and 4(3) of the Act prescribe the method of dissemination of this information. In order to improve the proactive disclosure, Government of India constituted a Task Force on Suo moto disclosure in May, 2011. After considering the recommendations of the Task Force, the Government of India has issued guidelines to Central Ministries / Departments for
Proactive Disclosure under section 4 of the RTI Act on 15.4.2013 and the same were, with slight modifications, reiterated on 07.11.2019. These guidelines envisage –
(a) Suo-moto disclosure of more items under section 4;
(b) guidelines for digital publication of proactive disclosure;
(c) detailing of certain clauses of section 4(1)(b) to make disclosure more effective;
(d) compliance mechanism for Suo-moto disclosure; and
(e) personal information of an individual not to be disclosed
16.25 As per the guidelines, Pubic Authorities may publish information relating to procurement, public private partnerships, transfer policy and orders, RTI applications, CAG and PAC paras, citizens’ charter, discretional and non-discretionary grants, foreign tours of Prime Minister and Ministers.
16.26 The guidelines further provide that each Central Ministry/ Public Authority should get its proactive disclosure package audited by a third party every year and that such audit should be communicated to the Central Information Commission annually through publication on their own websites along with the names of the third-party auditors. Under these guidelines it is mandatory that a senior officer of the level of Joint Secretary in the case of Ministry/Department and Additional HoD in the case of attached/subordinate offices, is nominated as nodal officer for ensuring compliance with the proactive disclosure guidelines.
16.27 The above guidelines have been reiterated duly incorporating a slight revision to Para 4.4 of the above guidelines allowing for third party audit by any Government Training Institute, in cases where no Training Institute exists under the concerned Ministry/Department/Public Authority. In course of a relaxation to the Central Public Authorities in aforesaid guidelines, it has been further provided that if any Training Institute, under any Ministry/Department/Public Authority, is recognized and functions as a separate Public Authority in terms of provisions of RTI Act, 2005, it may get third party audit of its proactive disclosure package done by any Government Training Institute. In course of the further relaxation, on the requests of various public authorities, the requirement of respective Government training institute was dispensed with by providing that the task of undertaking transparency audits may be given to any Government Training Institutes by Ministry/Department Public Authority, under the Central or State Governments.
16.28 State Governments were also requested to consider issuing similar guidelines, along with templates for disclosure at various levels, for better implementation of Suo moto disclosure at State level. Four areas have been identified for development of templates viz. Public distribution system, Panchayats, MGNREGA and Primary and Secondary Schools.
16.29 A facility to upload the reply of RTI applications and first appeals on the respective website of the Ministry/Department has been started from $31^{\text {st }}$ October 2014. All the Ministries/Departments of Govt. of India have been requested to upload the reply to RTI application and first appeal on their respective websites, except the replies relating to the personal information of an individual, if they do not serve any public interest.
IMPLEMENTATION OF RTI ACT, 2005 in DoPT
16.30 During the year ( $01^{\text {st }}$ April $2024-30^{\text {th }}$ January 2025) a total of 16385 RTI applications were received and 15713 RTI applications were disposed of in DoPT. In addition, 1267 RTI applications were disposed and 1191 RTI First Appeals were disposed of during the above period.
16.31 Third Party Audit on Suo-moto disclosures under the RTI Act, 2005 in respect of DoPT for the year 2023-24 was conducted by ISTM through online mode. The audit report is available on the website of this Department at Home > RTI > Proactive Disclosures > Proactive Disclosure (RTI) > Item No. $17>$ “Such Other Information as may be prescribed”.
CHAPTER 17
PUBLIC GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL MECHANISM & CITIZENS’ CHARTER
Citizens/ Client’s Charter and Sevottam Compliant Public Grievance System of the Department:
17.1 The Citizens’/Clients’ Charter of the Department contains the services provided by the various Divisions, name and contact, details of the responsible officer, service standards and time taken, the process involved and documents required. The charter also contains the name and contact details of public grievance officer. The services included in the citizens’/clients’ charter are:
i. Processing of proposals for ACC approval.
ii. Allocation of Service based on the result of the Civil Services Examination (Display on the website of this Department)
iii Nomination of the candidate to whom service allocated for Foundation Course (Display on the website of this Department)
iv Release of holiday list for the Government Department/organisations.
v. Release of Grants-in-aid to staff side Secretariat of National Council (JCM).
vi. Grant of advice on disagreement cases with UPSC on disciplinary matters.
vii. Clarification on ACRs/APARs.
viii. Processing for extension of ad-hoc appointment /Grant of approval.
ix. Processing of proposals for framing/amendment/relaxation of RRs (including proposals received online on RRFAMS).
x. Cadre Clearance for Deputation.
xi. NOC for filling up of posts in Government organisation.
xii. Nomination of officers under domestic Funding of Foreign Training- Long Term Training Programmes ( 6 months- 1 year) \& Short Term Training Programmes (up to 6 months).
xiii. Nomination of officers for Advanced Professional Programme in Public Administration (APPPA).
xiv. Advice/clarification to Ministries/Departments on the issue of Reservation in services to SC, ST, OBC, PWD and Ex-Servicemen.
xv. Payment to vendors for invoices submitted, except air bills, submitted complete in all respects.
17.2 Review of implementation of Citizens’/Clients’ Charter is a continuous process and the Department is committed to include more services and improve service standards.
Public Grievances Redressal System
17.3 The Department has been implementing the Centralized Public Grievances Redressal and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS), an online grievance redressal mechanism, developed and monitored by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
17.4. The Department received online grievances from various sources in CPGRAMS portal with the majority of grievances lodged directly by the common public. During the period from April, 2024 to $30^{\text {th }}$ January, 2025 the Department has received total 15367 grievances (including 603 brought forwarded grievances) in CPGRAMS portal, out of which, 14759 grievances have been disposed of by the concerned Divisions/Subordinate org./Attached Offices of DoP\&T and other concerned Ministries/Departments/States/UTs.
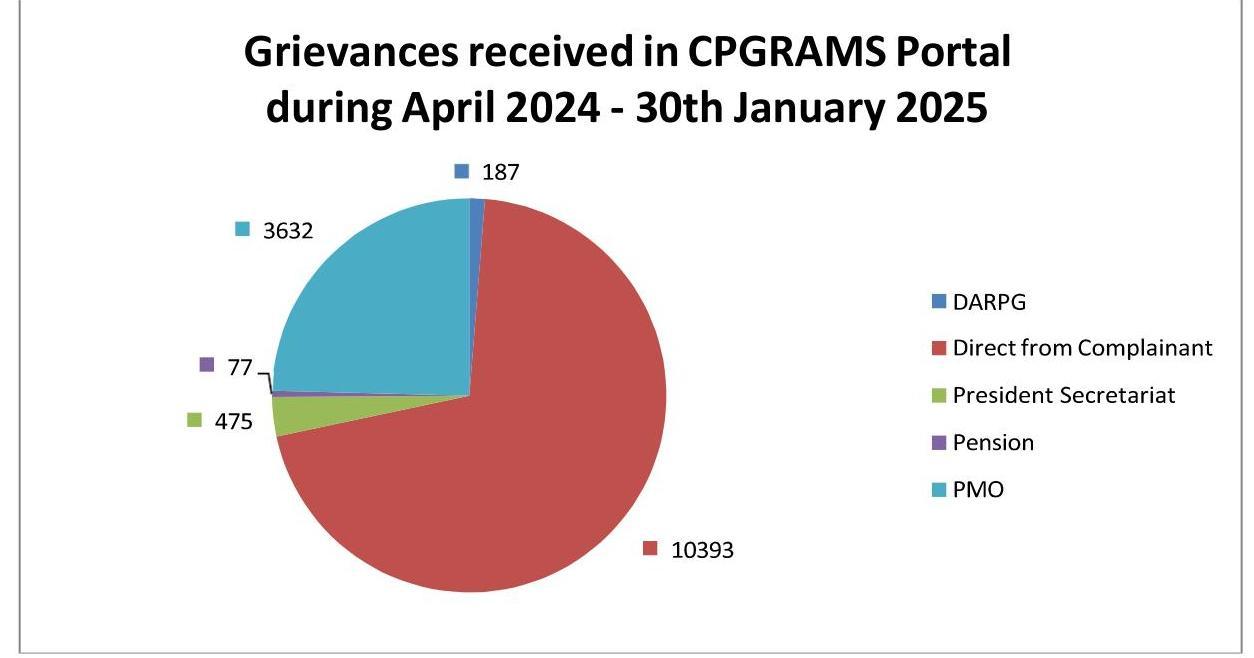
Figure 1: Grievances received during April 2024-30 th January 2025
17.5. The Department received 1422 grievances in physical form through letters written by the general public as well as forwarded by other Ministries/ Departments/organizations of the Government of India. These Grievances were forwarded to concerned Divisions in DoPT for examination and redressal. The grievances which do not pertain to this Department were forwarded to the concerned Ministries/ Departments endorsing copy to the petitioners.
17.6. The Deputy Secretary (Admn.), DoP&T, is the Nodal Officer of Public Grievances in DoP\&T. As per the instructions of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, Wednesdays are observed as meeting-less day so that the citizens can meet the officers concerned with their grievances.
CHAPTER-18
PROGRESSIVE USE OF HINDI IN OFFICIAL WORK
18.1 The Ministry continued to make concerted efforts to promote the use of Hindi in official work and to ensure compliance of the provisions of the Official Language Act, 1963 as amended in 1967 and Official Language Rules, 1976 framed thereunder. Various orders/instructions issued from time to time by the Department of Official Language with a view to ensure proper implementation of the Official Language Policy of the Union are also implemented in the Ministry.
18.2 MACHINERY FOR IMPLEMENTATION AND TRANSLATION
18.2.1 The Ministry has a full-fledged Official Language Division headed by a Joint Director (OL) with one (01) Deputy Director (OL) and two (02) Assistant Directors and other supporting staff. This Division caters to the needs of the Department of Personnel and Training. There is a separate Official Language Section under a Deputy Director (OL) with necessary supporting staff in the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances. Likewise, there is a separate OL Section headed by one (01) Assistant Director (OL) with necessary supporting staff also in the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare. Besides monitoring the implementation of the Official Language Policy and the Annual Programme, the Official Language Division arranges in-service training for the staff for learning Hindi Language, Hindi Stenography and Hindi Typewriting. It also undertakes translation of the material received from various sections/desks of the Department from English to Hindi and vice versa such as General Orders, Standard forms, Notifications, Resolutions, Cabinet Notes (except the annexure relating to other Ministries/Departments), Administrative and other Reports, Press Releases and Periodic Statements/Summaries etc. referred to in section 3(3) of the Official Language Act, 1963 in addition to all the Parliamentary and Budgetary matters.
18.3 VARIOUS COMMITTEES FOR EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF OFFICIAL LANGUAGE POLICY
18.3.1 Kendriya Hindi Samiti
Kendriya Hindi Samiti headed by the Hon’ble Prime Minister suggests various ways and means to the Ministries/Departments to promote the use of Official Language Hindi in the official work. Latest meeting of the committee was held on 04.11.2024 under the chairmanship of the Hon’ble Union Home Minister. The directions and follow up actions of the Committee are being implemented in the Department.
18.3.2 The Committee of Parliament on Official Language
The Committee of Parliament on Official Language was to be constituted under section 3 of the Official Languages Act, 1963 after ten years of the promulgation of the Act. This Committee was set up in 1976 under section 4 of the Act.
This is a high-level committee comprising of 30 members of Parliament, 20 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha. The Chairman of the Committee is elected by the members of the Committee. As a convention, the Union Home Minister (HM) has been elected as Chairman of the Committee from time to time.
The Committee of Parliament on Official Language inspected Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) on 10.10.2020. Recently First Sub-Committee of the Committee of Parliament on Official Language inspected SSC (HQ), New Delhi, a subordinate office of DoPT, on 21.11.2024. The Committee reviewed the implementation of the provisions of Official Language Act and suggested various ways and means to the Ministry/Department to promote the progressive use of Official Language Hindi
in the official work by creating a conducive and facilitative environment for the personnel of the Department.
18.3.3 Hindi Salahakar Samiti (Hindi Advisory Committee)
As per the guidelines from Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs, Hindi Advisory Committees are constituted in Ministries/Departments to put their advice regarding proper implementation of the official language policy of the Government of India. The minister concerned of the office chairs the committee.
This is a high-level committee consisting of 30 members. The committee is constituted for three years. The committee advises the Ministry and its subordinate offices regarding implementation of the directions issued by Department of Official Language regarding provisions made under the Constitution, Official Language Act and Rules. Reconstitution of the Hindi Salahakar Samiti of the Ministry is under process after the constitution of the $18^{\text {th }}$ Lok Sabha. The $15^{\text {th }}$ meeting of the committee is all set to be held at CSOI, New Delhi in the forthcoming month of February 2025 under the chairmanship of Hon’ble MoS (PP), Dr. Jitendra Singh.
18.3.4 Kendriya Rajbhasha Karyanvayan Samiti
Kendriya Rajbhasha Karyanvayan Samiti is headed by the Secretary, Department of Official Language, which reviews the ongoing progress of the use of Hindi in all the Ministries/Departments of Government of India. The last meeting ( $46^{\text {th }}$ meeting) of the said committee was held from 22.10.2024 to 23.10.2024 under the chairmanship of Secretary, Department of Official Language. The directions of this Committee are being complied with in the Department.
18.3.5 Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC)
The meetings of the Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC) of the Department of Personnel and Training are held periodically in the Department to discuss the Quarterly Progress Reports and suggest various measures for progressive use of Official Language Hindi in the Department. The meetings of Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC) are being held regularly in the Department. The last meeting was held on 23.10.2024. The Quarterly Progress Reports related to Official Language Hindi are reviewed in the meetings of Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC) and various measures are taken for progressive use of Official Language Hindi in the Department.
18.3.6 Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC) of Attached Offices
All the attached/subordinate offices of the ministry have their own Official Language Section and they have their own Official Language Implementation Committee (OLIC). The meetings of Official Language Implementation Committee are held regularly in these offices and the representatives of the Department also attend these meetings.
18.4 SPECIFIC MEASURES TAKEN FOR PROMOTING THE USE OF OFFICIAL LANGUAGE HINDI
18.4.1 Quarterly Progress Report and Annual Assessment Report
To assess the work done in Hindi by the personnel of the Department in their official work, a Quarterly Progress Report (QPR) is compiled after collecting relevant and real-time data from various Divisions/Sections in a prescribed proforma and sent to the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs on regular basis. Similarly, Annual Assessment Report (AAR) is also sent to the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs.
18.5 CASH AWARDS AND INCENTIVE SCHEMES
Various incentive schemes of the Department of Official Language to encourage officers and employees to do their official work in Hindi are in vogue in all the government departments. One such scheme is in vogue in this Department, under which cash awards are given to staff members, who carry out their official work (Noting & Drafting) in Hindi. During the year 2023-2024 entries from total three (03) officials have been received and are under scrutiny of committee constituted for this purpose and all the winners will be provided with cash prizes and commendation certificates after the declaration of the results for the same.
18.6 HINDI WORKSHOPS
Hindi Workshops are organized in the Department to remove the hesitation among the officers and employees to do their official work in Hindi in which all the participants are given practical training of Rajbhasha Hindi and relevant rules and procedures thereof. During the year 2024-25, Two Hindi Workshops were organized for the personnel of DoPT on 05.09.2024 (27 participants) and 22.11.2024 (11 participants) respectively.
18.7 ORGANISING HINDI FORTNIGHT/DIWAS
Hindi fortnight was organized in the Department from 14.09.2024 to
29.09.2024.
During the fortnight, Ten (10) competitions namely; Hindi Noting \& Drafting (for Hindi Speaking and Non-Hindi Speaking personnel), Hindi Essay Writing (for Hindi Speaking and Non-Hindi Speaking personnel), Official Language Hindi Knowledge, Translation \& Use of Hindi, Hindi Story Writing, Hindi Extempore, Hindi Typing and Hindi Poetry (Self-Composed) etc. were organized. On this occasion, a large number of officers and employees of the Department enthusiastically participated in these competitions. The participants who secured first, second and third positions and also those who performed well (2) were awarded with cash prizes. Commendation certificates are to be distributed to the winners at the earliest.


# Stills from competitions held during Hindi Fortnight 2024.
18.8 HINDI IN TRAINING INSTITUTIONS
The two Training Institutions under the Ministry viz. Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussoorie and the Institute of Secretariat Training and Management (ISTM), New Delhi have made considerable progress in providing the training material in Hindi. In LBSNAA, the teaching material of main subjects are provided in book form and translation of the lecture notes of the topics taken by the faculty members is provided immediately on the demand of trainee officers. Institute of Secretariat Training and Management (ISTM) also has its all the training material available in bilingual form.
18.9 MONITORING AND INSPECTION
The progress made in Hindi for effective implementation of the Official Language Policy is reviewed on the basis of Quarterly Progress Report (QPR) and Annual Assessment Report (AAR). The progress made in the progressive use of Hindi is discussed at length in the quarterly meetings of internal Official Language Implementation Committee, in which remedial measures are suggested to remove the observed shortcomings.
Besides, Divisions/Sections and the Attached Offices of the Ministry are inspected by Official Language Section of the Department of Personnel and Training in a phased manner and necessary measures are taken and directions are given to overcome the practical difficulties experienced in the course of implementing the Official Language Policy of the Union.
During inspection, ways for doing away with the problems faced by the officials in carrying out their works in Hindi are also suggested to give much needed fillip and thrust to progressive use of official language Hindi. During the year 2024-25, inspections of 26 internal sections & 05 Subordinate offices of DoPT were carried out to take the stock of the progressive use of Official Language.
18.10 RAJBHASHA SHIELD YOJANA
With a view to promote cooperative and competitive feeling and synergy among subordinate offices and headquarters for promoting progressive use of Rajbhasha Hindi in the official work of the Department, an ambitious shield scheme consisting of two parts entitled as Rajbhasha Shield Yojana was launched. The first part is meant for the sections located at Headquarters under which Rajbhasha
Shield would be given to the section using Hindi in its official work at premium with other sections and the officers and employees working there in Hindi would be rewarded. The second part of the scheme is meant for the Subordinate Offices, in which provisions have been made to give the Rajbhasha Shield to the Subordinate Office doing its official work in Hindi at premium with any of the Subordinate Offices. During the year under review, Admin-IV section of DoPT and SSC (HQ), New Delhi (under subordinate office category) were declared as the winners in their respective segments and are proposed to be awarded with Rajbhasha Shield and Certificate of Appreciation by Hon’ble MoS, Dr. Jitendra Singh Ji during the forthcoming Hindi Salahakar Samiti meeting scheduled to be held in the month of February 2025. The yojana has created a spirit of competition and dynamism for progressive use of Official Language Hindi among the officers and employees of the Department.
18.11 $4^{\text {th }}$ Edition of e-Magazine “KAUSHAL”
In a first of its kind initiative, the Department of Personnel and Training started an e-magazine christened as “KAUSHAL” in the year 2018 to provide a platform to the officers and employees of the Department to make a creative, conducive and positive environment for progressive use of Hindi Language in official work. The initiative is leading to a keen desire among the officers and employees to give vent to their creative urge in Hindi language. Hence, this ambitious initiative is helping create a positive synergy among the officers and employees to do their official work in Hindi, which in turn will make public administration more citizen-centric and decentralized with greater active participation of the citizens. It would also make public administration more responsive and accessible with increased popular participation and two-way communication between the Government and the citizens.
This is a progressive step to make Official Language Hindi more popular among the officers and employees of the Department, which would go a long way in translating the vision of ‘New IndiaAtmanirbhar Bharat’ of Government of India into reality by rendering public administration and public service delivery mechanism more inclusive.
The publication of the $4^{\text {th }}$ edition of the magazine is in the wings and the link of the same would be made available on the website of the Department shortly. Now, the E-Magazine is all set to be unveiled by Hon’ble MoS, Dr. Jitendra Singh Ji during the forthcoming Hindi Salahakar Samiti meeting scheduled to be held in the month of February 2025.
CHAPTER 19
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
19.1 The provision is for expenditure of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions in respect of:
a) Department of Personnel \& Training which is entrusted with the work relating to framing / interpretation of rules and regulations; recruitment, promotion and reservation policy; induction, training and refresher courses for all levels / grades of Civil Services posts; service conditions, career and manpower planning, vigilance, discipline and welfare activities of Central Government servants; investigation and prosecution in corruption cases and other serious crimes; redressal of grievances of public servants.
b) Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances which is entrusted with matters relating to Administrative Reforms, O\&M and policy, coordination and redressal of grievances including those pertaining to Central Government Agencies; hosting of Civil Service Day, PM’s Award, Chief Secretaries Conference etc.
c) Department of Pension \& Pensioners Welfare which administers all activities relating to retirement benefits including Gratuity, Pension, fringe benefits to pensioners, etc.
19.2 The provision is for establishment-related expenditure of the Central Bureau of Investigation which is entrusted with investigation and prosecution in corruption cases against public servants, private persons, firms and other cases of serious crimes. This also includes provision for various projects such as Modernization of Training Centres of CBI, Establishment of Technical and Forensic Support Units, Comprehensive modernization \& purchase of land/ construction of office/ residence buildings for CBI.
19.3 The provision is for establishment-related expenditure of the Staff Selection Commission including expenditure on the conduct of examinations for recruitment of staff in Central Ministries/ Departments etc.
19.4 The provision is for establishment-related expenditure of the Central Administrative Tribunal which is entrusted with the redressal of grievances exclusively of public servants. This also includes provision for Purchase of Land and Construction of Building for various Benches of CAT.
19.5 The provision includes establishment related expenditure of Institute of Secretariat Training \& Management (ISTM), Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA) \& Training Division, DOPT. These Organizations arrange several training programmes including foundation courses, refresher courses, mid-career training, etc. so as to equip all levels / grades of Secretarial functionaries with adequate exposure to the latest rules and regulations, aptitude etc., expenditure on domestic / overseas travel, course fees etc. in respect of CSS / CSSS officials who are to undergo mandatory training at ISTM as a pre-condition for consideration for promotion to next higher grade have also been included centrally in the budget of this Ministry.
19.6 The provision is for establishment related expenditure of Public Enterprises Selection Board and Central Information Commission.
19.7 The provision is for establishment and construction related Charged expenditure for Lok Pal.
19.8 The provision is meant for reimbursement to State Governments towards House Building Advances paid to All India Service Officers.
19.9 This also includes provision for Training schemes like Training for All, Domestic Funding for Foreign Training, Upgradation of LBSNAA to a Centre of Excellence, Augmentation of Training Facilities at ISTM.
19.10 This provision is meant for National Programme for Civil Services & Capacity Building – Mission Karmayogi.
19.11 This also includes Scheme provision for Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances scheme for Modernisation of Government Offices, Pilot projects on Administrative Reforms which consists of promotion of e-governance, fostering of good governance, learning from success, Sevottam etc.
19.12 This includes scheme provision for Department of Pension’s scheme “Pensioners Portal”.
19.13 This also includes Scheme provision for Integrated Building for Institute of Secretariat Training and Management and other Institutes of Department of Personnel and Training.
19.14 This also includes Grants in Aid allocations to Indian Institute of Public Administration and National Centre for Good Governance.
19.15 The provision includes Grants-in-aid assistance to Grih Kalyan Kendra, Central Civil Services Cultural \& Sports Board and National Recruitment Agency.
19.16 This includes fund allocations in respect of DOPT’s Propagation of RTI Act.
19.17 Organization Wise RE 2024-25 \& BE 2024-25 Allocations
Demand No-74,Ministry of Personnel ,Public Grievances \& Pensions
(Rs. in crore)
| S. No. | Organisations | Budget Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 4 – 2 5}$ |
Revised Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 4 – 2 5}$ |
Expenditure upto $\mathbf{3 1 . 0 3 . 2 0 2 5}$ |
Budget Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 5 – 2 6}$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\mathbf{1}$ | M/o PPG\&P | $\mathbf{2 3 2 8 . 5 6}$ | $\mathbf{2 5 7 6 . 1 5}$ | $\mathbf{2 5 0 9 . 6 5}$ | $\mathbf{2 6 5 6 . 4 6}$ |
| $\mathbf{2}$ | DoPT | 2187.92 | 2410.97 | 2371.06 | 2454.18 |
| $\mathbf{3}$ | D/o AR\&PG | 124.31 | 131.85 | 107.07 | 174.37 |
| $\mathbf{4}$ | D/o Pensions | 16.33 | 33.33 | 31.52 | 27.91 |
Organization wise details:
(Rs. in crore)
| S. No. |
Head/Organisation | Budget Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 4 – 2 5}$ |
Revised Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 4 – 2 5}$ |
Expenditure upto $\mathbf{3 1 . 0 3 . 2 0 2 5}$ |
Budget Estimates $\mathbf{2 0 2 5 – 2 6}$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DOPT Estt. | 202.59 | 165.88 | 148.39 | 187.40 |
| 2 | National Programme for Civil Services and Capacity Building (NPCSCB) |
86.13 | 110.00 | 92.87 | 110.00 |
| 3 | Training for All (TFA) |
19.57 | 9.57 | 9.56 | 26.16 |
| 4 | Domestic Funding of Foreign Training (DFFT) |
12.00 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 5 | LBSNAA Estt. | 77.15 | 75.39 | 81.24 | 77.53 |
| LBSNAA Scheme | 79.88 | 126.53 | 120.91 | 87.83 |
| 6 | ISTM Estt. | 20.90 | 21.43 | 19.70 | 23.96 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — |
| | Augmentation of
Training Facilities | 9.11 | 3.25 | 1.36 | 4.46 |
| | Integrated Building
for ISTM & DoPT | 55.50 | 20.00 | 12.16 | 55.00 |
| 7 | IIPA | 15.00 | 21.00 | 21.00 | 30.00 |
| 8 | CBI | 951.46 | 986.93 | 998.32 | 1071.05 |
| 9 | CAT | 157.72 | 166.66 | 160.17 | 164.62 |
| 10 | SSC | 418.15 | 584.92 | 609.33 | 515.15 |
| 11 | NRA | 10.00 | 10.00 | 3.75 | 14.20 |
| 12 | PESB | 5.78 | 7.13 | 6.38 | 7.48 |
| 13 | CIC | 33.66 | 34.38 | 28.51 | 35.01 |
| 14 | LOKPAL | 33.32 | 67.65 | 57.41 | 44.32 |
| | DoPT \& its offices | $\mathbf{2 1 8 7 . 9 2}$ | $\mathbf{2 4 1 0 . 9 7}$ | $\mathbf{2 3 7 1 . 0 6}$ | $\mathbf{2 4 5 4 . 1 8}$ |
19.18
Major Capital Allocations (Rs. in crore)
| S. No. | Head | Budget
Estimates
2024-25 | Revised
Estimates
2024-25 | Expenditure
upto
31.03.2025 | Budget
Estimates
2025-26 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1. | CBI Projects | 55.12 | 38.72 | 41.28 | 42.91 |
| 2. | CAT Project | 20.27 | 20.27 | 17.0384 | 12.62 |
| 3. | Augmentation
of Training
facilities in
ISTM | 1.51 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 1.16 |
| 4 | Integrated
Building for
ISTM and other
Institutes of
DoPT | 55.50 | 20.00 | 12.15 | 55.00 |
| 5. | Improvement of
infrastructure
and upgradation
of essential
facilities at
LBSNAA | 62.88 | 105.65 | 100.56 | 67.33 |
| 6. | National
Programme for
Civil Services \&
Capacity
Building:
NPCSCB (SPV) | 8.20 | 5.40 | 5.00 | 0.64 |
| 7. | Lokpal | 10.02 | 41.02 | 32.10 | 2.14 |
| 8. | HBA to AIS
Officers | 2.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
19.19 AUDIT OBSERVATION IN RESPECT OF MINISTRY OF PERSONNEL, PUBLIC GRIEVANCES & PENSIONS
19.19.1 Public Accounts Committee
No PAC para is pending in this Ministry.
19.19.2 Comptroller \& Auditor General of India
Four C\&AG paras are pending.
19.19.3 Statutory Audit Paras
| S. No. | Name of the office | No. of Outstanding paras as on 31/12/2023 |
No. of Outstanding paras as on 31/12/2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Department of Personnel \& Training | $\mathbf{2 5}$ | $\mathbf{2 4}$ |
| 2 | Staff Selection Commission | $\mathbf{6 0}$ | $\mathbf{2 8}$ |
| 3 | Union Public Service Commission | $\mathbf{9}$ | $\mathbf{1 0}$ |
| 4 | Institute of Secretariat Training \& Management |
$\mathbf{1 5}$ | $\mathbf{1 5}$ |
| 5 | Department of AR \& PG | $\mathbf{0}$ | $\mathbf{0}$ |
| 6 | Dept. of Pensions \& Pensioners’ Welfare |
$\mathbf{0}$ | $\mathbf{0}$ |
| 7 | Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration |
$\mathbf{1 4}$ | $\mathbf{2 3}$ |
| 8 | Central Administrative Tribunal | $\mathbf{6 1}$ | $\mathbf{5 6}$ |
| 9 | Central Vigilance Commission | $\mathbf{2 4}$ | $\mathbf{2 4}$ |
| 10 | Central Information Commission | $\mathbf{2 5}$ | $\mathbf{2 5}$ |
| 11 | Central Bureau of Investigation | $\mathbf{1 9 5}$ | $\mathbf{1 4 6}$ |
| Total | $\mathbf{4 2 8}$ | $\mathbf{3 5 1}$ |
Annexures
Organizational Chart of Department of Personnel & Training
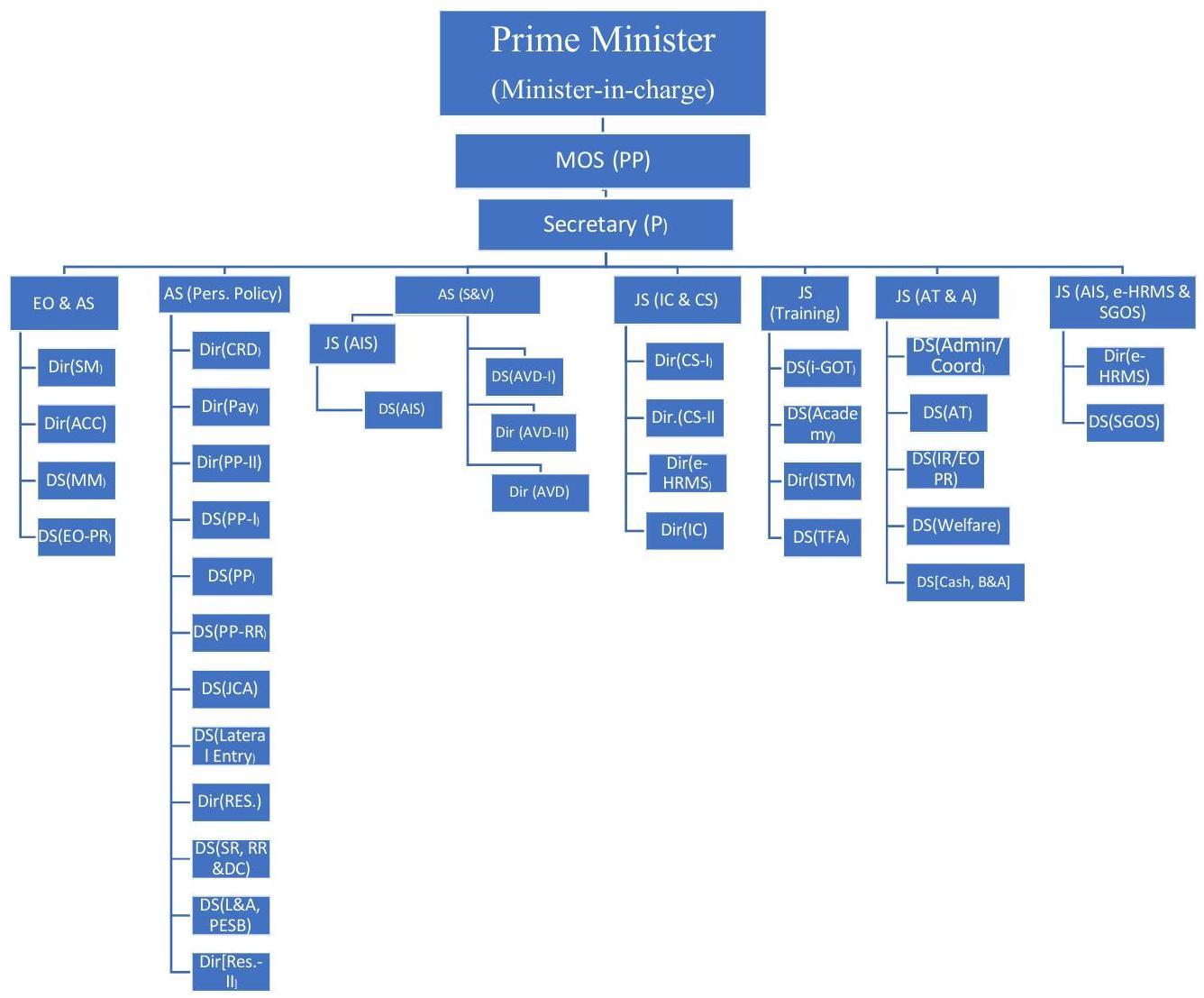
Department of Personnel & Training
Incumbency Position of Group ‘A’ Officers in D/o Personnel and Training as on 31.03.2025
| Post | Name of Incumbent (Sh./Smt./Ms.) |
|---|---|
| Secretary | Ms. Rachna Shah |
| Additional Secretary | 1. Manisha Saxena |
| 2. Avinash P. Das Joshi | |
| 3. Manoj Kumar Dwivedi | |
| Joint Secretary | 1. S. D. Sharma |
| 2. Chhavi Bhardwaj | |
| 3. J. Ashok Kumar | |
| 4. P. Bala Kiran | |
| Director | 1. Sushil Kumar Patel |
| 2. Prashant Shukla | |
| 3. Pallavi Singh | |
| 4. Navpreet Kaur | |
| 5. Sakshi Mittal | |
| 6. Sh. Harmit Singh Pahuja | |
| 7. Anindya Bhattacharya | |
| 8. Murali Bhavaraju | |
| 9. Syed Imran Ahmed | |
| 10. Sandeep Mukherjee | |
| 11. Shivendra Chaturvedi | |
| 12. Vadali Rambabu | |
| 13. Deo Nath Sah | |
| Principal Staff Officer | 1. P. Suresh |
| 2. Ashok Kumar | |
| Deputy Secretary | 1. Charulata Somal |
| 2. Yashu Rustagi | |
| 3. Annies Kanmani Joy | |
| 4. Kumar Abhinav | |
| 5. Vijay S. | |
| 6. Sushant Ranjan | |
| 7. Sheikh Arshad Ayub | |
| 8. G.K. Rajnish | |
| 9. D.S. Nagalakshmi | |
| 10. Sandeep Saxena | |
| 11. J. Sriram Murty | |
| 12. Ram Dutt | |
| 13. Shamik Bhowmick | |
| 14. Parveen Jargar | |
| 15. Priya Mahadevan | |
| 16. S.K. Dahiya | |
| 17. Naresh Kumar | |
| 18. Varinder Kaur Bhalla | |
| Senior Principal Private Secretary | 1. Savita Sen |
| 2. Yati Raj Sehgal | |
| 3. R. K. Malhotra | |
| Principal Private Secretary | 1. Deepak Chandra Upreti |
| 2. Kartika Chandra Sahoo |
| 3. Naresh Kumar Mendratta | |
|---|---|
| 4. Dilip Kandulna | |
| 5. Amit Munjal | |
| 6. Laxmi Narain | |
| 7. Arvind Bhardwaj | |
| 8. Jaipal Singh | |
| 9. Zahid Hussain | |
| 10. Sarada Behera | |
| 11. Jay Prakash Singh | |
| 12. Ishwar Singh Bhandari | |
| 13. Jenender Kawatra | |
| 14. S. Rama Prasad | |
| 15. Rajesh Kumar | |
| 16. C Sundar | |
| 17. Sudheer Sharma | |
| 18. Harish Kumar Ohri | |
| 19. Surender Singh | |
| 20. Mritunjaya | |
| 21. Varad Rawat | |
| Joint Director (OL) | Jagmohan Singh Negi |
| Under Secretary | 1. Rahul Handa |
| 2. Anurag Saxena | |
| 3. Swati | |
| 4. Gautam Kumar | |
| 5. Sujit Kumar Mishra | |
| 6. Rishi Pal | |
| 7. Hemant Sharma | |
| 8. Dilip Kumar Jha | |
| 9. Naveen Kumar | |
| 10. Satyendra Singh | |
| 11. Sunil Kumar | |
| 12. Rajeev Nayan | |
| 13. M. Kiran Kumar | |
| 14. L Raghavendran | |
| 15. Preeti Wadhwa | |
| 16. Kumar Rajiv Ranjan | |
| 17. Rajiv Kumar | |
| 18. Arun Kumar Dahiya | |
| 19. Nabhlakshmi Jain Gangh | |
| 20. Anshuman Mishra | |
| 21. Sanjay Kumar Chaurasia | |
| 22. Kavita Chauhan | |
| 23. Bhupinder Pal Singh | |
| 24. Rupesh Kumar | |
| 25. Subodh Verma | |
| 26. Manoj Gupta | |
| 27. Pijush Mohanta | |
| 28. Bhupinder | |
| 29. Satyam Srivastava | |
| 30. Rajeev Kumar Khare | |
| 31. Santosh Kumar | |
| 32. Amit Kumar |
| 33. A. M. U. Mahesh | |
|---|---|
| 34. Deepak Sharma | |
| 35. Alok Suman | |
| 36. Kundan Nath | |
| 37. Subir Kumar | |
| 38. Ramesh Chandra Jha | |
| 39. Ajay Lawania | |
| 40. Praveen Pal Singh | |
| 41. Anil Bajpai | |
| 42. Vijay Kumar Darak, Dy. Director | |
| 43. Rajesh Kumar | |
| 44. Santanu Dhar | |
| 45. Ashok Giri | |
| 46. Jasmine | |
| 47. Rajesh Sharma | |
| 48. Ambrish Kumar Gopal | |
| 49. Rakesh Kumar Sinha | |
| 50. Amit Choubey | |
| 51. Lalit Kumar | |
| 52. Jata Shankar Kanth | |
| 53. Vikas | |
| 54. Charu Vijay | |
| 55. Ajay Kumar Sinha | |
| 56. Gandharv Kumar Sandilya | |
| 57. Randhir Kumar | |
| 58. Deshraj Yadav | |
| 59. Rajeev Kumar Choudhary, IAS | |
| 60. Oruganti Phani | |
| 61. Ram Bhagat Kushwaha | |
| 62. Shampa Ghosh | |
| 63. Vijay Kumar | |
| 64. Rakesh Kumar (IFD) | |
| 65. Shefali Saraf (ISTM) | |
| Assistant Director (OL) | Sandeep Mohan |
Incumbency Position of Group ‘A’ Officers in Public Enterprises Selection Board
| Post | Name of Incumbent (Sh./Smt./Ms.) |
|---|---|
| Chairman | Mallika Srinivasan |
| Member | Soma Mondal |
| Secretary | Nita Kejrewal |
| Director | Deepak Sajwan |
| Principal Staff Officer | Surender Kumar Sharma |
| Senior Principal Private Secretary | Girish Kumar Ahuja |
| Principal Private Secretary | Rajneesh Jain |
| R. Suresh | |
| Under Secretary | Mohammad Jainuddin |
List of Courses – ISTM
| S. No. | Name of the Course | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Code of Conduct for Government Employees | 00:35:00 |
| 2 | Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace | 01:51:59 |
| 3 | Annual Performance Appraisal Report (APAR) | 00:38:00 |
| 4 | Leave Rules | 00:55:00 |
| 5 | Noting and Drafting | 02:00:00 |
| 6 | Conduct Rules | 01:22:17 |
| 7 | Right to Information Act – Part 1 | 00:55:00 |
| 8 | Right to Information Act – Part 2 | 01:22:00 |
| 9 | Office Procedure | 02:17:00 |
| 10 | Government E Marketplace | 01:09:05 |
| 11 | Pay Fixation | 01:26:00 |
| 12 | Parliamentary Procedures | 02:00:00 |
| 13 | Government Accommodations – Hindi | 00:22:00 |
| 14 | Central Government Employees Group Insurance Scheme (CGEGIS) | 00:12:00 |
| 15 | Heart in Governance | 00:18:23 |
| 16 | Budget | 01:40:00 |
| 17 | Leave Rules (Hindi) | 00:45:00 |
| 18 | Swachh Bharat Mission An Overview | 00:45:00 |
| 19 | Team Building and Team Management | 01:25:00 |
| 20 | Stakeholders in Governance | 01:43:00 |
| 21 | Public Grievance Handling and CPGRAM 7.0 | 02:00:00 |
| 22 | Financial Effects of Penalties | 00:22:00 |
| 23 | Conduct of Enquiry in Disciplinary Matters | 42:00:00 |
| 24 | Chargesheet under CCS(CCA) Rules 1965 | 00:23:00 |
| 25 | Judicial Review and Reading a Judgement | 00:25:00 |
| 26 | Leave Travel Concession (LTC) | 01:07:53 |
| 27 | Central Government Health Scheme CGHS and Central Services MA Rules | 01:10:00 |
| 28 | Gender Sensitization – 1 | 01:15:00 |
| 29 | Project Management | 00:15:00 |
| 30 | Preparation of Cabinet Notes | 05:10:00 |
| 31 | Interpersonal Skills | 01:37:41 |
| 32 | Pensionary Benefits | 00:55:00 |
| 33 | Travelling Allowance (Hindi) | 00:25:00 |
| 34 | Annual Performance Appraisal Report (Hindi) | 01:04:00 |
| 35 | Leave Rules – Updated | 00:55:00 |
| 36 | Vigilance Clearance | 00:40:00 |
| 37 | Do’s and Don’ts for Government Employees- Hindi | 00:54:00 |
| 38 | Travelling Allowance | 00:55:00 |
| 39 | Formulation of Public Policies | 01:15:00 |
| 40 | Mission Karmayogi Guidelines | 01:30:00 |
| 41 | Constitutional Provisions at Workplace | 02:00:00 |
| 42 | Problem Solving | 00:35:00 |
| 43 | Principles of Natural Justice (Hindi) | 00:35:00 |
| 44 | Annual Performance Appraisal Report (APAR) – Updated | 00:38:00 |
| 45 | Role of Inquiry Officer in Disciplinary Proceedings (Hindi) | $00: 55: 00$ |
|---|---|---|
| 46 | Decision Making | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 47 | Procurement of Goods and Services | $01: 10: 00$ |
| 48 | Gender Sensitization -2 | $00: 50: 00$ |
| 49 | Fundamental Rules and Supplementary Rules | $00: 50: 00$ |
| 50 | AIS Discipline and Appeal Rules 1969 Part I Overview and Suspension | $00: 50: 00$ |
| 51 | Duties and responsibilities of Personal Assistant | $00: 13: 55$ |
| 52 | Getting Along with the Boss | $00: 31: 07$ |
| 53 | Central Government Employees Group Insurance Scheme (Hindi) | $00: 20: 00$ |
| 54 | The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 | $01: 20: 00$ |
| 55 | Delegation of power in day-to-day administration | $01: 25: 00$ |
| 56 | Handling Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) Cases | $01: 19: 00$ |
| 57 | Joining Time on Transfer | $00: 38: 00$ |
| 58 | Data Driven Decision Making | $04: 30: 00$ |
| 59 | Parliament at Work | $05: 41: 00$ |
| 60 | Handling CAT Cases | $02: 34: 00$ |
| 61 | Modified Assured Career Progression Scheme (MACPS) | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 62 | Time Management | $02: 20: 00$ |
| 63 | Parliament at Work – Legislative Process | $00: 40: 00$ |
| 64 | Official Meeting – Role of Personal Staff | $00: 15: 52$ |
| 65 | Public Administration | $01: 15: 00$ |
| 66 | अनुशासनाठक कायNवाही खडपिउधत अधिकारी की भूिमका | $00: 15: 00$ |
| 67 | Evaluation of Evidence | $01: 32: 00$ |
| 68 | Office Procedure – Updated | $02: 17: 00$ |
| 69 | Sustainable Development Goals India Stand (Hindi) | $02: 20: 00$ |
| 70 | Biodegradable Waste Management | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 71 | Sustainable Development Goals | $00: 49: 00$ |
| 72 | Know Your Ministry | $03: 00: 00$ |
| 73 | Transfer and Posting | $00: 30: 00$ |
| 74 | Matters relating to Pay Module | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 75 | Plastic Waste Management | $00: 40: 00$ |
| 76 | Reform Initiatives of Government of India | $01: 50: 00$ |
| 77 | सरकारी आवास | $00: 22: 00$ |
| 78 | Appeal Revision and Review | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 79 | Pay Fixation – Updated | $00: 47: 00$ |
| 80 | Aspects of Decentralised Wastewater Management | $00: 40: 00$ |
| 81 | Evaluation of Evidence (Hindi) | $00: 48: 00$ |
| 82 | Stakeholders in Governance (Hindi) | $01: 47: 00$ |
| 83 | Technical Resignation and Lien | $00: 30: 00$ |
| 84 | Deputation and Absorption | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 85 | Appeal, Revision and Review (Hindi) | $01: 13: 00$ |
| 86 | Central Deputation and Foreign Services | $00: 55: 00$ |
| 87 | Secretariat Functioning in File | $00: 53: 00$ |
| 88 | Cadre Review of Central Civil Services | $00: 55: 00$ |
| 89 | Role of Liaison Officer in Reservation | $00: 45: 00$ |
| 90 | Budget (Hindi) | $00: 55: 00$ |
| 91 | Landmark Judgement on Constitutional Provisions – Supreme Court | $00: 40: 00$ |
| 92 | Reform Initiatives of GOI- Hindi | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 93 | Management Fundamentals in Government Services | $01: 00: 00$ |
|---|---|---|
| 94 | Consultation with UPSC in Disciplinary Cases | 00:44:00 |
| 95 | वेतन िनधाNरण | $01: 26: 00$ |
| 96 | Central Secretariat Functionaries – Role of an ASO | 00:32:00 |
| 97 | सूचना का अिधकार अिधिनयम, 2005 – भाग 1 | $01: 42: 00$ |
| 98 | Reservation Policy – Reservation in Service | 02:55:00 |
| 99 | एश्साहत ताभ | $01: 28: 00$ |
| 100 | Sanction for Prosecution | 00:45:00 |
| 101 | Landmark Judgments- RTI Act, 2005 | $01: 10: 00$ |
| 102 | Consultation with CVC in Disciplinary Cases | 00:45:00 |
| 103 | Consolidated Instructions on Suspension | 01:02:00 |
| 104 | Sarbajanik Nitiyon ka Nirupan | 00:47:00 |
| 105 | Statistical Tools and Data Visualization | 02:05:00 |
| 106 | Central Secretariat Functionaries – Role of an Assistant Section Officer (ASO) | 00:35:00 |
| 107 | Classification, Character and Status of Posts | 00:30:00 |
| 108 | Constitutional Provisions at Workplace- Hindi | 02:00:00 |
| 109 | CAT and Appointment of its Members Chairperson | 00:25:00 |
| 110 | Handling of Complaints | 01:00:00 |
| 111 | Basic Principles of Management in Government Service (Hindi) | 00:55:00 |
| 112 | Non-Functional Selection and Upgradation for Organized Group | 00:38:00 |
| 113 | Budget and Related Activities | 00:45:00 |
| 114 | अनुशासिनक मामलों खसीवीसी के साथ िवचार-िवमशN | 00:45:00 |
| 115 | Level-III Training Programme to Develop Domain Competencies | 01:47:01 |
| 116 | आस्रण नीित – नौकरी खआसण | 02:55:00 |
| 117 | Sustainable Sanitation and Water Management | 00:40:00 |
| 118 | द $^{\text {TM }}$ विेज खसिचवालय का कामकाज | 01:00:00 |
| 119 | Sanitation Technologies | 00:35:00 |
| 120 | क सरकार 4ाv योजना) सीजीएचएस (अंछा5ीयसेवाएं) एम ए (िनयम | 01:36:00 |
| 121 | Formalities of Joining Service | 01:05:00 |
| 122 | अनुशासनांक कायNवाही खउपिउधत अिधकारी की भूिमका | 00:32:00 |
| 123 | Level-III Training Programme to Develop Functional Competencies | 16:40:37 |
| 124 | Grey Water Management | 00:40:00 |
| 125 | CCS (CCA) Rules part 1- CCS CCA Rules – An Overview and Suspension | 01:00:00 |
| 126 | Operation and Maintenance And Sustainability | 00:35:00 |
| 127 | International Cooperation and Trade | 00:50:00 |
| 128 | Constitutional Provisions Relating to Disciplinary Proceedings – Hindi | 01:03:00 |
| 129 | Seniority Principles | 01:10:00 |
| 130 | अिभयोग चलाने के ितए मंजूरी úदान करना | 00:45:00 |
| 131 | Judicial Review and How to Read Judgement – Hindi | 01:00:00 |
| 132 | CCS (CCA) Rules Part IV – Appeals, Revision and Review | 00:50:00 |
| 133 | Sanitation Capacity Building Platform | 00:40:00 |
| 134 | Faecal Sludge Management | 00:40:00 |
| 135 | Action Consequent Upon Conviction | 00:40:00 |
| 136 | Framing of Policies Schemes for Promoting Welfare Measures | 00:35:00 |
| 137 | Carbon Trading | 01:10:00 |
| 138 | Risk Management in Infrastructure Projects | 01:10:00 |
| 139 | Training Design (DOT) | 01:10:00 |
| 140 | Gender Budgeting – Basic | $00: 45: 00$ |
|---|---|---|
| 141 | Level-I CSSS Course to Develop Domain Competencies (Part-I) | $01: 34: 48$ |
| 142 | Creation of Posts | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 143 | AIS Travelling Allowance Rules | $00: 31: 00$ |
| 144 | Financial and Debt Markets in India | $01: 10: 00$ |
| 145 | National Infrastructure Pipeline Domains – Part I | $00: 50: 00$ |
| 146 | सूचना का अिधकार अिधिनयम, 2005 – भाग 2 | $01: 36: 00$ |
| 147 | Contempt of Court | $00: 45: 00$ |
| 148 | Central Secretariat Functionaries – Role of an ASO (Hindi) | $00: 38: 00$ |
| 149 | Direct Trainer Skills | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 150 | House Rent Allowance (HRA) | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 151 | Induction Course PM SVANidhi | $01: 10: 00$ |
| 152 | AIS Discipline and Appeal Rules 1969 Part IV | $00: 40: 00$ |
| 153 | Metro Rail Policy 2017 | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 154 | Framing of Policies Schemes for Promoting Welfare Measures | $00: 35: 00$ |
| 155 | E-waste disposal | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 156 | सांिक्रिय टूल डेटा ििवज़ुअलाइज़ेशन | $01: 55: 00$ |
| 157 | Roles of Secretarial Staff in Central Secretariat | $01: 30: 00$ |
| 158 | AIS (Leave) Rules 1955 | $01: 10: 00$ |
| 159 | Records Management | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 160 | Level-III CSSS Course to Develop Behaviour Competencies | $02: 18: 27$ |
| 161 | Roles and Competencies of Branch Officers | $00: 55: 00$ |
| 162 | DoPT and its Training Institutes | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 163 | सांिक्रिय टूल डेटा डाइवर एवं ििडसीजन बनाना | $04: 15: 00$ |
| 164 | Presentation Sanitation Systems | $00: 45: 00$ |
| 165 | Handling Appointment Matters in CS Wing of DoPT | $00: 45: 00$ |
| 166 | AIS (Conduct) Rules, 1968 | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 167 | Level-II CSSS Course to Develop Domain Competencies | $02: 20: 53$ |
| 168 | Contract Management | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 169 | All India Services Deputation Guidelines | $00: 50: 00$ |
| 170 | Debt Management | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 171 | Framing and Amendment of Recruitment Rules | $01: 55: 00$ |
| 172 | AIS Discipline and Appeal Rules 1969 Part II | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 173 | अनुशासनाठक मामलों क्यूपीएससी के साथ परामशN | $00: 44: 00$ |
| 174 | Used Water Management | $02: 30: 00$ |
| 175 | िनलंबन पर समिेकत िनद’श | $01: 50: 00$ |
| 176 | Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Urban Livelihoods Mission | $01: 05: 00$ |
| 177 | Financial Administration | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 178 | AIS Part III Procedure for Imposing Penalties. | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 179 | Indian Administrative Services (IAS) Pay Rules | $01: 00: 00$ |
| 180 | लोक ùशासन | $02: 10: 00$ |
| 181 | दा TM ावेज रासरकारी कामकाज | $02: 30: 00$ |
| 182 | Effective management of urban services in cities through ICCC | $01: 08: 00$ |
| 183 | केट मामलों को संभालना | $02: 37: 00$ |
| 184 | सावपजिनक नींितयों का िनVपण | $01: 14: 00$ |
NAME, DATE OF SETTING, NO. OF COURTS AND LOCATION OF VARIOUS BENCHES OF CENTRAL ADMINISTRATIVE TRIBUNAL
| S. No. | Name of the Bench | Date of setting | No. of courts | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Principal Bench | 01.11 .1985 | 6 | New Delhi |
| 2. | Ahmedabad | 30.06 .1986 | 1 | Ahmedabad |
| 3. | Allahabad | 01.11 .1985 | $\mathbf{3}$ | Allahabad |
| 4. | Bangalore | 03.03 .1986 | 2 | Bangalore |
| 5. | Chandigarh | 03.03 .1986 | 2 | Chandigarh |
| 6. | Madras | 01.11 .1985 | 2 | Chennai |
| 7. | Cuttack | 30.06 .1986 | 1 | Cuttack |
| 8. | Ernakulam | 01.09 .1988 | 2 | Ernakulam |
| 9. | Guwahati | 03.03 .1986 | 1 | Guwahati |
| 10. | Hyderabad | 03.06 .1986 | 2 | Hyderabad |
| 11. | Jabalpur | 30.06 .1986 | 1 | Jabalpur |
| 12. | Jaipur | 15.10 .1991 | 1 | Jaipur |
| 13. | Jodhpur | 30.06 .1986 | 1 | Jodhpur |
| 14. | Calcutta | 01.11 .1985 | 2 | Kolkata |
| 15. | Lucknow | 15.10 .1991 | 1 | Lucknow |
| 16. | Mumbai | 01.11 .1985 | 2 | Mumbai |
| 17. | Patna | 30.06 .1986 | $\mathbf{1}$ | Patna |
| 18. | Jammu | 08.06 .2020 | $\mathbf{2}$ | Jammu |
| 19. | Srinagar | 23.11 .2021 | $\mathbf{2}$ | Srinagar |
STATEMENT SHOWING THE NAME OF BENCH AND PLACES WHERE CIRCUIT SITTINGS ARE HELD
| S No. | BENCH | PLACES |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Principal Bench, New Delhi | Nainital |
| 2 | Calcutta Bench | Port Blair, Gangtok |
| 3 | Chandigarh Bench | Shimla |
| 4 | Madras Bench | Pondicherry |
| 5 | Guwahati Bench | Shillong, Itanagar, Kohima, Agartala, Imphal, Aizwal |
| 6 | Jabalpur Bench | Indore, Gwalior, Bilaspur |
| 7 | Bombay Bench | Nagpur, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, Goa |
| 8 | Patna Bench | Ranchi |
| 9 | Ernakulam Bench | Lakshadweep |
| 10 | Jammu | Leh |
| 11 | Srinagar | Kargil |
STATEMENT SHOWING THE POSITION OF INSTITUTION, DISPOSAL AND PENDENCY OF CASES IN THE CENTRAL ADMINISTRATIVE TRIBUNAL SINCE INCEPTION UPTO DECEMBER 2024.
(As provided by Central Administrative Tribunal, Principal Bench from time to time)
| S.NO. | PERIOD | INSTITUTION | DISPOSAL | PENDENCY AT THE END OF THE YEAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1985 | 2,963 | 30 | 2,933 |
| 2. | 1986 | 23,177 | 8,934 | 17,176 |
| 3. | 1987 | 19,410 | 15,084 | 21,502 |
| 4. | 1988 | 19,425 | 13,769 | 27,158 |
| 5. | 1989 | 18,602 | 13,986 | 31,774 |
| 6. | 1990 | 19,283 | 15,495 | 35,562 |
| 7. | 1991 | 21,623 | 17,552 | 39,633 |
| 8. | 1992 | 25,184 | 23,782 | 41,035 |
| 9. | 1993 | 27,067 | 28,074 | 40,028 |
| 10. | 1994 | 26,230 | 26,409 | 39,849 |
| 11. | 1995 | 25,789 | 23,668 | 41,970 |
| 12. | 1996 | 23,584 | 20,667 | 44,887 |
| 13 | 1997 | 23,098 | 21,981 | 46,004 |
| 14. | 1998 | 21,911 | 18,394 | 49,521 |
| 15. | 1999 | 22,944 | 24,566 | 47,899 |
| 16. | 2000 | 25,146 | 31,398 | 41,647 |
| 17. | 2001 | 25,977 | 31,953 | 35,671 |
| 18. | 2002 | 25,398 | 29,514 | 31,555 |
| 19. | 2003 | 25,089 | 28,076 | 28,568 |
| 20. | 2004 | 23,825 | 27,735 | 24,658 |
| 21. | 2005 | 21,528 | 22,408 | 23,778 |
| 22. | 2006 | 18,722 | 17,774 | 24,726 |
| 23. | 2007 | 17,725 | 18,674 | 23,777 |
| 24. | 2008 | 18,287 | 20,352 | 21,712 |
| 25. | 2009 | 24,496 | 23,681 | 22,527 |
| 26. | 2010 | 26,620 | 25,477 | 23,670 |
| 27. | 2011 | 25,869 | 24,750 | 24,789 |
| 28. | 2012 | 27,733 | 24,206 | 28,316 |
| 29. | 2013 | 27,442 | 21,654 | 34,104 |
| 30. | 2014 | 27,913 | 24,739 | 37,278 |
| 31. | 2015 | 29,089 | 25,150 | 41,217 |
| 32. | 2016 | 26,984 | 26,266 | 41,935 |
| 33. | 2017 | 25,402 | 20,055 | 47,282 |
| 34. | 2018 | 26,309 | 23,538 | 50,053 |
| 35. | 2019 | 24,998 | 26,040 | 49,011 |
| 36. | 2020 | 25,888 | 12,616 | 62,283 |
| 37. | 2021 | 29,679 | 17,395 | 74,567 |
| 38. | 2022 | 25,465 | 19,487 | 80,545 |
| 39 | 2023 | 25,742 | 31,672 | 74,615 |
| 40 | 2024 | 32,998 | 35,460 | 72,153 |
| 41 | Upto March, 2025 | 7,411 | 9,625 | 69,939 |
| TOTAL | 9,62,025 | 8,92,086 |
*It includes 19,000+ cases transferred from High Court of J&K during the years 2020 and 2021.
Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women in Workplace
An Internal Complaints Committee has been constituted in the Department of Personnel & Training for the prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women in the Workplace. It has been constituted with the following:
- Ms. D. S. Nagalakshmi, DS
- Smt. Kavita Chauhan, US
- Shri Santosh Kumar, US
- Smt. Kuljit Kaur, Secretary General, AIWC
- Ms. Orunganti Phani, US
- Chairperson
- Member
- Member
- NGO member
- Member Secretary
Women employees are being made aware of the existence of the said Committee from time to time through circulars, display on Notice Boards, and interactions. Department of Personnel \& Training complies with the guidelines of Ministry of Women \& Child Development regarding Prevention of Sexual Harassment at workplace and is fully on-boarded on She-Box Portal.
DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS AND PUBLIC GRIEVANCES
CHAPTER 20
DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS AND PUBLIC GRIEVANCES
Vision
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances defines its vision driving administrative reforms throughout government as well as redressal of all public grievances about public services.
Mission
The Mission of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is excellence in governance and pursuit of administrative reforms, promoting citizen centric governance with emphasis on grievance redressal, e- Governance, Awards and Documentation and Dissemination of Best Practices.
Objectives
Promoting administrative reforms in government policies and processes.
- Formulation of policy and coordination of issues relating to redress of grievances.
- Dissemination of governance knowledge and best practices.
- Promoting reforms through e-Governance.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
20.0 The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is the nodal agency of the Government of India for administrative reforms as well as redressal of public grievances relating to the States in general and those pertaining to Central Government agencies in particular. The Department endeavors to document and disseminate successful governance practices by way of audio-visual media and publications. The Department also undertakes activities in the field of international exchange and cooperation to promote public service reforms. There are 8 divisions in the Department namely Administrative Reforms, Organization & Methods, e-Governance, Documentation \& Dissemination, International Exchange \& Cooperation, Administration \& Coordination, Public Grievances and Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC)/e-Office.
20.1 The Department is headed by the Secretary, Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances and Pensions \& Pensioners’ Welfare. Available Staff Strength is one Secretary, 1 Additional Secretary, 2 Joint Secretaries, 7 Directors/Deputy Secretaries and 16 Under Secretary level officers in the Department. An organizational chart of the Department is at Annexure-VII. Incumbency position of Under Secretary and above level officers is at Annexure-VIII. Information regarding steps taken by this Department for Prevention of sexual harassment of women at workplace and welfare of SC, ST, OBC and Persons with Disability (PWD) are at Annexure-IX and Annexure-XIII respectively.
20.2 As per the Government of India Allocation of Business Rules, the following subjects have been allocated to the Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances:
- Administrative Reforms, including e-governance and dissemination of best practices.
- Organization and Methods.
- Policy, coordination and monitoring of issues relating to –
(a) Redress of public grievances in general; and
(b) Grievances pertaining to Central Government agencies.
(c) Monitoring of implementation of e-Office in Central Ministries / Departments - (a) Research in public management;
(b) with State Governments, professional institutions etc. in public management matters. - Administration of Central Secretariat Manual of Office Procedure:
PERFORMANCE (2024-25)
| Sl. No. | Objective | Achievements in the FY 2024-25 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Formulation of policy and coordination of issues relating to redress of grievances. | (1.1) Review of pendency of grievances in Ministries / Departments / Organizations as well as States and UTs |
| (1.2) Training of CPGRAMS to Ministries/Departments. | ||
| (1.3) Capability building of Administrative Training Institutes for improved service delivery in their respective State Government Departments through capacity building. | ||
| (1.4) Universalization of CPGRAMS Reforms version 7.0 in Central Ministries for user friendly and faster grievance redressal. | ||
| (1.5) Integration of State Government portals with CPGRAMS | ||
| (1.6) Developing departmental dashboards from the analysis of call centre and further systematic analysis of the same | ||
| (1.7) Use of Common Service Centers (CSC) to take the facility of CPGRAMS to unconnected rural population. | ||
| (1.8) Using Bhashini interface with CPGRAMS to ensure that grievances can be filed in all languages | ||
| (1.9) Introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML) tools in the system in partnership with IIT, Kanpur to categories grievances and assess quality of resolution. | ||
| (1.10) Systemic improvements in CPGRAMS portal for citizen centricity like User Interface, Dashboards and AI/ML in Mobile Application |
| 2. | Dissemination of governance knowledge and best practices | (2.1) Production of documentary films on good governance practices. (2.2) Publishing of books containing articles on shortlisted and awarded initiatives. (2.3) Publication of biannual e-magazine ‘Minimum Government-Maximum Governance’. (2.4) Organizing of Regional Conferences |
|---|---|---|
| 3. | State Collaboration Initiative | (3.1) The D&D Section has handled 23 running SCI projects in various States/UTs and 14 new projects have been sanctioned in the FY 2024-25. |
| 4. | Promoting reforms through e-Governance | (4.1) Organizing National Conference on eGovernance and presenting National Awards for eGovernance (4.2) Publishing of Compendium of select papers on issues of e-Governance, a booklet on excellence in eGovernance, a booklet on citations for National eGovernance Award Winners, and a compilation of conference papers and Development of case studies on e-Governance initiatives (4.3) Publishing of National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) Way Forward Monthly Report (4.4) Convening of the National e-Governance Webinar (NeGW) Series with the awardees of National e-Governance Awards for dissemination of best practices and replication of successful projects driving advancement in e-governance across the nation |
| 5. | Transparency/Service delivery in the Department | (5.1) The Citizens’ Charter of Ministries/Departments as well as States/UTs is available on goicharters.nic.in. Review meetings held for updation of Citizens Charters. |
| 6. | Administrative Reforms | (6.1) Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration. (6.2) Organizing Civil Services Day. (6.3) Development of case studies on best practices. (6.4) Promotion of Administrative Reforms through simplification of procedure such as abolition of affidavits and promotion of self-certification. (6.5) Designing, Developing \& publishing Good Governance Index, recommended by Sectoral Group of Secretaries on Governance to present a state-wise comparative picture about the strong and weak areas of |
| service delivery, which would help them in generating performance improvement mechanism. (6.6) Developing District Good Governance Index of States/UTs. |
||
|---|---|---|
20.3 FUNCTIONS
(i) Matters relating to administrative reforms.
(ii) Organization of Civil Services Day and Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration.
(iii) Capacity building, change management and Government Process Re-engineering to provide reform through e-Governance.
(iv) e-Office Mission Mode Project under NeGP.
(v) Organization of National Conference on e-Governance and National awards on eGovernance.
(vi) Management of Public Grievance Redressal Mechanism.
(vii) Documentation and dissemination of Good Governance Practices – innovations, adaptation and replication
20.04 PUBLIC GRIEVANCES
Background
20.4.1 CPGRAMS (Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System), developed and monitored by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG), is an apex
level online platform for filing grievances to the government authorities by the citizens. This single portal connects to all Ministries /Departments of Government India along with their attached /subordinate offices/ autonomous organizations/ PSUs etc. and also the Departments of State governments / UTs. About 103675 Grievance Redressal Officers (GRO’s) are mapped on CPGRAMS.
CPGRAMS is also available through the mobile App. Each complaint receives a unique registration ID, allowing users to track its progress. The grievances filed on CPGRAMS usually to be decided within 21 days except for those cases where resolution might take longer time due to policy / process involvement. The platform offers appeal facility to higher authorities If the citizen is dissatisfied with the resolution. The Government closely monitors effectiveness of the grievance’s redressal process through feedback calls made to the citizens after their grievances are disposed of.
Comprehensive Policy Guidelines on Grievances introduced
20.4.2 On 23rd August 2024, DARPG has introduced a comprehensive guideline to improve grievance redressal, focusing on transparency, efficiency, and accountability. These guidelines ensure that grievances are resolved quickly and fairly under whole of government approach. The 2024 Policy Guidelines highlight the government’s commitment to addressing grievances effectively and showcase the improvements made through the 10 -step reform process. The key features of these guidelines are as follows:
- Integrated Platform: CPGRAMS (www.pgportal.gov.in) serves as the central platform for filing grievances, offering a seamless user experience.
- Nodal Officers: Every Ministry/Department has appointed Nodal Officers to ensure timely and effective grievance resolution. Nodal Officers will handle grievance categorization, monitor pendency, analyze feedback, and supervise Redressal Officers.
- Grievance Cells: Dedicated grievance cells in each Ministry/Department are staffed with knowledgeable personnel for better service.
- Reduced Timelines: Grievance redressal must be completed within 21 days, with interim replies if more time is required.
- Escalation Process: Appellate officers and sub-nodal officers are in place to oversee grievance escalations within Ministries/Departments.
- Whole of Government Approach: A unified approach ensures that grievances are addressed effectively across all government bodies.
- Feedback System: Feedback is sent via SMS/email, with citizens able to file an appeal if dissatisfied with the resolution. AI-powered tools, such as the Tree Dashboard, analyze feedback to drive process improvements.
- Grievance Redressal Index: Monthly performance rankings of Ministries/Departments based on grievance redressal effectiveness.
- Training and Capacity Building: Grievance officers are trained under the SEVOTTAM scheme (Service Excellence through Total Quality Management) at State/UT Administrative Training Institutes.
- Regular Review: Senior officers regularly review grievance redressal performance and ensure stakeholder awareness.
These guidelines aim to enhance the grievance redressal system, ensuring faster and genuine resolutions with better citizen engagement.
20.4.3 CPGRAMS integrates 92 Central Ministries, Departments, and Organizations with 36 States/UTs, offering a seamless platform supported by over 73,000 active subordinate users. With 96,295 organizations registered, CPGRAMS has significantly improved citizen engagement and service delivery. From 2022 to 2024, the system enabled the resolution of $70,03,533$ grievances and mapped 1,03,183 Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) as on 31 October 2024.
20.4.4 In December 2024, the Fourth Sushasan Saptah and Prashasan Gaon ki Ore Campaign acted as a catalyst for grievance redressal, aimed at resolving public grievances and improving service delivery across India. Held in over 700 districts from December 19-25, the campaign achieved the following milestones:
- 2,99,64,200 applications disposed under service delivery
- $14,84,990$ grievances redressed on state portals
- 3,44,058 grievances redressed on CPGRAMS
20.4.5 A crucial feature of CPGRAMS is its ability to generate granular analytical reports, including metrics such as, Receipts vs. disposal, Age-wise pendency ( $2-6$ months, $6-12$ months, $>12$ months), and Ministry-wise and State-wise resolution trends. All these reports support targeted interventions and seniorlevel reviews of grievances.
20.4.6 The integration of grievance channels has significantly advanced. The PMO’s public grievance mechanism (accessible via www.pmoindia.gov.in) is now fully integrated with pgportal.gov.in, allowing seamless grievance transfer and monitoring. Additionally, the President’s Secretariat, Directorate of Public Grievances (DPG), DARPG, and Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare are now connected via CPGRAMS 7.0. Pension-related grievances which operate through CPENGRAMS also operate from CPGRAMS data base thereby streamlining response pathways for one of the largest citizen categories served by government welfare mechanisms.
Sevottam Training and Capacity Building
20.4.7 Training and Capacity Building has remained a priority. Under the Sevottam Scheme, DARPG provides financial support to State ATIs/CTIs for conducting training programmes for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs). Over the past three financial years (2022-23, 2023-24, and 2024-25), as part of Sevottam, 756 training courses have been conducted, training 24,942 officers from various State Governments. In the past financial year 3 National Workshops on “Effective Redressal of Public Grievances” on November 18, 2024, in New Delhi and February 20, 2025, in Bhopal, and on 25 April 2025 at Trivandrum with participation from Central Ministries, State Governments, and State Administrative Training Institutes (ATIs) were conducted. The National workshop served as a vital platform for knowledge exchange and collaboration, bringing together diverse stakeholders to deliberate on best practices, innovative strategies, and key reforms in grievance redressal.
Appeal Mechanism
20.4.8 Appeal Mechanism Introduction marks a pivotal improvement in accountability. Aligned with the 100th Report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee, CPGRAMS introduced the appellate function across all Ministries. Citizens now receive a prompt to rate their grievance resolution, and dissatisfied users are routed to a designated Nodal Appellate Authority. This functionality not only supports escalation but also ensures Ministries re-examine potentially unresolved cases.
10 Step CPGRAMS Reform
20.4.9 DARPG launched the 10-Step CPGRAMS Reform Program in 2022. This framework has been a cornerstone of the CPGRAMS transformation and was actively in operation through the last financial year. Transformation achieved through 10 steps reforms are summarized as under:
1. Universalization of CPGRAMS 7.0
CPGRAMS 7.0 which was based on categorization of grievances and their mapping with last mile officers was implemented across the Ministries. This has enabled auto-routing of grievances directly to the appropriate officer at the last-mile level, enhancing ownership and reducing manual delays.
2. Technological Enhancements via AI/ML
CPGRAMS is amongst the early digital platforms to use AI/ ML enabled dashboards which helped in extensive data analysis towards exploratory and predictive insights for root cause of grievances and enable suitable intervention towards systemic reforms. It has developed Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) which allows better grievance classification and root cause analysis while offering advanced semantic search and graphical data visualization. These innovations have enhanced grievance redressal efficiency, driving systemic improvements and informed policy interventions.
3. Language Inclusivity
A regional language interface has been developed for CPGRAMS in partnership with Bhashini under MeitY, to make the platform inclusive and accessible to every citizen in their native language.
4. Grievance Redressal Index (GRAI)
In order to improve overall efficiency of CPGRAMS, DARPG has designed an output and outcome-oriented monitoring mechanism in the form of Grievance Redressal Assessment Index (GRAI). It provides a holistic analysis of performance of Ministries/ Departments on four broad parameters – Efficiency, feedback, Organizational Commitment and domain strength covering 11 indicators and encourages the adoption of best practices in grievance redressal. The GRAI 2023, reveals that in most of the Dimensions and Indicators, Ministry/ Departments have shown significant improvement. 85 out of 89 Ministries and Departments demonstrated significant improvements against all parameters as compared to GRAI 2022. Several Ministries have shown more than a $50 %$ growth reflecting enhanced resolution rates within the prescribed timelines.
5. Feedback Call Centre
A 50-seater multilingual facility, active since July 2022, contacts every citizen post-resolution. To facilitate the Ministries to utilize the feedback and use them in improving systems, DARPG has created a separate portal where all feedback along with detailed call records and comments from citizens are available. Ministries have access to this portal so that they can analyse the feedback and work on the areas of poor/low feedback. Feedback is also considered while ranking the Ministries in GRAI. As of February 2025, it had conducted over 20.48 lakh feedback calls, with insights driving further reform.
6. One Nation One Portal Integration
CPGRAMS is available to all States/ UTs. However, where the States have independent grievance portals, CPGRAMS integrated with those systems through APIs to ensure a seamless experience to the citizens. It has been integrated such 19 grievance portals of States /UT to ensures no duplication or fragmentation.
7. Inclusivity and outreach
To enhance the outreach of CPGRAMS for rural and underprivileged population the government has leveraged the network of Common Service Centres 5 lakh with Common Service Centres (CSC). Citizens in rural/remote areas can file grievances at Common Service Centres (CSCs); a special CSC-CPGRAMS Day is observed every month to enhance such engagements. Facebook live on the grievances relating to the PM KISSAN, PMAAY and Banking and Insurance were organized by the CSC where Secretaries of the respective Ministries participated and answered the queries of the Department in collaboration with CSC and In addition to this the Government has also utilized network of AIR / Prasar Bharati to enhance the outreach of CPGRAMS.
8. Training & Capacity Building (Sevottam
DARPG is supporting the capacity building of the grievance officers to enable them handle the public grievances with satisfaction of citizens. State Administrative Training Institutes (ATIs) are partners for providing training to the grievance officers in States under SEVOTTAM scheme. The Scheme was revised in July 2024 with enhanced support to ATIs for Rs 1500/ per person / day for training programmes of GROs. 22 ATIs have been approved an amount of Rs 3.87 Cr in 20242025 to train 18,000 GROs in 688 programmes. DARPG has partnered with the Administrative Staff College of India (ASCI) to conduct a Training Needs Assessment (TNA) of Grievance Officers. This will culminate in the development of a standardized training curriculum and andragogical framework, enabling uniformity in training delivery across States. Further, the Department organized National level workshops on Effective redressal of Grievances and SEVOTTAM in Pune (May 2023) and Bhopal (February 2025) and Thiruvananthapuram (April 2025) with participation to showcase best practices in grievance redress and capacity building. The Department has also developed an online course in collaboration with ISTM for iGOT Karmyogi platform.
9. High level monitoring through Structured review
In order to ensure that citizen feedback is effectively utilized in enhancing responsiveness of the platform, the government has introduced a monitorable framework for review of feedback and unresolved grievances at the level of Secretaries to the government of India in CPGRAMS. Monthly reports generated and shared with all Ministries and States, including data on ageing, feedback, and disposal rates.
10. Data Strategy Unit and Dashboards
A new analytics wing within DARPG uses AI-powered dashboards for visualizing data clusters, root cause analysis, and policy feedback loops. This dashboard is now available to all Ministries for internal review.
Impact of CPGRAMS
20.4.10 These reforms have made grievance redressal timely, meaningful and accessible and helped to bring down the pendency in Govt of India at its lowest level of 53000 Public Grievances as on 31 October 2024 with average timelines of redressal coming down from 28 days in 2019 to 13 days in 2024 and citizen satisfaction, as indicated by feedback calls, improved from $\mathbf{4 0 . 7 4 %}$ in 2023 to $\mathbf{5 2 \%}$ in 2024.
Next Gen CPGRAMS
20.4.11 The technological advancement over the years have opened the new dimensions in handling public grievances. Therefore, a comprehensive approach utilizing latest technology in Grievance redressal has
been envisaged. DARPG got approval for NEXT GEN CPGRAMS with an outlay of Rs 128 cr for two years 2024-2026. The proposal includes complete overhauling of technology infrastructure of CPGRAMS to enhance user experience at all levels and make it an effective tool for multidimensional analysis to drive efficiency in multi-layered ecosystem of Government Departments and its programmes and policies. Building on CPGRAMS 7.0, it will offer features like grievance filing via Social Media Multilingual tools, voice-to-text lodging, instant alerts, and auto-escalation. Monitoring bodies can track grievances by grouping, sector, and Ministry. NextGen CPGRAMS is set to launch in FY 2025-26, further enhancing the grievance resolution process.
CPGRAMS: Global Recognition and Citizen Impact
20.4.12 CPGRAMS has garnered global recognition as a model of effective governance. At the Third Biennial Pan-Commonwealth Heads of Public Service Meeting in April 2024, the Commonwealth Secretariat highlighted it as a future-ready governance tool. The system has proven effective in addressing citizens’ grievances with swift resolutions and improved public safety.
20.4.13 CPGRAMS has become a key tool in improving how the government addresses citizens issues. By simplifying the grievance process and ensuring quicker resolutions, it has built a stronger connection between the public and the government. With significant improvements in service delivery and global recognition for its effectiveness, CPGRAMS is helping India move towards a more responsive and citizenfocused government
Citizens’ Charter
20.04.14 The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances in its efforts to provide more responsive and citizen-centric governance coordinates the efforts of Ministries / Departments to formulate and operationalize Citizen’s Charters in Central Government Ministries / Departments as well as State Governments and UT Administrations. It provides guidelines for formulation and implementation of the Citizen’s Charters.
Important events/achievements of the Department
20.05 Prime Ministers’ Awards for Excellence in Public Administration
20.05.01 Government of India has instituted a scheme “Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration” in 2006 to acknowledge, recognize and award the extraordinary and innovative work done by the Districts/ implementing units and organizations of Central and State Governments.
20.05.02 Since its inception and till 2015, the awards were conferred under three categories, viz., individual, group and organizations. The structure of the Awards Scheme was changed in 2015-16 to focus on excellence in implementation of identified Priority Programmes wherein the States were grouped in three categories namely; (i) North Eastern and Hilly States; (ii) Union Territories and (iii) Other States. The PM Awards Scheme was restructured in 2020 to recognize the performance of District Collectors towards economic development of the District. The Scheme for Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration was again revamped in 2021 with the objective to encourage Constructive Competition, Innovation, Replication and Institutionalization of Best Practices. The Award Scheme was further revamped in 2023 to recognize the performance of the District Collector through targeted individual beneficiaries and implementation with a saturation approach. For the year 2024, the scheme for Prime Minister’s Awards has been restructured by including the ‘Aspirational Blocks Programme’ category to assess the overall performance of the Aspirational Blocks along various parameters. The Aspirational Blocks would be evaluated based on the progress made during the evaluation period. With this in focus, the applications for Awards would be evaluated on three parameters; Quantitative, Qualitative and Governance.
20.05.03 Prime Minister’s Awards are awarded by the Hon’ble Prime Minister on Civil Services Day (CSD) held on 21st April of every year. This is an occasion for Civil Servants of the Country to rededicate themselves to citizens and renew their commitment to public service and excellence in work. So far 16 Civil Services Day have been celebrated.
20.06 INTERNATIONAL EXCHANGE AND COOPERATION
20.06.01 The Department works as the nodal point in respect of matters relating to international cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance, which includes organizing programmes and visits of the foreign delegations to India and visits of Indian delegations abroad as part of projects / bilateral measures taken up in accordance with the Memorandum of Understandings (MOUs) / Agreements signed between India and other countries (bilateral or multilateral).
20.07 Minimum Government Maximum Governance Initiatives (Implementation of eOffice Mission Mode Project)
e-Office is one of the Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) under the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP). The project is aimed at significantly improving the operational efficiency of Central Government Ministries and Departments through improvement in the workflow mechanisms and associated with office procedure manuals. The DAR&PG is the nodal Department for implementation of “e-office” in Central Government Ministries/ Departments. Effective steps have been taken by DAR\&PG to expedite implementation of eoffice in all Central Government Ministries / Departments by conducting regular review meetings and also by establishing a project monitoring unit in the Department. Adoption of e-Office has gained significant momentum in Central Secretariat after 2014. Over the past 3 years, Ministries/ Departments have upgraded from e-Office version 5.6 to version 7.0. As of now total 3815768 e-files have been created out of these total 3388912 are active e-files. At present 94 percent of total files in the Central Secretariat are e-files and 95 percent of receipts are being handled as e-receipts.
20.08.01 Implementation of e-Office in Attached, Subordinate Offices and Autonomous Bodies
Adoption of e-Office has enhanced the efficiency and transparency of the file movement process and has led to least paper work and faster decision-making. In the backdrop of successful implementation of the eOffice platform in Central Secretariat, e-Office has also been implemented in 92 attached/subordinate offices and autonomous bodies of Government of India, as part of DARPG’s 100-days agenda of Government in June, 2025. DARPG issued detailed guidelines for adoption of e-Office in attached, subordinate offices and autonomous bodies on $24^{\text {th }}$ June 2024.
20.08.02 Sharpening of e-Office Analytics dashboard
The e-Office Advanced Analytics Dashboard launched in 2023 facilitates in-depth data analysis \& strengthens decision making in the Central Secretariat. It also helps as a tool to validate the extent of digitization and delayering in the Central Secretariat. It allows monitoring of pendency of e-files and pfiles statistics, levels of file movement statistics, inter-ministerial file movement statistics and statistics of e-Receipts out of total receipts, File Signing Status using DSC/eSign and VPN usage in Central Government during the month. The monthly reports of the eOffice analytics dashboard are circulated by DARPG to all Ministries/Departments under the theme “Secretariat Reforms”.
20.08.03 National workshop on eOffice
During the Special Campaign 4.0 activities, a National workshop on e-Office was organised on $29^{\text {th }}$ October, 2024 in CSOI, Chankaya Puri, New Delhi to sensitize Ministries / Departments on timely adoption of e-Office in all central government offices on a saturation basis, the use of the advanced analytics dashboard, use of virtual private networks and the cyber security features for operating e-Office.
User experience and feedback were shared by some Ministries/Departments during the workshop. e-Office Analytics Guidelines have been issued by DARPG on $17^{\text {th }}$ January, 2025
20.09 Promoting Documentation and Dissemination of Good Governance
Initiatives
The Documentation and Dissemination Division of the Department primarily carries out the activities of documentation and dissemination of good governance practices of Central and State Governments and Union Territory Administration with a view to facilitate sharing of experience with one another and replication elsewhere.
This Department brings out its e- Magazine titled ‘Minimum Government – Maximum Governance’ (MGMG) as an e-Book in its endeavors to document and disseminate successful good governance practices. In the e- Magazine, write-ups based on the shortlisted initiatives of PM Awards and National eGovernance Awards instituted by DARPG have been compiled and published on the website of the Department in e-Book form biannually.
20.10 Promoting e-Governance ( National Conference on e-Governance and National eGovernance Awards)
20.10.1 Promoting e-Governance (National Conference on e-Governance and National eGovernance Awards) The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances along with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, in association with one of the State/UT Governments, has been organizing the National Conference on e-Governance every year since 1997. This Conference provides platform for the senior officers of the Government including IT Secretaries of State Governments, IT Managers of the Central Government, and resource persons, experts, intellectuals from the industry and academic institutions, etc. to discuss, exchange views and experiences relating to various e-Governance initiatives. National Awards for e-Governance are also presented during the Conference for excellence in e-Governance.
20.10.2 National e-Governance Awards, National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA), NeSDA-Way Forward and E-Gov. Web series.
CHAPTER 21
ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS
Civil Services Day and Prime Minister’s Awards Scheme for Excellence in Public Administration
21.1 The Government of India celebrates April, 21 every year as ‘Civil Services Day’ for the civil servants to rededicate themselves to the cause of citizens and renew their commitment to public service and excellence in work. The first such function was held in Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi on 21st April, 2006. On the occasion, the Hon’ble Prime Minister confers the “Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration” to acknowledge, recognize and award the extraordinary and innovative work done by officers of the Central and State Governments including Districts. This date coincides with the date when the first Home Minister of Independent India Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel addressed the first batch of Indian Administrative Services Officers at Metcalf House, New Delhi. Technical sessions on governance related subjects, exhibitions, release of books and documentaries are part of the event, which is attended by Ministers and senior bureaucrats of the country.
21.1.1 In 2024, the Civil Services Day could not be held due to the General Elections. In 2023, the $16^{\text {th }}$ Civil Services Day function was held in Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi on $20^{\text {th }}-21^{\text {st }}$ April, 2023, on the theme “VIKSIT BHARAT-Empowering Citizens. & Reaching The Last Mile” The Hon’ble Prime Minister graced the occasion on $21^{\text {st }}$ April and conferred the Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration 2022 for effective implementation of identified Priority Programmes and Innovation to districts/ implementing units and other Central/ State organizations. 15 awards were conferred by the Hon’ble Prime Minister to recognize the extraordinary and innovative work done by Ministries/Departments of the Central and State Governments and Districts.

Hon’ble Prime Minister addressing the CSD event on 21 April, 2023
21.2 Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration’ 2024:
21.2.1 The Scheme for Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration was revamped in 2021 with the objective to encourage Constructive Competition, Innovation, Replication and Institutionalization of Best Practices. For the year 2024, the Scheme for PM’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration has been approved to recognize the contribution of civil servants under the following schemes: –
Category 1: Holistic Development of Districts.
Category 2: Aspirational Blocks Programme.
Category 3: Innovation
21.2.2 Awards – The total number of awards under the Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration 2024 is 16. The Award would consist of a (i) trophy, (ii) scroll and (iii) an incentive of Rs. 20 lakh to the awarded District/organization to be utilized for implementation of project/ programme or bridging resource gaps in any area of public welfare. There are 5 awards each under Category 1 and Category 2, and a total of 6 Awards will be presented under Category 3-Innovation. 2 awards each will be conferred for Central, State level organisations and Districts.
21.2.3 Applications for Prime Minister’s Awards are received online on a designated portal and are evaluated by three hierarchical Committees. The shortlisting of applications is done by Screening Committees chaired by the Additional Secretary level officers, Expert Committee chaired by Secretary, Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances and the Empowered Committee chaired by the Cabinet Secretary. The Empowered Committee then makes its recommendations for the consideration of the Hon’ble Prime Minister for final selection of the Awards.
21.2.4 For the Prime Minister’s Awards 2023, the Hon’ble Prime Minister has approved the recommendations of the Empowered Committee for final selection of the awards. For Prime Minister’s Awards 2023, 16 awards will be presented under two categories –
Category 1 – Holistic Development of Districts (10 awards to Districts)
Category 2- Innovation (6 Awards, 2 each for Central, State level organisations and Districts)
21.2.5 For the Prime Minister’s Awards 2024, the portal for registration and submission of nominations has been operationalized on 20.01.2025.
21.2.6 The Prime Minister’s Awards will be conferred by the Hon’ble Prime Minister during the $17^{\text {th }}$ Civil Services Day on $21^{\text {st }}$ April, 2025.
21.3 State Collaboration Initiatives
The State Collaborative Initiative (SCI) is designed to foster collaboration with State Governments to enhance public service delivery and replicate initiatives that have received the Prime
Minister’s Award and the National e-Governance Award. In 2024, a total of $₹ 10,39,58,048$ has been sanctioned for the initiative, with $₹ 5,23,64,250$ released for 18 ongoing projects and $₹ 5,15,93,798$ released for 14 new projects sanctioned.
21.4 National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)
21.4.1 The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) was set up in the year 2014 by the Government of India as an apex-level autonomous institution under the aegis of Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions. The Centre traces its origin to the National Institute of Administrative Research (NIAR), which was set up in 1995 by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA). NIAR was subsequently rechristened and subsumed into NCGG. DARPG is the administrative Department for NCGG since 08.11.2017.
21.4.2 NCGG deals with a gamut of public policy and governance issues from local, state to national levels, across all sectors. The Centre is mandated to work in the areas of good governance, policy reforms, capacity building and training of civil servants and technocrats of India and other developing countries. It also works as a think tank for governance and Policy Reforms.
21.4.3 The affairs of the NCGG are managed under the overall superintendence and direction of the Governing Body, which is headed by the Cabinet Secretary. It has Secretaries of 9 Ministries/ Departments and provision of 5 eminent persons viz. academicians, eminent administrators, specialists, eminent innovators, and heads of reputed institutions as members. The Director General who is the Chief Executive of NCGG acts as the Member-Secretary of the Governing Body. The 3rd Governing Body meeting was held on September 9, 2022. There is a Management Committee headed by the Secretary, DARPG to guide NCGG in its work to achieve the stated objectives. 11 meetings of the Management Committee have been held. The $11^{\text {th }}$ meeting was held on $10^{\text {th }}$ October, 2024.
21.5 Mandate of NCGG
(i) Promote Governance and policy reforms;
(ii) Design and conduct capacity building and training programmes for International as well as domestic civil servants;
(iii) To function as a national repository on best practices, initiatives that promote good governance.
(iv) Collaborate with several developing countries to foster the exchange of information, knowledge, ideas, and expertise in governance;
(v) To undertake policy research on issues relating to good governance;
(vi) Encourage the adoption and replication of innovative ideas and best practices; and
(vii) Organizing consultations, workshops, seminars, webinars, symposia to promote good governance
21.6 Activities of the NCGG
Capacity Building Programmes: Over the years, NCGG has created a niche for itself in the field of capacity building and leadership development programmes. The Ministry of External Affairs has identified NCGG as a key institution for developing and conducting highly customized capacity development programmes for the civil servants and technocrats of other developing countries. Similarly, NCGG is asked by the Government of India to organize specialized programmes for domestic civil servants and technocrats. The capacity building programmes conducted by NCGG are in the following two categories:
A. International programmes: During the year, NCGG developed and imparted customized capacity building programmes to 746 civil servants of 45 countries in 21 batches.
i) Bangladesh:
In 2013, the Ministry of External Affairs entrusted NCGG to train 1,500 civil servants of Bangladesh. After successful completion of the training of 1,500 civil servants, the Ministry of Public Administration, Government of Bangladesh signed an MoU with NCGG on $11^{\text {th }}$ February,2019, to train another 1,800 civil servants of Bangladesh in next six years. In 2024-25, two batches comprising 45 civil servants and 16 Senior Deputy Commissioners from Bangladesh, received training. NCGG has trained a total of 2,722 Bangladeshi civil servants upto January 2025.

ii) Sri Lanka
The Memorandum of Understanding was signed between NCGG and the Sri Lankan Institute of Development Administration on Training and Capacity Building Programme for Civil Servants of Sri Lanka on $10^{\text {th }}$ December, 2024. The MoU is valid for a period of 5 years and provides for training of 1500 Civil Servants of Sri Lanka.
NCGG has conducted Capacity Building Programmes for 6 batches covering the training of 214 Sr Lankan Civil Servants up to January, 2025. During the year 2024-25, 4 batches comprising 160 Civil servants of Sri Lanka received training.
iii) Maldives
During the official state visit of Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on June 8, 2019, India and Maldives signed an MoU to implement a Capacity Building Training Programme (CBTP) for 1,000 Maldivian civil servants over five years.
Since then, NCGG has successfully conducted 32 capacity-building programs, including one for a highlevel delegation and two specialized programs for the Anti-Corruption Commission (ACC) of Maldives and the Information Commission Office of Maldives (ICOM).
The MoU was renewed on August 9, 2024, through a Note Verbale for another five years to train an additional 1,000 Maldivian civil servants. In 2024-25, 101 civil servants from the Republic of Maldives have been trained across three batches. As of January 2025, NCGG has trained a total of 1,106 Maldivian civil servants.
iv) Cambodia
The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG), in collaboration with the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), has been conducting Capacity Building Programs on Public Policy and Governance for Cambodian civil servants.
As of January 2025, NCGG has successfully conducted eight programs, training a total of 314 Cambodian civil servants. To further strengthen cooperation, an MoU was signed on April 22, 2024, between the Ministry of Civil Services of the Kingdom of Cambodia and the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions, Government of India, for a five-year partnership in human resource development in civil services.
v) Gambia
The National Centre for Good Governance, in collaboration with the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances and the Ministry of External Affairs, has conducted capacity-building programme for Gambian Civil Servants. During 2024-25, total of 30 Civil servants of Gambia have been trained by NCGG. The programme was specially designed to equip decision- makers in Gambia’s civil service, such as Permanent Secretaries, their deputies, Secretaries, and Generals, with the latest knowledge, skills, and tools to create effective public policy in an increasingly complex and interdependent world. The training aimed to promote good governance and sustainable development while providing cross- country exposure to avoid duplicating efforts. NCGG has trained 126 civil servants of Gambia up to January, 2025.
vi) Tanzania
NCGG, in the year 2024-2025, organized 1 training program for Tanzania from May 6 to May 17, 2024, for 29 mid-career civil servants on Project and Risk Management for Public Works. The program provided insights into effective project planning, risk assessment strategies, infrastructure management, and best practices in public sector project execution, equipping participants with the necessary skills to enhance governance and implementation efficiency.
vii) Kenya
viii)
This year, NCGG conducted a training program for senior civil servants of Kenya, benefiting 29 participants. The program provided insights into India’s successful governance models and future prospects, equipping participants with valuable knowledge and best practices.

ix) Multi-Country Programme for Civil Servants of the African Region, SEA&IOR and BIMSTEC Countries
This year, NCGG conducted four international training programs-one for the African region with 40 participants, one for the SEA IOR region with 30 participants, one for BIMSTEC with 36 participants, and one for Latin American countries with 22 participants. The participants were trained by top experts on good governance models and best practices, equipping them with valuable insights and strategies for effective governance.
x) Multi-Country Programme for Civil Servants of FIPIC/IORA Countries
The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG), successfully completed 1 Advanced Leadership Development Programme on Public Policy and Governance for civil servants of multi-countries from the FIPIC/IORA region. The program was organized from August 5-16, 2024, with 40 distinguished
participants from Seychelles, Somalia, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Madagascar, Fiji, Kenya, Maldives, and Mozambique. The participants hold key positions such as Director General, Secretary, District Administrator, General Manager, Senior Human Resource Officer and Industry Coordinator.
xi) Advanced Leadership Development Program on Public Policy and Governance for Latin American & Caribbean Countries
The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) commenced its 1st Advanced Leadership Development Programme on Public Policy and Governance specifically designed for Latin American and Caribbean nations. This two-week program is being organized from 2nd to 13th September 2024 bringing 22 Civil Servants from 10 countries, including Civil Servants from Argentina, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guyana, Honduras, Jamaica, Paraguay, Peru, St. Kitts \& Nevis, and Suriname.
B. Domestic Programme
i) Capacity Building programme on Digital Governance
NCGG conducted a specialized five-day training program on “Digital Governance” at IIM Visakhapatnam, attended by 19 officers from various government departments. The program focused on leveraging emerging technologies, enhancing digital service delivery, and improving governance through data-driven decision-making. Participants from states including Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Rajasthan, Puducherry, Punjab, Gujarat, Sikkim, Karnataka, Uttarakhand, and Goa also received training on CPGRAMS, enhancing their understanding of public grievance redressal mechanisms.
C. NCGG Internship Programme
In an initiative towards research to contribute to public policy, the NCGG has started Internship programme in the year 2023. A select number of students undergoing post-graduate studies are engaged for a brief period for research on various topics of public policy, under the mentorship of educationists from various renowned Universities of India. During the FY 2024-25, 02 such programmes have been conducted and research papers are published by the NCGG in the form of Compendiums available on NCGG’s website (www.ncgg.org.in). The details of the conducted programmes are as follows:
- 3rd batch of Internship Programme: 17 interns participated from 2nd April – 30th July, 2024.
- 4th batch of Internship Programme: Commenced on $20^{\text {th }}$ January 2025. Currently ongoing with 16 interns.
- $\quad$ Total Interns: 33 (FY 2024-25)
D. INSA – NCGG LEADS Programme
One of the significant collaborations has been with the Indian National Science Academy (INSA) to conduct the Leadership Development Programme in Science and Technology (LEADS). This initiative, the first of
its kind, aims to build the leadership capabilities of scientists and professors in India’s science and technology ecosystem. During the FY 2024-25, two batches have been conducted and trained 81 Scientists/ Professors. The details of the same are as follows:
- 2nd batch of LEADS Programme: 44 participants from 1st – 7th April, 2024.
- $\quad 3$ rd batch of LEADS Programme: 37 participants from 8th – 14th July, 2024.
- $\quad$ Total Participants: 81
Valedictory Ceremony of the $2^{\text {nd }}$ batch of INSA – NCGG Leadership Development Programme in Science & Technology held at INSA, New Delhi on $7^{\text {th }}$ April, 2024.
21.07 National Good Governance Webinar Series (NGGWS)
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances has initiated a unique initiative of organizing National Good Governance Webinar Series on a monthly basis from April 2022, which has been very popular amongst practicing administrators. Very large participation has been observed in the 26 Webinars held up to January 2025.
The Hon’ble Vice President of India released the compendium of the National Good Governance Webinar Series on $20^{\text {th }}$ April, 2023 in the inaugural session of Civil Services Day events 2023.
The speakers present their exemplary work in these National Webinars on their PM Award winning initiative and highlight the best practices adopted by them for replication by other States/Districts. Doing so would also infuse a new spirit and enthusiasm among administrators and other stakeholders involved in the implementation of different government programmes. These webinars covering Initiatives help in broadening of skills, dissemination of best practices as well as in replication of best practices.
During 2024-2025, the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances organized a series of six National Good Governance webinars. These webinars mainly focused on various themes under the good governance initiative, which had been shortlisted upto the level of Expert Committee under the Prime Minister’s Award for Excellence in Public Administration. The webinars encompassed a range of areas such as environment, Education- samagrashiksha, har ghar jal yojana, aspirational district programme, innovation category and social sectors, where states had been awarded for their exceptional work. The primary objective of these webinars was to disseminate best practices as examples for other states to emulate.
Table:PM’s Award-Winning Initiatives Webinar
| S. No. | Categories/ Initiatives |
Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Innovation – State Category |
$26^{\text {th }}$ July, 2024 |
| 2. | Aspirational District Programme |
$30^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024 |
| 3. | Innovation (General) – District |
$27^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024 |
| 4. | Innovation (General) – District |
$25^{\text {th }}$ October, 2024 |
| 5. | India@100- Administrative Reforms |
$29^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024 |
| 6. | HarGhar Jal Yojana | $24^{\text {th }}$ January, 2025 |
21.08 Good Governance Week (GGW)
The Good Governance Week 2024 (Fourth Sushasan Saptah) event was successfully held in Dr. Ambedkar International Centre on $23^{\text {rd }}$ December 2024 with Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions as the Chief Guest. The Hon. Minister also inaugurated the Exhibition on Best Practices of various Ministries/Departments during Special Campaign 4.0 in which Ministries/Departments installed their panels.
The Hon’ble Prime Minister extended his greetings and best wishes for the success of the $4^{\text {th }}$ SushasanSaptah. The Message of Hon’ble Prime Minister for Good Governance Week 2024was also displayed in the Exhibition. The Hon. Minister released/launched the ‘Assessment Report of Special Campaign 4.0 ‘.
As part of Sushasan Saptah 2024, for promoting Good Governance and Citizen Centric initiatives, the “Prashasan Gaon Ki Ore” – a very successful Nationwide campaign for Redressal of Public Grievances and Improving Service Delivery was held in 700+ districts across India from December 19-24, 2024. Following were the key highlights of the campaign
- Applications disposed under service delivery – 2,99,64,200
- Public Grievances Redressed on State Portals – 14,84,990
- Public Grievances Redressed on CPGRAMS – 3,44,058
- Total Number of Camps held – 51,618
- PIB Statements issued – 1720
- Best Good Governance Practices – 1,167
- Success stories of Public Grievances – 724
- District Vision @ 100 documents prepared – 272
21.08.01 Good Governance Index (GGI)
In pursuit of the recommendations made by the Group of Secretaries (GoS) on Governance, for developing of an index to gauge the performance of the States, the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG), in collaboration with Centre for Good Governance Hyderabad as technical partner, designed and developed the Good Governance Index (GGI) framework. GGI is a comprehensive and implementable framework to assess the state of governance across the States and UTs which enables ranking of States/UTs.
The key objective is to create a tool which can be applied uniformly across the States/UTs to assess impact of various interventions taken up by the Central and State/UT Governments. GGI provides a comparative picture among the States/UTs while developing competitive spirit for improvement. In selecting the sectors for GGI, the focus was on citizen-centric approach and on consensus through extensive consultations at national and state-level.
The 10 sectors of GGI are (1) Agriculture and Allied Sectors, (2) Commerce \& Industry, (3) Human Resource Development, (4) Public Health, (5) Public Infrastructure \& Utilities, (6) Economic Governance, (7) Social Welfare \&Development, (8) Judiciary \& Public Safety, (9) Environment, and (10) CitizenCentric Governance.
The performances all States/UTs in each of these sectors are assessed on the basis of indicators. The data points for indicators are selected on the basis of its availability across States/UTs and its authenticity. The first GGI was released in 2019, the second GGI was released in 2021.
21.08.02 District Good Governance Index (DGGI)
The DGGI represents next generation administrative reform in bench-marking governance at District level and is expected to provide guidance to the State as well as the District administration and other stakeholders in their efforts to address existing gaps, plan to bridge these gaps and aid as decision making tool. The ranking brings healthy competition amongst districts in their quest to provide citizen centric administration and governance.
The first ever District Good Governance Index (DGGI) for Jammu and Kashmir encompassing 10 Governance Sectors and 58 indicators was released on 22nd January, 2022. This was the first attempt of benchmarking Governance at Districts who are the basic unit for administration and governance. Subsequently, more states have come forward to undertake DGGI in collaboration with DARPG.
In furtherance of the achievement of releasing for Jammu \& Kashmir, in 2023-24 DARPG released DGGIs for the States of Gujarat on 21st May 2023; Arunachal Pradesh on 8th June 2023. In 2024-25 DARPG released DGGI Maharashtra on 26th December 2024 in collaboration with the State Governments concerned.
CHAPTER 22
Public Grievances
Abstract
The Public Grievances Division is responsible for issuing policy guidelines and coordinating & monitoring of issues regarding redress of public grievances for the Central Government. In accordance with federal principle of governance, the grievances relating to States are forwarded to concerned State Government for appropriate action. To provide a more responsive and citizen-centric governance, the PG Division coordinates efforts to formulate and operationalize the Citizen’s Charters of various Ministries/Departments and State and UT Governments. The PG Division also handles Sevottam which is a part of a citizen-centric quality management framework for better service delivery.
22.1 The Allocation of Business Rules, 1961, allocates to DARPG inter alia, the responsibility for Policy, Coordination and Monitoring of issues relating to (a) Redress of Public Grievances in general and (b) Grievances pertaining to Central Government Agencies, in particular. The Public Grievance Division is responsible for this activity since December 1987. From 1997, the Division has also been made responsible for several Citizen-Centric Initiatives under the platform of ‘Responsive Government’. These include Citizens’ Charter, and Sevottam, for bringing improvement in public service delivery on a continuous basis.
22.2 The management of Public Grievances today envisages reduction in grievances, by bringing continuous improvement in Public Service Delivery and in the Public Grievance redressal system.
22.3 The Public Grievances Division has undertaken various measures during the year to make the grievances redressal system accessible, effective and meaningful.
22.4 CPGRAMS (Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System) has evolved since 2007. This is an apex level online platform for filing grievances to the government authorities by the citizens. This single portal connects to all Ministries /Departments of Government India along with their attached /subordinate offices/ autonomous organizations/ PSUs etc. and also the Departments of State governments / UTs. About 103675 Grievance Redressal Officers (GRO’s) are mapped on CPGRAMS.
22.4 CPGRAMS is also available through the mobile App. Each complaint receives a unique registration ID, allowing users to track its progress. The grievances filed on CPGRAMS usually
to be decided within 21 days except for those cases where resolution might take longer time due to policy / process involvement. The Government closely monitors effectiveness of the grievance’s redressal process through feedback calls made to the citizens after their grievances are disposed of. Citizens can use a Mobile App for lodging of public grievances and the action Status can also be viewed on the mobile itself. This mobile app is integrated with Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance (UMANG). The app is available in Android version. A new mobile app called My Grievance is also available which is independently for CPGRAMS.
22.5 CPGRAMS facilitates forwarding of public grievances received online from the citizens to both the Central Government Ministries / Departments / Organizations as well as the State Governments concerned. The inflow of these Centre and State related grievances are in two forms (i) online registered grievances through CPGRAMS and (ii) offline grievances received through post. The grievances received through post are digitized, uploaded on CPGRAMS and forwarded online through the System as well as by post to the Central Ministries/Departments / Organizations / State Government concerned.
The CPGRAMS interlinks 92 Central Ministries/Departments / Organizations. Under its One Nation – One Portal Grievance platform, all States / UTs have been integrated with CPGRAMS. Public grievance mechanism of PMO, the President’s Secretariat, the Directorate of Public Grievances (Cabinet Secretariat), Department of Pensioners Welfare have been fully integrated through the common data base of CPGRAMS thus enabling grievances lodged to any of these entities to be transferred to the Central Ministries / Departments and State Governments seamlessly through CPGRAMS. A total of 102163 Grievance officers are mapped in CPGRAMS.
Introduction of an Appeal Mechanism/functionality in CPGRAMS
A separate workflow and functionality for escalation of grievances to appeal authorities in CPGRAMS has been operationalized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances. The time line for resolution of an Appeal by the Nodal Appellate Authority is 30 days of receipt of the same. The Appellate Authority to whom a dissatisfied Complainant can raise / escalate a public grievance is one level above the existing designated Nodal Grievance Officers.
Operationalization of Feedback Call Centre: –
DARPG is operating a Feedback call Centre w.e.f. 01.7.2022. Call Centre is taking direct feedbacks from the citizens on the resolution provided to them by Ministries / Departments and the States / UTs. The call center also assists the citizen in filing appeal if they are not satisfied with the disposal. The calls are made in 12 different languages (English, Hindi, Gujarati, Marathi, Bangla, Telugu, Assamese, Odiya, Tamil, Malayalam, Kannada & Punjabi). Till December, 2024
total 8.74 lakh successful calls were made to the Citizen.
22.5.1 Introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning (ML) tools: –
A MoU have been signed with IIT, Kanpur for Introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning (ML) tools in the system in partnership with IIT, Kanpur. The Intelligent Grievance Monitoring System (IGMS) has been developed by IIT Kanpur to facilitate tabular analysis of priority, repeat and spam Grievances filed & disposed according to a geographical area. IGMS also helps in root cause analysis of the grievance and provides an intuitive context based semantic search capability. In addition to this Data Strategy Unit (DSU) of DARPG has developed AI/ ML enabled “Tree Dashboard” for exploratory analysis on any given parameter. These technologies have helped the Government for granular analysis of problem areas and leveraged grievances as building blocks for reforms towards Ease of Doing Business and Ease of living for citizens.
22.5.2 Redressal of Public Grievances during Special Campaign and Good Governance Week: –
A special campaign 3.0 was launched on disposal of pending matters including Public Grievances and cleanliness drive was undertaken from $2^{\text {nd }}$ October to $31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2023 in every Ministry / Department of government of India including their attached / subordinate offices and autonomous organizations across the country and abroad. During the Special Campaign total 501296 Grievances and 20662 Appeals were addressed.
22.5.3 Leverage strength of Common Service Centres (CSC)
CPGRAMS has been integrated with Common Service Centres (CSC) from 7th June, 2022 and is available at more than 5 lakh CSCs, associating with 2.5 lakh Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs). This integration has helped the citizens in availing CPGRAMS related services in remote corners of the country. DARPG and CSC e-Governance Services India Limited has been taking various initiatives to create awareness about CPGRAMS among the citizens through the CSCs. There is a constant increase in the number of grievances being filed through the CSCs. In order to further create awareness about CPGRAMS among the citizens, CSC has started observing 20th of every month as CSC – CPGRAMS Grievance Day. DARPG also conducted awareness programs through CSC with the Ministry of Rural Development, Department of Agriculture and Farmers welfare and Department of Financial Services for Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs) focusing on schemes like PMAY, PM-KISAN and on Banking related grievances. In 2024-25, a total of 1,72,312 grievances have been registered through the Common service Centres.
22.3.12 Advertising of CPGRAMS through All India Radio and Doordarshan
From the current Financial Year, DARPG has engaged with Prasar Bharti to have a wider dissemination campaign for CPGRAMS. This would ensure that the commons citizen is well
versed with the CPGRAMS portal and its mandate. DARPG’s promotional video on CPGRAMS has been consistently broadcast on Doordarshan News during prime and morning slots. The same has also been broadcast on 88 Local Radio Stations ( In regional languages), 42 Vivid Bharti Stations across the country and in the National News on All India Radio.
22.3.13 Categorisation of Grievances in CPGRAMS:
Since October 2024, DARPG has started to re-work on the categorisation matrix of Ministries/Departments of Government of India. Till now around 30 Ministries have given their updated categorisation to DARPG. DARPG is in the process of further updating these categories to keep them in line with the priorities of Ministries and to ensure citizen centricity.
Important Events of PG Divisions:
1. CPGRAMS Recognized as Best Practice by the Commonwealth Secretariat
From April 22-24, 2024, an Indian delegation led by the Secretary, Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, attended the Third Biennial Pan-Commonwealth Meeting of Heads of Public Service at Marlborough House, London, where CPGRAMS was recognized in the Outcome Statement as “India’s State-of-the-Art Grievance Redressal System” and a best practice in governance that can be replicated across Commonwealth nations.

2. National Workshop on Effective Redressal of Public Grievances

The National Workshop on Effective Redressal of Public Grievances, organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) was held on $18^{\text {th }}$ November 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi, which brought together over 500 officers from Central Ministries, State Governments, and Administrative Training Institutes. The workshop focused on promoting citizen-centric governance, addressing systemic challenges in grievance redressal, and showcasing innovative practices and technologies. The event also featured the launch of several key initiatives, including the
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023, CPGRAMS Mobile App, and the Monthly Reports for October 2024.
3. Release of CPGRAMS Annual Report, 2024

Hon’ble MoS (PP) Dr Jitendra Singh released the CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024 at the Good Governance Day celebration on $25^{\text {th }}$ December, 2024 as part of the “Sushasan Saptah”.
4. Introduction of Secretary level Review of PG Cases
In PRAGATI meeting held in December 2024, Hon’ble Prime Minister emphasised review of grievances by Secretaries of Central Ministries and State Chief Secretaries at least once in a month for timely and qualitative disposal of grievances In compliance with the direction issued by the Hon’ble Prime Minister a dedicated module in the CPGRAMS Portal has been operationalized by DARPG for the Nodal Grievance Redressal Officers. A D.O letter dated 30th January, 2025 by Cabinet Secretary and an OM dated 14th February, 2025 by Secretary DARPG were also sent to all Ministries/Departments.
DARPG also conducted a 3-hour capacity-building workshop on 5th March and 12th March, 2025, for Nodal Grievance Officers (GROs) of Central Ministries/Departments on the newly operationalized Review Meeting Module in the CPGRAMS Portal. This module enables Secretary-level reviews of public grievances, ensuring effective redressal and maximizing citizen satisfaction.
5. Year-end review of ‘Effective Redressal of Public Grievances 2024’
Hon’ble Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions Dr Jitendra Singh chaired the year-end review meeting on “Effective Redressal of Public Grievances 2024”. The review meeting was attended by more than 350 distinguished participants –

the Nodal Appellate Officers and Nodal Public Grievance Officers from all the Central Ministries/Departments.
6. The National Workshop on Sevottam and Effective Redressal of Public Grievances was organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) and hosted by RCVP Noronha Academy of Administration and Management, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh on 20th February, 2025, with the objective of promoting citizen-centric governance. The workshop served as a critical platform for deliberating on systemic challenges in grievance redressal, strengthening the Sevottam framework, and showcasing transformative practices and technological advancements that can drive greater efficiency and transparency in public service delivery.
7. Signing of MSA with Bhashini:
In pursuance of the directions of the Prime Minister of India to effect qualitative improvements in Grievance Redressal systems to make them more sensitive, accessible and meaningful, DARPG signed a Master Service Agreement with Digital India Bhashini on $28^{\text {th }}$ March, 2025 to implement a multimodal, multilingual e-Governance solution for CPGRAMS.
With the multilingual multimodal solution, it is envisaged that citizens cutting across regions will be able to file grievances on the CPGRAMS portal through 22 regional languages in an intuitive interface that will make grievance lodging much easier. Citizens can use voice in their regional language to lodge grievances. This solution will also enhance ease of accessibility and navigation on CPGRAMS portal. This collaboration of DARPG-Bhashini will create a future roadmap for a more efficient, accessible and responsive governance system for citizens. The integration of Bhashini with CPGRAMS marks a significant milestone in AI-powered, multilingual citizen engagement, ensuring that language barriers no longer hinder grievance redressal and public service accessibility. The solution in expected to go live by July 2025.

22.5.4 Capacity building Programme under SEVOTTAM
DARPG is supporting the capacity building of the grievance officers to enable them handle the public grievances with satisfaction of citizens. State Administrative Training Institutes (ATIs) are partners for providing training to the grievance officers in States under SEVOTTAM scheme. The Scheme was revised in July 2024 with enhanced support to ATIs for Rs 1500/ per person / day for training programmes of GROs. A total of Rs 2.76 crores has been released to 23 ATIs, namely Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Assam, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Tripura, J&K, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Delhi, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Manipur, Odisha and Karnataka in the year 2024-25. DARPG has partnered with the Administrative Staff College of India (ASCI) to conduct a Training Needs Assessment (TNA) of Grievance Officers. This will culminate in the development of a standardized training curriculum and andragogical framework, enabling uniformity in training delivery across States. The Department has also developed an online course in collaboration with ISTM for iGOT Karmyogi platform.
22.6 CITIZENS’/ CLIENTS’ CHARTERS
22.6.1 DARPG monitors effective delivery of services through Citizen Charters. Citizen Charters were required to include (i) standards of service (ii) time limits for public service delivery (iii) avenues for grievance redress. Guidelines for formulating the Charters as well as a list of do’s and don’ts have been communicated to various government departments / Organisations by DARPG to enable them to bring out focused and effective charters.
Chapter 23
ORGANISATION AND METHODS DIVISION
Mandate
- Formulation and simplification of office procedures. Publication and updating of comprehensive Central Secretariat Manual of Office Procedures (CSMOP) for Physical as well as electronic files.
- Aiding and advising the Central Ministries / Departments and States / UT Governments on O&M aspects.
23.1 Increasing Efficiency in Decision making
The initiative for Increasing Efficiency in Decision Making reiterates the Government’s focus on good governance ensuring accountability, efficiency, effectiveness, transparency, and decentralization. The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) is the nodal department for the initiative adopting a four-pronged approach, that is, (i) Delayering by review of levels of disposal and channels of submission to ensure that levels in the channel of submission do not exceed four (ii) Delegation of powers in Ministries/Departments as well as attached/subordinate offices and autonomous/statutory bodies for expeditious decision making (iii) Desk Officer System; and (iv) Digitization of Central Registration Units and adoption of eOffice version 7.0 .
The Central Secretariat Manual of Office Procedure (CSMOP) has been a guiding framework for effective functioning of the Central Secretariat offices. The outcome of this initiative is evaluated, its progress is periodically reviewed and the thrust of this initiative is reiterated to Ministries/Departments from time to time.
A workshop was organized by DARPG under the Chairmanship of Hon’ble MoS(PP) on 23 December, 2024, in which several Ministries presented their good governance practices.
The initiative for Increasing Efficiency in Decision Making has been adopted in almost all Ministries / Departments of the Central Secretariat. This initiative represents one of the most complicated and far-reaching administrative reforms witnessed in the Central Secretariat and it has has transformed work culture, reduced hierarchies and resulted in significant adoption of new technology. It has also enabled responsive communication and enhanced efficiency in processing receipts. Reduction in paper consumption was also witnessed. The advanced analytics dashboard for e-office helps as a tool to validate the extent of digitisation and delayering in the Central Secretariat. E-Office is successfully implemented in all scheduled 75 Ministries/Departments. EOffice is implemented in 92 attached/subordinate offices and autonomous organisations under 100 days agenda of Government. The percentage of e-files have grown to 90.57 as on November 2024 as against $83 %$ in 2021. In 69 Ministries/Departments all Joint Secretaries report directly to Secretary and in 24 Ministries/Departments decision making is within four levels for all subjects. Out of 273 Joint Secretaries, 235 report directly to Secretaries and 39 report through Additional Secretaries. The average distinct level of channel of submission has come down to 4.38 in Nov2024 from 8.01 in 2020. Financial powers are delegated to field units to expedite procurement and
improve the ease of doing business. Desk Officer System is implemented in 40 Ministries/Departments as against 28 Ministries/Departments in 2022.
23.2 Special Campaign 4.0 on Swachhata and Reducing Pendency (2nd October, 2024 to $31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024)
Special Campaigns for institutionalising swachhata and reducing pendency in government enables changing old practices, weeding out old files and papers in Government Offices better utilisation of free space improve sanitisation protocols and above all technology adoption. Special Campaigns have been highly successful in driving cleanliness and reducing pendency in government. The Hon’ble Prime Minister has advised that Swachhata be made a permanent part of the culture of Government for which the Special Campaigns should be conducted annually for the next 5 years. Special Campaign is conducted from $2^{\text {nd }}$ October to $31^{\text {st }}$ October every year since 2021 by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances, Government of India, as the nodal Ministry.
Special Campaign 4.0 was conducted from $2^{\text {nd }}-31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024 in all Central Ministries/Departments and their attached/subordinate offices/PSUs/autonomous organizations. DARPG issued detailed guidelines for conduct of Special campaign 4.0 and as the Nodal Department coordinated the campaign across the Central Ministries and their offices. The Preparatory Phase was from $16^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024 to $30^{\text {th }}$ September 2024, the Implementation phase from $2^{\text {nd }}$ October, 2024 to $31^{\text {st }}$ October, 2024. The evaluation phase is from $14^{\text {th }}-29^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024. The campaign was monitored on real time basis through a dedicated portal https://scdpm.nic.in/specialcampaign4/ and the outcomes are evaluated and documented. The achievement under various parameters is as follows:
| S. No. | Parameter | Achievement |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleanliness Campaigns | $5,97,276$ |
| 2. | Reference from MPs | 3,334 |
| 3. | Parliamentary Assurances | 332 |
| 4. | IMC References | 108 |
| 5. | State Government References | 659 |
| 6. | Public Grievances | $5,41,362$ |
| 7. | Pubic Grievance Appeals | 13,343 |
| 8. | PMO References | 903 |
| 9. | Easing of Rules/Processes | 1,150 |
| 10. | Physical Files Reviewed | $39,28,048$ |
| 11. | No. of Physical Files weeded out | $22,26,675$ |
| 12. | e-Files Reviewed | $5,82,138$ |
| 13. | e-Files closed | $2,92,092$ |
| 14. | Space freed (In lakh sq.ft) | 190 |
| 15. | Revenue earned (In Rs. crore) | 650.10 |
The cumulative progress achieved in the four Special Campaigns from 2021-2024 is as follows:
- No. of offices covered under Swachhata Campaign – 11.50 lakh
- Space Freed -643.82 lakh square feet
- Files Weeded out/ Closed-131.46 lakh files
- Revenue earned from sale of scrap – Rs. 2364 crore
The Campaign was reviewed by Cabinet Ministers, Ministers of State and Secretaries to the Government of India providing leadership and guidance in implementation. It gained significant traction on social media with over one lakh social media posts by Ministries/Departments; 14,251 tweets by all Ministries/Departments with 90.2 million reach, 299 K interactions; 1200 infographics on #SpecialCampaign4 and issue of 256 PIB Statements.
Preservation of historical records as also archiving historical records which are of great importance which was undertaken during the Campaign. Numerous records of historical importance including records pertaining to ‘Organisational Restructuring of Central Secretariat’ in 1938 and 1947 have been preserved and placed on Abhilekh Patal of NAI. An exhibition ‘Sushasan aur Abhilekh’ of preserved Records of historical value was organised by NAI from $2^{\text {nd }}$ October- $31^{\text {st }}$ October.
Several steps were initiated for ease of living during the campaign. Post Offices, Railway Stations, Air Ports, Sea Ports, schools and other public interface offices in Agriculture and Fertilizer sector implemented the Special Campaign 4.0 in a commendable manner.
The Campaign was conducted across the length and breadth of the country from Nubra valley in Ladakh to Nicobar Islands in Andamans & Nicobar Islands and from Kandla in Gujarat to Lepa Rada in Arunachal Pradesh. The saturation approach was also extended to Schools, Road Transport Offices, Krishi Vigyan Kendras, Anganwadi centres and EPFO Offices. All overseas mission and posts. Embassies at Mauritius, Australia, Papua New Guinea, Tunisia, Cambodia, Japan, Saudi Arabia actively participated during the Campaign.
More than 80 best practices emerged as an outcome of the Special Campaign 4.0 from various central government offices in the categories of inclusivity, digitalisation, sustainable environment, environment friendly practices, waste to art, waste to wealth, reclaiming of unused spaces, capacity building of safai mitras, etc. For e.g., waste spaces were converted into recreation rooms, creches, and cafeterias for the employees and waste material was upcycled into beautiful artefacts for enhancing office spaces and effectively utilising scrap produced in offices.
As part of Special Campaign 4.0 DARPG convened the National workshop on eOffice and eOffice advanced Analytics Dashboard on October 29, 2024, at the Civil Services Officers’ Institute (CSOI), Vinay Marg, New Delhi that highlighted the introduced substantial transparency by eOffice Analytics Dashboard within the system.
Hon’ble Prime Minister appreciated Special Campaign 4.0 outcomes in his tweet dated $10^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024
“Commendable!
By focussing on efficient management and proactive action, this effort has attained great results. It shows how collective efforts can lead to sustainable results, promoting both cleanliness and economic prudence.”
The Campaign was mentioned by the Hon’ble Prime Minister in his Mann ki Baat.

To maintain the thrust of the campaign throughout the year, DARPG has issued guidelines for continuation of the campaign for swachhata and reducing pendency to the minimum.
Monthly Report on Secretariat Reforms
DARPG release Monthly Report on Secretariat Reforms every month and circulate it among all Ministries/departments including PMO and Cabinet Secretariat. This report includes Swachhata campaign and reducing pendency practices during the month, Parameter wise performance of Ministries/Departments, Increasing Efficiency in Decision Making, e-Office analytics and implementation.
CHAPTER 24
e-GOVERNANCE
24.1 27th National Conference on e-Governance
The 27th National Conference on e-Governance (NCeG), held at the Jio World Convention Centre in Mumbai on the 3rd and 4th of September 2024, has successfully underscored the theme of “Viksit Bharat: Secure and Sustainable e-Service Delivery.” Organized by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) in association with the Ministry of Electronics \& Information Technology (MeitY) and the Government of Maharashtra, the conference brought together government officials, scholars, industry leaders, and innovators to explore new frontiers in e-Governance.
The Conference was inaugurated by the Hon’ble Chief Minister of Maharashtra, Shri Eknath Shindes and presided over by Shri Devendra Fadnavis, Hon’ble Deputy Chief Minister, Government of Maharashtra, alongside Shri Deepak Kesarkar, Hon’ble Minister of School Education and Marathi Language, Government of Maharashtra. Hon’ble Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh, Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science and Technology and Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Earth Sciences, Minister of State in Prime Minister’s Office, Minister of State in Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, Minister of State in the Department of Atomic Energy and Minister of State in the Department of Space delivered a keynote address via video message during the valedictory session
A highlight of the two-day conference was the presentation of the prestigious National Awards for e-Governance (NAeG) 2024 by Deputy Chief Minister Shri Devendra Fadnavis. These awards recognized 16 trailblazing initiatives in e-Governance, which were divided into five categories. The awards aimed to spotlight innovative solutions at the Central, State, District and Research levels, which contribute to streamlining government services and enhancing citizensentric service delivery.

Lighting of Lamp by Shri Eknath Shinde, Honorable Ex-Chief Minister Government of Maharashtra
The Conference was attended by over 1500 delegates which included delegates from Government of India, State/UT Governments, Industry, Academia and Private Sector.
An Exhibition including Wall of Fame showcasing the awarded and other best practices of the country was also organized during the Conference.

Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’bleMoS(PP) delivering Keynote Address
The conference also saw the release of several important publications. The DARPG launched four books, namely the Citation Booklet of NAeG 2024 Awardees, Excellence Booklet, Background Papers of the 27th NCeG, and a Compendium Booklet of Selected Papers.
Additionally, the Government of Maharashtra released an e-Booklet by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), underscoring the state’s commitment to digital excellence.
The 27th NCeG represented a platform for constructive exchange of ideas on some of the latest technologies for promoting e-Governance. 56 Distinguished speakers shared their knowledge and insights in 06 plenary sessions and 06 breakout sessions on the following contemporary subjects/issues:
Plenary Sessions:
- Digital Platforms and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Viksit Bharat
- Shaping Service Delivery for Tomorrow
- Data Governance: Privacy and Security in the Digital Age
- Use of AI in Governance
- Creating Sustainability with E-Governance
- Cybersecurity and Emergency Response Readiness
Breakout Sessions:
- Excellence in E-Governance Initiatives by Gold Awardees of NAeG 2024
- Emerging and Future e-Governance Initiatives/ e- Commerce Initiative/ Emerging Technologies
- Excellence in E-Governance Initiatives by Silver Awardees of NAeG 2024
- District Level Initiatives in E-Governance
- Project by Maharashtra State Government
- Innovation and Future Trends in RTS
The roadmap for e-Governance of the country for the next year was drawn up during the Conference. The key takeaways from the 27th NCeG are – Closer synergy amongst researchers, academia, industry and start-ups in the field of e-Governance is the way forward for India; The policy maxim of Maximum Governance-Minimum Government is best reflected in a Digitally Empowered Nation – Digitally Empowered Citizen – Digitally Transformed Institution; Citizen Centricity as an important area of focus and Digital Transformation of Institutions.
24.2 National Awards for e-Governance
To recognise the implementation of e-Governance initiatives, the National Awards for eGovernance 2024 were presented during the Inaugural Session of the Conference. Total 16 awards, which included 9 Gold, 6 Silver and 1 Jury Award were presented to Central Ministries/Departments, State/UT Governments, Districts, Local Bodies, Public Sector Undertakings and Academic & Research Institutions, under the following 5 categories/subcategories of the National Awards for e- Governance Scheme – 2024:
Category I- Government Process Re-engineering for Digital Transformation
(i) Central level initiatives; (ii) State/UT level initiatives
Category II – Application of Emerging Technologies for providing Citizen Centric Services
(i) Central level initiatives; (ii) State/UT level initiatives. (iii) Startups
Category III- District level initiative in e-Governance
Category IV- Research on Citizen Centric Services by Academic/Research Institutions
Category V – Replication of Top Technological Solutions/Initiatives and Scalling up
(i) State/UT level initiatives (ii) District level initiatives
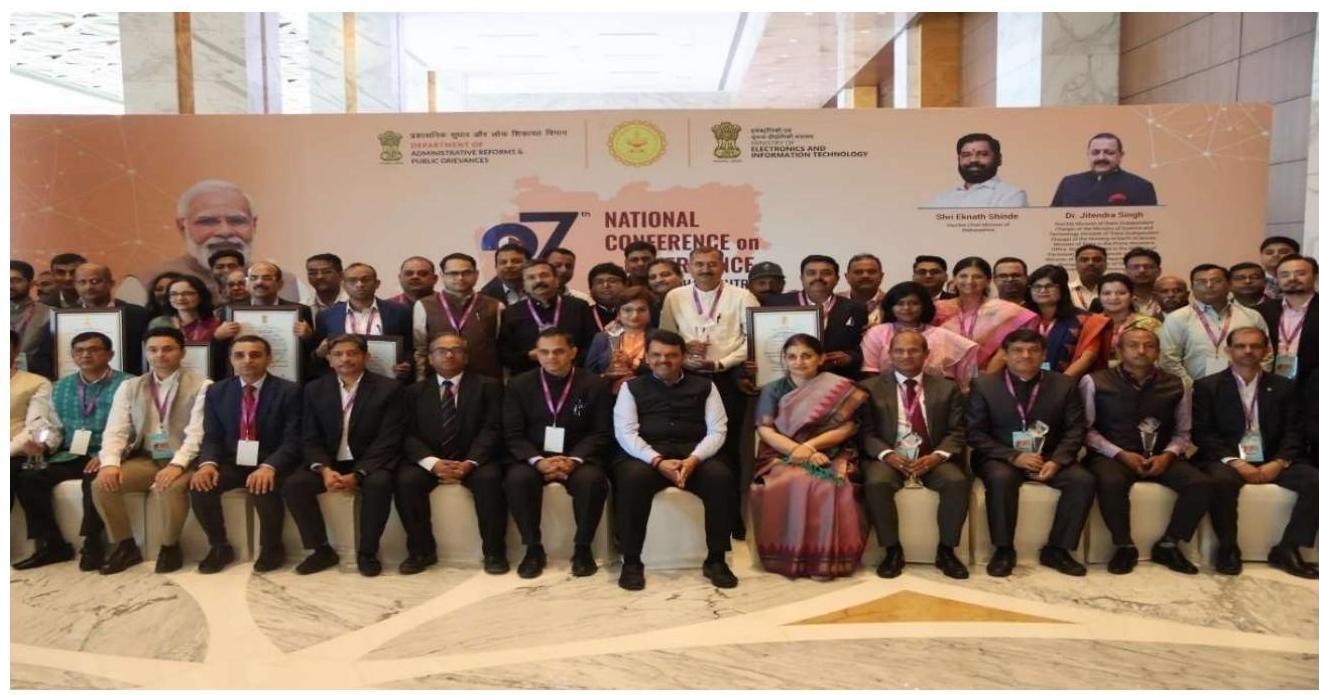

The Project Heads of the Awarded Projects with Shri Devendra Fadnavis and other dignitaries
Promoting Reforms through e-Governance
24.3 National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA)
The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) had formulated the National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) framework in 2019 as part of its mandate to boost the e-government endeavours and drive digital government excellence. This was based on the Online Service Index (OSI) of UNDESA e-Government Survey, customized for the Indian federal structure and the e-Governance landscape of the States/UTs. The study assesses States, Union Territories (UTs) and focus Central Ministries on the effectiveness of e-Governance service delivery. NeSDA helps the respective governments to improve their delivery of citizen centric services and shares best practices across the country for all States, UTs and Central Ministries to emulate.
DARPG conducts NeSDA study biennially. While the first of its kind benchmark exercise was conducted by DARPG in the year 2019, the Department successfully released 2 editions of NeSDA study report, viz., NeSDA 2019 and NeSDA 2021. The NeSDA 2023 report has been prepared and submitted.
24.4 National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) Way Forward Monthly Reports
NeSDA Way Forward has been developed for regular monitoring of the implementation of recommendations given in the NeSDA 2021 report. A dashboard namely “NeSDA- Way Forward, Status of Implementation” has also been designed in line with the focus areas of e-Governance. On the basis of inputs uploaded on the above portal by respective States/UTs, the monthly reports
are released by the Department. These reports institutionalize the nation’s endeavour for improved delivery of e-services and prepare States/UTs for subsequent NeSDA studies.
So far, 20 NeSDA Way Forward Monthly Reports and Annual Report 2023 have been published to monitor the status of e-service delivery, across States/UTs. The NeSDA Way Forward project by DARPG has achieved significant progress in expanding e-services across India. The number of services offered has risen by $71 %$ to a total of 19,834 since inception of the NeSDA Way Forward initiative in 2023, with Karnataka and Jammu & Kashmir leading the way. Local Governance and Utility Services account for the largest share $(6,535)$ of these offerings. When it comes to mandatory services, the States/UTs have achieved an impressive $78 \%$ saturation rate, with 1,584 out of 2,016 services now available online. Ten states – Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Gujarat and Karnataka – have even reached $100 \%$ saturation for these mandatory services. This is a significant improvement from just a few years ago, with saturation rising from $48 \%$ in 2019 to $78 \%$ in January, 2024.
In line with the objective of NeSDA Way Forward to the enhance the e-service delivery experience nationwide, DARPG has embarked on a collaborative initiative with the Chief Commissioners and Appellate Officers of the Right to Service (RTS) Act across various States/UTs. The department held a virtual meeting on 15.01 .2025 to align ongoing efforts with the objectives of the NeSDA Way Forward initiative.
24.5 National e-Governance Webinar (NeGW) Series
The Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances (DARPG) launched the National e-Governance Webinars in 2023. This monthly series provides a distinguished platform for public administrators to share their award-winning initiatives recognized by the prestigious National Award for Excellence in e-Governance (NAeG), their experiences and implementation challenges. Through knowledge exchange and best practice dissemination, NeGW aims to inspire replication of successful projects, driving advancements in egovernance across the nation.
The National e-Governance Webinars held during the year focused on the following themes:
- Outstanding Research on Citizen Centric Services by Academic/ Research Institution
- Excellence in Providing Citizen Centric Delivery at State/UT Level
- Special Webinar on Citizen Centric Services provided by Panchayati Raj Institutions under National e-Governance Webinar
- Special Webinar on Building Efficient State Portals for Enhanced Citizen Engagement DARPG has successfully convened four NeGW webinars. The webinars have been well received with participation of over 1000 participants from across the country which includes state functionaries, academia, Panchayati Raj Institutions, start-ups and have served as catalysts for innovation and collaboration, fostering engagement among administrators and stakeholders invested in the implementation of diverse initiatives.
CHAPTER 25
INTERNATIONAL EXCHANGE AND COOPERATION
25.1 The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) deals with matters relating to international exchange and cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance, which includes, among other things, organizing programmes and visits of Indian delegations to foreign countries and visits of foreign delegations to India as part of projects / bilateral measures in furtherance of activities included in the Memorandum of Understandings (MOUs) / Agreements signed between India and other countries (bilateral or multilateral).
25.2 The aim of international exchange and cooperation component is to share information, best practices and personnel across national governments. Presently bilateral MoUs in the areas of Public Administration and Governance have been signed with Portugal, United Kingdom, Singapore, Australia, The Gambia, France, Cambodia and Malaysia.
The following activities were held during the year 2024-25:
25.3 India – Singapore Cooperation
- The MoU for cooperation in the field of ‘Personnel Management and Public Administration’ was signed by the Department with the Public Service Division (PSD) of the Republic of Singapore on 1st June, 2018 under the (i) Workforce, Workplace and Jobs; Public Service Delivery; Human Resource Management; Public Sector Reform; Leadership/Talent Development; and E-Governance / Digital Government.
- The first bilateral meeting under the aegis of the MoU was held on 6th July, 2021. The Second bilateral meeting on “Personnel Management and Public Administration” was held on 29th September, 2022 in New Delhi. The bilateral meeting was led by Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG from Indian side and Mr. Loh Khum Yean, Permanent Secretary, PSD, Singapore from Singapore side.
- Mr. Loh Khum Yean, Permanent Secretary, PSD also addressed inaugural session of National Good Governance webinar jointly with Secretary (DARPG) on the theme ‘Public Service Delivery held on 30th September, 2022 which was attended by more than 850 participants from all over India.
- MoU between India and Singapore in the field of Personnel Management and Public Administration was signed on 6th July, 2023 in New Delhi. The MoU was signed by Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary DARPG on behalf of DARPG and Mr.Simon Wong, High Commissioner of Republic of Singapore to India on behalf of PSD Singapore. The MoU was extended for a period of five years from 1st June 2023 to 31st May 2028.
- A bilateral introductory meeting between Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG and Ms. Tan Gee Keow, Permanent Secretary, PSD, Singapore was successfully held on 30th January, 2024 through video conferencing. During the VC India and Singapore committed themselves to strengthen cooperation in the field of Personnel Management and Public Administration.
- India Singapore Joint Working Group meeting was held on 10.09.2024. Secretary DARPG, Gol, Shri V. Srinivas and Permanent Secretary, Public Service Division (PSD) Singapore Ms Tan Gee Keow formulated the contours of the future India-Singapore co- operation in the field of Administrative Reforms and technology induction. Both sides shared the developments and practices in good governance and administrative reforms and a presentation on best practice covering CPGRAMS, NESDA, PM Awards, NCGG, Bhavishya and e-Office was made. The Singapore side shared Life SG, Service SG, Wellness Ambassadors and work of Civil Services College.
25.4 India – Australia Cooperation
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms was signed by the Department with the Australian Public Service Commission (APSC) during Indo-Australia Virtual Summit held on 4th June, 2020 between the Prime Ministers of both the sides under that areas of Promoting transparency and accountability in delivery of public services; Building effective service delivery in the public service ; Recruitment and promotion in the public service; Developing a framework for values and competencies; Training and capacity building of the public service; Public Sector Management and Reform; Public Grievance Redress Mechanism; Facilitating short-term foreign training programmes for officers of Government of India or Australia; and Promoting and utilizing potential of retired government servants.
- 2nd Joint Working Group meeting between DARPG and Australian Public Service Commission, under the aegis of the MoU signed between the two countries on “Cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms” was held on 18.11.204 thereby identifying the following areas for collaboration by both the countries to continue the dialogue on digital service delivery and explore potential areas of collaboration; to finalize the details of the joint session on digital service delivery, including the specific topic and format, the Australian delegation expressed interest in learning more about India’s public administration reforms and digital initiatives.
25.5 India – Gambia Cooperation
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Department and the Public Service Commission, Office of the President, The Gambia was signed on 08th July, 2021 on ‘Refurbishing Personnel Administration and Governance Reforms’. The First meeting of India-Gambia Joint Working Group (JWG), formed under the MoU, was held virtually between the Department of
Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances and the Public Service Commission (PSC) of The Gambia on 22nd November, 2021.
- The India-Gambia 2nd Joint Working Group meeting to Implement the bilateral MOU was held under chairmanship of Secretary DARPG V. Srinivas and Chairman Public Service Commission of Gambia Mr. Lamin Samateh by video conference on 21.08.2023. Mr. Lamin expressed the possibility to extend it for 5 years and welcomed the extension of MoU for further 5 years beyond 2024. The 3rd Joint Working Group meeting between DARPGand Public Service Commission of The Republic of The Gambia was held on 09.11.2023 through VC. Both sides agreed tocontemplate the extension of MoU for five (05) years beyond 7th July, 2024 and take forward the cooperation in the identified areas.
- The MoU on ‘Refurbishing Personnel Administration and Governance Reforms’ between the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances and Public Service Commission, Office of the President, The Republic of Gambia has been extended for a further period of five (05) years upto 2029.
25.6 India France Cooperation
The Department of Administrative Reforms, Public Grievances and Pensions, Government of India and Mio Public Sector Transformation \& the Civil Service of the French Republic signed the Letter of Intent on 02nd November, 2023 for Cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Administrative Reforms for three years. The Letter of Intent was signed by Shri V Srinivas, Secretary, on behalf of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances and H.E. Mr. Thierry Mathou. Ambassador of France to India at a ceremonial function in New Delhi on behalf of the Ministry of Public Sector Transformation and the Civil Service of French Republic under areas of co-operation in the field of Civil Service, Human Resource Management, Public Administration and Administrative Reforms.
25.7 India-Portugal Cooperation
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between DARPG and the Ministry of the Presidency and of Administrative Modernization of the Portuguese Republic was signed on 24th June, 2017 on Co-operation in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms. The First Meeting of Senior Consultative Body was held in Lisbon, Portugal on 8-9 May, 2018.
- The Second meeting of the Senior Consultative Body between the DARPG and the Administrative Modernization Agency of Portugal co-chaired by Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG and Ms. Silvia Esteves, Head of International Relations, AMA, was held on 12th December, 2023 through VC. From the Indian side, Shri V. Srinivas Secretary DARPG, and Shri Puneet Yadav Joint Secretary DARPG presented the New Paradigms in Governance in India from 2019-2024 From the Portuguese side, Ms. Silvia Esteves. Head of International Relations at AMA,
and Ms. Carina Americo Head of AMA Academy presented the http://ePortugal.gov and AMA academic programs in digital transformation.
25.8 India Malaysia Cooperation
- MoU between Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, Govt. of India and Public Service Department, Prime Minister’s Department, Government of Malaysia has been signed on Cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms’ for a period of five (05) years on 20 August, 2024 during the visit of Prime Minister of Malaysia to India.
- A Joint Working Group Meeting between DARPG and Public Service Department, Malaysia under the aegis of the MoU signed between the two countries on “Cooperation in the field of Public Administration and Governance Reforms” was held on 13.11.2024 in which the following collaborations were identified:
- A Joint Working Group to be constituted for formulating training of the Malaysian Civil Servants in National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG). The Joint Working Group will include DG NCGG, DDG PSD Malaysia, Sr. officials from DARPG and MEA;
- A joint webinar would be organized for sharing of best practices by both the Governments which may include areas like right sizing of Government, Public Services Act’ performance based rewards etc.
25.9 India-Maldives Cooperation
A protocol document for extension of the MoU between National Center for Good Governance (NCGG), DARPG and Maldives Civil Service Commission, Republic of Maldives was signed on $9^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024 during the Hon’ble External Affairs Minister’s recent visit to Male, Maldives. The MoU was signed on Training and Capacity Building Program.
25.10 India-Cambodia Cooperation
DARPG signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Ministry of Civil Service, Cambodia on cooperation in the field of Human Resource Development in Civil Service on $22^{\text {nd }}$ April 2024 in a ceremonial function held in Phnom Penh. The MoU was signed by Excellency Mr. Hun Many, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Civil Service, on behalf of the Kingdom of Cambodia and Dr. Devyani Khobragade, Ambassador of India to the Kingdom of Cambodia on behalf of Government of India. Secretary, DARPG and two other officers of DARPG attended the ceremony virtually from High Commission of India in London. 158 Civil servants have been trained by NCGG till December, 2024
25.11 India-Bangladesh Cooperation
A four-member delegation of NCGG headed by Secretary, DARPG visited Bangladesh from 2830 April 2024. Both sides agreed on renewal of the MoU which envisages capacity building programs for 1500 officers from 2025-2030. Secretary, DARPG held bilateral meetings with Senior Secretary of Ministry of Public Administration and the Rectors of the Bangladesh Civil Service Administration Academy and the Bangladesh Public Administration Training Centre. Secretary, DARPG addressed the Officers of $131^{\text {st }}, 132^{\text {nd }}, 133^{\text {rd }}$ and $134^{\text {th }}$ Law & Administration courses at the Bangladesh Civil Service Administration Academy during the 3-day visit.
25.12 India-Sri Lanka Cooperation
A 05-member Indian delegation of National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) to Sri Lanka led by Mr. V. Srinivas, IAS, Secretary to Government of India, Department of Administrative Reforms \& Public Grievances, Department of Pensions \& Pensioner’s Welfare, and Director General, National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) on invitation of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka visited Sri Lanka from 07- 09 July, 2024. During the visit it was decided to sign the MoU. The MoU between the National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG), India and the Sri Lanka Institute of Development Administration (SLIDA) on Training and Capacity Development Programme for Civil Servants of Sri Lanka was signed on $10^{\text {th }}$ December, 2024. The MoU was exchanged on 16 December, 2024 during the State visit of H.E. Anura Kumara Disanayaka, President of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka to India from 15-17 December, 2024.
25.13 Common wealth
A three-member delegation led by Secretary, DARPG attended the 3rd Biennial PanCommonwealth Heads of Public Service Meeting held from 22-24 April 2024 at Marlborough House, London. Secretary, DARPG addressed the $3^{\text {rd }}$ meeting of the Commonwealth Heads of Public Service/Secretaries to Cabinet on India’s Grievance Redressal System “CPGRAMS”recognized as a state-of-the-art initiative for effective grievance redressal by the Commonwealth Secretariat on $23^{\text {rd }}$ April, 2024. India’s public grievance redressal system was praised at key commonwealth meet in London. Secretary, DARPG held bilateral meetings with delegates of various countries like Kenya, Bangladesh, Maldives, Namibia.
25.14 Cooperation with International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS)
DARPG is an institutional member of IIAS since 1998. International Institute of Administrative Sciences (IIAS) is the leading non-profit scientific international organization at the global level in the field of public administration. IIAS, with its headquarters at Brussels, Belgium, was established in 1930 for the purpose of promoting the development of Administrative Sciences, better organization and operation of public administrative agencies, improvement of administrative matters and techniques and for the progress of International Administration. DARPG filed the nomination for the President, IIAS (International Institute of Administrative Sciences), headquarter at Brussels, Belgium for the upcoming election of IIAS Council of Administration. India will be in leading position to align the Indian academic institutions to the world’s top international Universities if secured the president ship.
25.15 IIAS Extraordinary General Assembly meeting 2024
A two-member delegation, attended Extraordinary General Assembly meeting of IIAS Council of Administration, held at Brussels, Belgium on 17th December, 2024. The nomination of Secretary DARPG to the post of president in IIAS was discussed in the meeting. Meetings were also held with CoA members and officers of High Commission of India in Brussels.
25.16 IIAS-DARPG India Conference
DARPG in association with the International Institute of Administrative Sciences organized the IIAS-DARPG India Conference, 2025 at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi from 10-14th February, 2025 .
Established in 1930, IIAS is a non-profit international association headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. It is a federation of member states, national sections and academic research centers, in which, at present, 98 countries are associated. IIAS inter alia promotes worldwide development of administrative sciences, better organization and operation of public administrative agencies and improvement of administrative methods and techniques. It connects governments, administrative bodies, international organizations, educational institutions, and experts to achieve its goals.
DARPG is an institutional member of the IIAS since 1998. Secretary, DARPG is a member in the CoA of IIAS from India. India intends to benefit from IIAS’s global knowledge resource in administrative sciences by on-boarding more and more Indian institutes and universities to the IIAS platform. India is contesting for Presidency in the Council of Administration (CoA) for the IIAS as IIAS will enable India to present its viewpoint on governance in many countries of Europe and Africa.
The International Institute of Administrative Sciences IIAS-DARPG India Conference 2025 was successfully held from 10th to 14th February 2025 in New Delhi. The five-day event comprising 66 breakout sessions and 7 plenary sessions witnessed the participation of over 750 delegates from 58 countries, including policymakers, academics, and practitioners, who engaged in discussions on transformative governance models and inclusive public administration.

A 710-page volume edited by distinguished authors and experts titled “Viksit Bharat@2047: Governance Transformed” was launched. The book delves into India’s governance evolution and outlines a strategic road map to achieve developed nation status by 2047

25.17 Common Wealth Secretary General Meeting
During the $3^{\text {rd }}$ Pan Biennial Conference held in London, a Bilateral Meeting with the Secretary General Commonwealth was held. India discussed its support for the Commonwealth AI Consortium and replication of technology advancement in governance in Commonwealth Member Countries and the Convening of the $4^{\text {th }}$ Annual Meeting of the Commonwealth Heads of Public Service/Secretaries to Cabinet in New Delhi in 2026.

A meeting between Secretary, DARPG and Common Wealth Secretary General-Elect, Ms. Shirley Botchway was held on 21/03/2025 in Jawaharlal Nehru Bhavan, New Delhi. Senior officers from Ministry of External Affairs and DARPG also attended the meeting. During the visit of Ms. Shirley Botchway DARPG presented the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS), the initiatives for improving public service delivery and the digitaization of Secretariat through e-Office.
CHAPTER- 26
DOCUMENTATION AND DISSEMINATION DIVISION
26.1 The Documentation and Dissemination Division of the Department primarily carries out the activities of documentation and dissemination of good governance practices of Central and State Governments and Union Territory Administration with a view to facilitate sharing of experience with one another and replication elsewhere.
1. REGIONAL CONFERENCES:
During the year, the department has organised two Regional Conference in collaboration with Government of Assam and Chhattisgarh.
(i) Regional Conference at Guwahati: – The 26th Regional Conference on e-Governance, held in Guwahati, Assam, on January 9th and 10th, 2024. The large-scale participation for award winning initiatives served as a vital forum for in-depth discourse over five dedicated sessions. The primary objective of the conference was to facilitate convergence between national and state level public administration bodies. This facilitated the cross-pollination of experiences in pioneering public administration practices. The theme encompassed the transformation of future public solutions with a focus on enhancing quality of life, promoting good governance, and accelerating e-governance and digital governance initiatives. The distinguished presence of His Excellency Shri Gulab Chand Kataria, Hon’ble Governor of Assam, and Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble Minister for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, resonated with the conference’s theme of fostering progress in the Northeast through digital transformation.

Regional Conference at Guwahati held on January 9 ${ }^{\text {th }}-10^{\text {th }}, 2024$
During the conference, Department’s biannual e-journal on Minimum GovernmentMaximum Governance showcasing the shortlisted initiatives for National e-Governance awards.

Regional Conference at Guwahati held on January $9^{\text {th }}-10^{\text {th }}, 2024$
(ii) Regional Conference at Raipur: the $27^{\text {th }}$ Regional Conference on Good Governance was organised at Raipur on November $21^{\text {st }}$ and $22^{\text {nd }}, 2024$. The conference at Raipur demonstrated the government’s relentless focus on transforming governance into an efficient, transparent, and people-oriented mechanism. By leveraging technology, fostering state collaboration, and modernizing administrative frameworks, the Centre continues to drive initiatives aimed at building a more equitable and prosperous India.
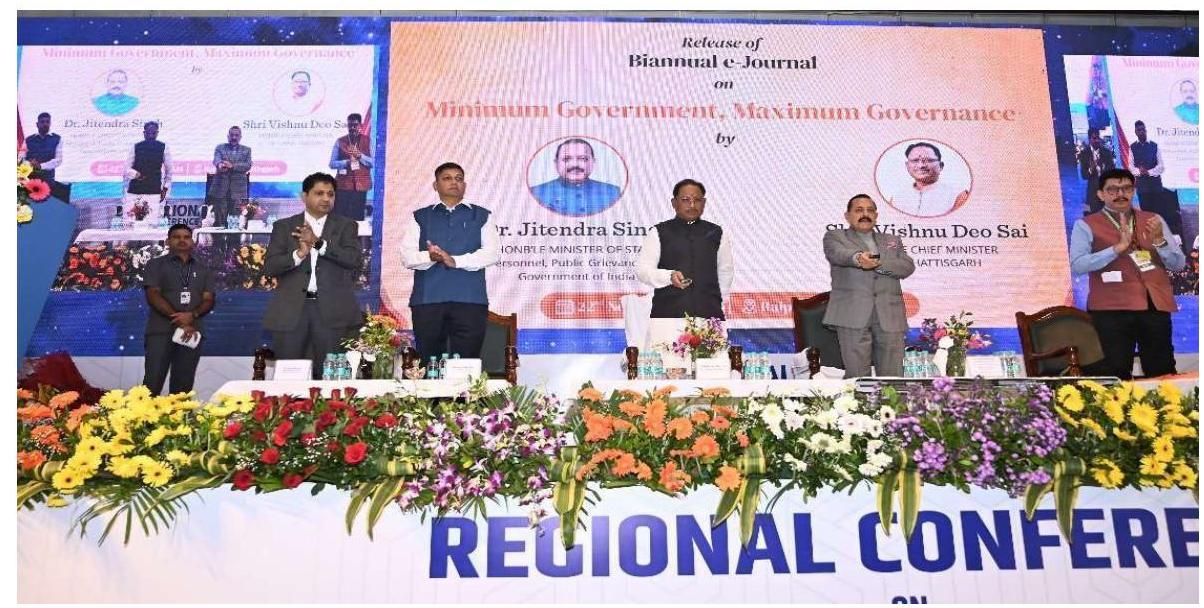

- Publication of e-Journal (MGMG): The DARPG also published a biannual e- journal titled “Minimum Government Maximum Governance.” The journal featured shortlisted selected achievement stories related to the National e-Governance Awards. A special edition of MGMG was published, highlighting the shortlisted initiatives for the National e-Governance Awards.

- Films on Special Campaign 4.0: – Three films on the Special Campaign 4.0 were produced and screened multiple times on DD News and Sansad TV. Additionally, several panel discussions on Special Campaign 4.0 were organized on DD News and Sansad TV to showcase innovative projects related to waste management. Also, 16 films were developed for National Conference on e-Governance held in Mumbai on 3-4 September 2024. The Department has also developed one film for Good Governance Week observed 19-25 December 2024.
Chapter – 27
Official Language Division
27.01 Implementation of the Official Language Policy of the Union
Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is committed to the effective implementation of the Official Language Policy of the Union, and due to these efforts, the use of Official Language in the Department, is increasing successively. The summary of the efforts and the achievements of the year 2024-25, are given below:
27.02 Rajbhasha Kirti Puraskar
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances was awarded Rajbhasha Kirti Puraskar (First Prize) for the best performance in Official Language Hindi, in the category of Ministries / Departments with less than 300 personnel, by the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs for the year 2024-25.
This award was given to the Secretary, Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, Mr. V. Srinivas, by the Hon’ble Home Minister and Cooperation Minister, Shri Amit Shah Ji on Hindi Diwas Celebrations and All India Official Language Conference, organized on $14^{\text {th }}$ September, 2024, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, by the Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home Affairs.
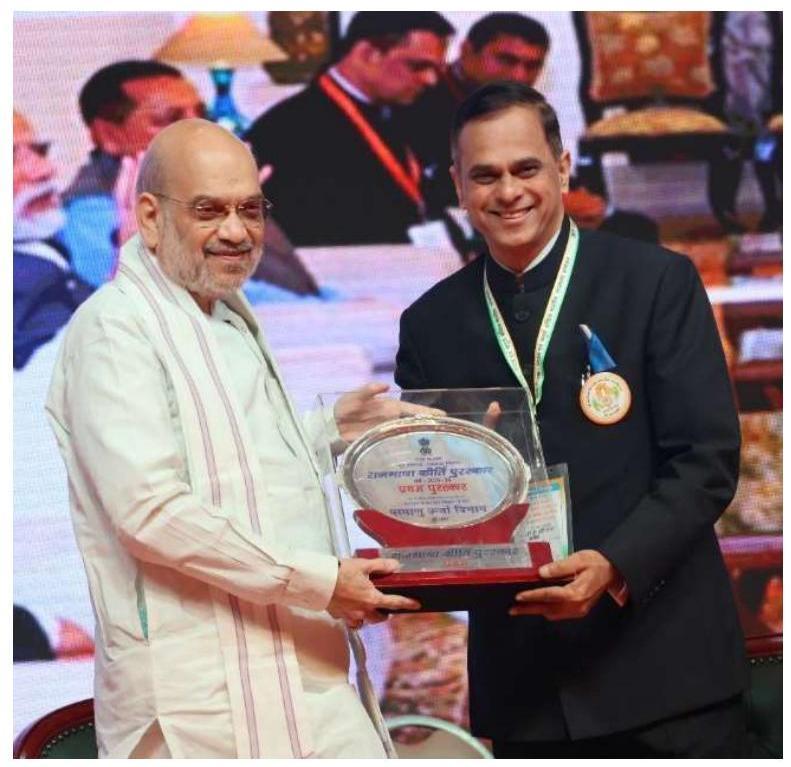

27.03 Implementation of the Official Language Policy
The Official Language Division of the Department is headed by Joint Secretary (Admn.). The Official Language Division has sanctioned posts of one Dy. Director, one Assistant Director, one Sr. Translation Officer, one Jr. Translation Officer, one steno and one DEO.
The Division duly monitors the implementation of the Official Language Policy of the union in the Department and its Autonomous office.
The Division is discharging its responsibility of translation of diverse material received from various Sections of the Department, from English to Hindi such as General Orders, Rules, Standard Forms, Notifications, Resolutions, Cabinet Notes, D.O. letters to be issued by and senior officers, Administrative and other Reports and Press Releases etc, referred to in section 3(3) of the Official Language Act, 1963, in addition to Parliamentary and Budgetary matters.
27.04 HINDI SALAHAKAR SAMITI
DARPG, DOPT and DOP&PW have a joint Hindi Salahkar Samiti. Hon’ble Minister of State for Personnel, is its chairperson. It has 15 non-official members, (4 nominated members (MPs), from M/o Parliamentary Affairs, two (MPs), from Parliamentary Committee on Official Language, 3 Hindi scholars form Department of Official Language, one representative from Kendriya Sachivalya Hindi Parishad, One representative from the Hindi Institute, involved in propagation of Hindi and 4 members are nominated by the Ministry). Besides, Heads of all attached offices of the ministry, and JS and above Level officers of the ministry are official members of the Samiti. The tenure of the Samiti is expired and it is being reconstituted.
27.05 Official Language Implementation Committee
In the Department, Official Language Implementation Committee has been Constituted under the chairmanship of Secretary, DARPG. Head of the autonomous office of DARPG and officers of the level of Under Secretary and above of the DARPG, are its members. The meetings of the committee were successfully 212 rganized in every quarter in the Department as mandated. Implementation of the Official Language Policy of the union was duly reviewed in the meeting with respect to the Department and its Autonomous office and various measures were considered to increase the progressive use of Hindi.
27.06 Quarterly Progress Report (QPR) and Annual Assessment Report
A Quarterly Progress Report is compiled after collecting the data from various sections to assess the work done by the personnel in Hindi in their official work and sent to the Department of Official Language on regular basis. Likewise, an Annual Assesment Report relating to the progressive use of Hindi is also sent to the Department of Official Language, which is further forwarded to the Parliament by the Department of Official Language.
27.07 Organisation of Hindi Pakhwada (Fortnight)
On the occasion of Hindi Diwas on $14^{\text {th }}$ September, like every year, Hindi fortnight was 212 rganized in the department from 14 September to 28 September, 2024 and 06 competitions were held in which approximately 150 personnel participated enthusiastically. A Hindi incentive scheme is also in vogue in the Department. The officers who did their official work maximum in Hindi were also 212 rganized212. Awards to Successful participants, were given by Secretary, in the prize distribution ceremony, 212 rganized on $09^{\text {th }}$ November, 2024 at CSOI Vinay Marg, New Delhi. This year the participants who couldn’t get the award, were given mementos.
27.08 Hindi Workshops
Four (4) Hindi Workshops under the Chairpersonship of Joint Secretary (Admin.) were organized during the year to promote the use of official language Hindi among the personnel, in doing their official work.
27.09 Major Initiatives of Official Language Division
- DARPG’s E-Office has been integrated with the Kanthastha software of the Official Language Department.
- The information on Facebook/Twitter is being issued in bilingual form.
- Translation of voluminous document of Abhinav Portal.
- Translation of voluminous work of Viksit Bharat- Bringing Citizens and Government Closer- through Administrative Reforms (Volume I & II) and Minimum Government Maximum Governance “Shining Gems of e-Governance”.
- A separate page on Rajbhasha has been created on Department’s website where Hindi version of all the documents is uploaded.
- A notice board has been installed in STC building where an English word and its Hindi equivalent is written daily.
- Monthly Summary, PIB statements, NESDA Reports, CPGRAMS Report, Secretariat Reforms Report, M.O.U. to be signed by India between different Countries, PM Awards relating documents are issued in bilingual form.
CHAPTER 28
DEPARTMENT OF PENSION AND PENSIONERS’ WELFARE
Major Highlights
Strengthening Pensioners’ Grievance Redressal Machinery (CPENGRAMS)
In F.Y. 2024-25, the total receipts of the pension grievances is $1,17,812$ with the redressal of $1,14,371$, registering increase of $30 %$ and $31 \%$ in the receipts and redressal respectively, as compared to F.Y. 2023-24.
The redressal rate has kept momentum with the receipts of the grievances owing to the breaking of silos, achieved through active monitoring and coordination with the stakeholders viz. Ministries/Departments and their Pay and Accounts Offices (PAOs), CPAO and Banks.
Out of 1,14,371 redressal, feedback has been received in 60,215 cases through Feedback Centre of DARPG and availing of facility of grading of redressal, available on CPENGRAMS Portal. To comply with the directions of Hon’ble Prime Minister for sensitive, accessible, and meaningful redressal of grievances, DoPPW issued comprehensive guidelines on 16.10.2024 with emphasis on quality redressal of pensioners’ grievances within 21 days under ‘whole of the Government approach’.
It was ensured that the guidelines are properly followed, thereby resulting in increased satisfaction among pensioners which is evident from the analysis of the feedback of 60,215 redressed cases in F.Y. 2024-25. The percentage of the cases, graded as ‘Excellent’ has increased from $25 \%$ to $33 \%$ while the percentage of cases, graded as ‘Poor’, decreased from $42 \%$ to $35 \%$. This improvement is crucial as the number of receipts of grievances has increased by $30 \%$ as compared to previous F.Y. Re-registration is being done by Feedback Unit after analysis of cases, graded as ‘Poor’, in deserving cases.
Over the last 04 years, steep increase in the defence pensioners’ grievances has been witnessed and around 85,000 defence pensioners’ grievances were filed in F.Y. 2024-25, accounting for $72 \%$ of the total grievances received on the portal.
Accordingly, level of interaction with Ministry of Defence was elevated and meetings with Secretary (Defence), Secretary (ESW) and Controller General of Defence Accounts (CGDA) were conducted on regular intervals, apart from monthly InterMinisterial Review Meetings (IMRMs).
These concerted efforts have contributed towards the motto of DoPPW- ‘Pensioners First’ duly supported by the examination of feedback of 41,784 defence pensioners/family pensioners redressed in F.Y. 2024-25. The $33 \%$ complainants have graded their response as ‘Excellent’ as compared to $25 \%$ in last F.Y. Also, corresponding decline in ‘Poor’ feedback from $42 \%$ to $35 \%$ has been noticed.
As a part of above, a month-long Special Campaign, to redress Family Pension grievances, was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MoS (PP) on 1st July, 2024.
A total of 1891 family pension related grievances, pertaining to 46 Ministries/ Departments/Organizations were selected. The campaign was widely publicized through
various means such as Akashwani/AIR talk, PIB statements, tweets highlighting 50 Success Stories under #SpecialCampaignFamilyPension.
The Campaign achieved the success rate of $94 %$ with the redressal of 1769 Family Pension cases, out of the total 1891 family pension cases.
DoPPW, as a part of National Good Governance Week, 2024, organized a National Workshop on Effective Redressal of Pension Grievances on 19.12.2024 in New Delhi. Various initiatives undertaken by CPENGRAMS to make Grievance Redressal Mechanism more sensitive, accessible and meaningful were discussed.
Anubhav Awards
The Scheme is the watershed moment in the history of Anubhav Portal with many firstsTo ensure maximum and widespread participation in the scheme, an outreach campaign was conducted by DOPPW from 23.01.2025 to 31.03.2025.
In this series, various initiatives, including conducting of a workshop for the Anubhav Nodal Officers of Ministries/Departments including 12 PSBs and CPSEs on 23.01.2025, operationalization of dedicated cell, release of informative video, sending of e-mails and SMSs to eligible retired officers/officials and regular meeting with the Anubhav Nodal Officers were taken.
These initiatives had a positive impact as the number of write-ups published on Anubhav portal increased steeply from 423 to 1,459 during the outreach campaign period. It
includes 124 write-ups from the senior officers from Level-13 and above. Further, due to outreach campaign, number of Ministries/Departments/Organizations whose employees have submitted their writeups increased remarkably from 17 to 42, maximum in the history of Anubhav.
Nationwide “Anubhav Awardees Speak” Webinar Series
The series completed its 21st edition in February, 2025 and total 32 speakers from 15 different Ministries/ Departments/ Organizations have participated in the series so far. It has been well received by the audiences and retiring employees join the webinar series from more than 500 locations spread across the country.
Workshop on National Anubhav Awards Scheme, 2025
To ensure maximum and widespread participation in the scheme, an outreach campaign was conducted by DOPPW from 23.01.2025 to 31.03.2025. In this series, various initiatives, including conducting of a workshop for the Anubhav Nodal Officers of Ministries/Departments including 12 PSBs and CPSEs on 23.01.2025, operationalization of dedicated cell, release of informative video, sending of e-mails and SMSs to eligible retired officers/officials and regular meeting with the Anubhav Nodal Officers were taken.
The published write-ups will now be evaluated through a 2 -tier process for finalizing the outstanding write-ups for 05 Anubhav Awards and 10 Jury Certificates, to be conferred in the upcoming Annual Anubhav Awards Ceremony.
100 Days action Plan
As part of 100 days Plan for 2024-25, Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) has implemented several initiatives in 2024 aimed at enhancing the welfare of pensioners, streamlining grievance redressal, and promoting digitization in pension processes. Month long campaign for effective redressal of family pensioners grievances redressed 1737 family pensioners grievances. 54th Pre-Retirement Counselling Workshop was held at Jammu under the chairmanship of Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions to facilitate officials who are about to retire in the superannuation process. Instructions were issued for enhancement of maximum limit of retirement gratuity and death gratuity for central government employees from Rs. 20 lakhs to Rs. 25 lakhs on reaching the Dearness Allowance rates to 50 percent. 5 Anubhav Awards and 10 Jury Certificates were conferred under Anubhav Awards Scheme 2024.
Pension Adalat
3 Pension Adalats were held in 2024-25 including one thematic Pension Adalat on Super senior pensioners where a total of 403 grievances were taken up and 330 grievances were resolved on the sport. The success rate of Pension Adalat is more than $70 %$. The last pension Adalat was held in February, 2025 with success rate of $79 \%$.
Bhavishya
- At present, 99 Ministries/ Departments, 1032 Offices and 9341 DDOs are on Board and 277188 e-
PPOs have been issued till 31.03.2025.
- DoPPW vide its notification dated 16th July, 2024 released New Single Simplified Pension Application Form 6-A. In this new form, a total 9 Forms/Formats have been merged. This form will be available in Bhavishya/e-HRMS to all the Central Government Employees who are going to retire in December 2024 and onwards. This New form and its integration with Bhavishya /e-HRMS were launched on $30^{\text {th }}$ August 2024, at National Media Center, New Delhi, under auspicious presence of Dr Jitendra Singh Hon’ble MoS (PP).
- This new form is integrated with Bhavishya/ e-HRMS. The retiring officials, who are on e-HRMS, are filling Form 6-A through e-HRMS (only Superannuation cases) and the retiring officials, who are not on eHRMS, are filling Form 6-A in Bhavishya w.e.f 16.10.2024. As on 31.03.2025, more than 18853 retiring officials have submitted new Form 6A in Bhavishya.
Integration of CGHS with Bhavishya
- Ministry of Health \& Family Welfare (MoHFW) proposed for integration of CGHS Card application with Bhavishya Portal for the retiring central government employees. DoPPW immediately agreed to the proposal of MoHFW.
- The CGHS Application Form duly filled in by the retiree will be sent for approval of $\mathrm{AD} / \mathrm{CMO}$ post which the retiree will be asked to make predefined payment for CGHS Card through the Bharatkosh portal. Once the payment has been successfully made by the applicant, CGHS e-Card will be generated immediately and an intimation will be sent to Bhavishya Portal. Subsequently, the card printed or delivered at home by CGHS. Application/Apps have been developed and testing is going on.
Jeevan Pramaan
The Face Authentication Technique is a game changer and very beneficial for pensioners as no external device is required and DLC generation is very fast, in less than a minute. It can be submitted through any smart phone and is being widely used. From $1^{\text {st }}$ April, 2024 to $31^{\text {st }}$ March, 2025 out of total 1.62 crore DLCs generated, 52.73 lakhs DLCs were through Face Authentication, i.e. $32 %$. The Digital Empowerment of pensioners featured in Hon’ble PM’s Mann ki Baat and Constitution Day Address.
Standing committee of Voluntary agencies (SCOVA)
The $34^{\text {th }}$ meeting of the Standing Committee of Voluntary Agencies (SCOVA) was held at New Delhi on $11^{\text {th }}$ March, 2025 under the Chairmanship of Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble Minister of State for Personnel, Public
Grievances and Pensions. 10 major agenda items relating to welfare of pensioners were taken up in the meeting.
Report in Detail
28.1 The Allocation of Business Rules broadly allocates the following areas of working to the Department: – Formulation of policy and co-ordination of matters relating to retirement benefits to Central Government employees. The Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules, 2021; the Central Civil Services(Implementation of National Pension System) Rules, 2021; the Central Civil Services (Payment of Gratuity under National Pension System) Rules, 2021; the Central Civil Services (Commutation of Pension) Rules, 1981; the Central Civil Services (Extraordinary Pension) Rules, 2023; any other scheme relating to Central Government pensioners, entrusted to the Department; pension structure and relief to pensioners; new facilities of fringe benefits to the Central Government pensioners; matters relating to amendment to or relaxation of Pension rules or any other rule concerning retirement benefits; Policy and co-ordination relating to welfare of Central Government Pensioners. Matters with financial implication shall be subject to the concurrence of Ministry of Finance. Action in respect of other matters involving recurring financial implications by way of relaxation or liberalization of any rule shall be subject to guidelines as agreed to between the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare and the Ministry of Finance, Department of Expenditure. Department
was set up in 1985 as part of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions to formulate policy and coordination of matters relating to retirement benefits of Central Government employees. Being the nodal Department for pension and pension related matters, the Department receives a large number of references from Ministries/ Departments and also renders advice on interpretation of Pension Rules.
28.2 The approximate number of Central Government Pensioners as on 31.12.2025 is as follows:
| S. No. |
Pensioner/Family Pensioner |
Number of Pensioners including Family Pensioners (in lakhs) |
|---|---|---|
| A. | Pensioners (including Family Pensioners) of all Ministries/ Departments under the Accounting jurisdiction of Controller General of Account, M/O Finance. |
11.51 |
| B. | Defence Pensioners (including Family Pensioners) |
32.64 |
| C. | Railway Pensioners (including Family Pensioners) |
15.16 |
| D. | Telecom Pensioners (including Family Pensioners) |
4.33 |
|---|---|---|
| E. | Postal Pensioners (including Family Pensioners) |
2.91 |
| Grand total of pensioners (including Family Pensioners) |
$\mathbf{6 6 . 5 5}$ |
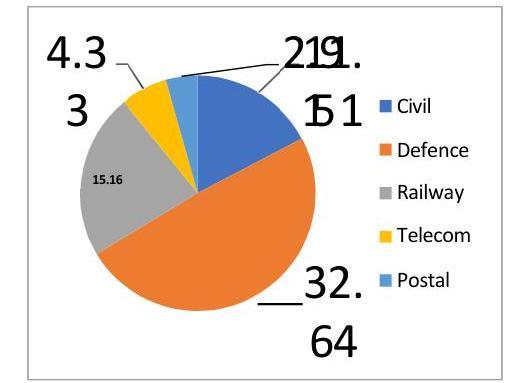
28.3 Pensioners’ Portal
‘Pensioners Portal Scheme’ was started with an objective to serve as a one stop information source for the pensioners of Government of India and also facilitate redressal of their grievances online. With the passage of time, new activities were added under the ‘Pensioners Portal’ such as CPENGRAM, Bhavishya, Anubhav and Sankalp etc. with an objective to create a single window system for civil pensioners.
Pensioners’ Portal through its website provides pensioners with updated information on pension rules, personalized
pension road map, online calculator for calculation of pension/family pension and redressal of Pensioners’ grievances through CPENGRAM. With effect from 01.01.2017, for ensuring transparency and accurate and timely settlement of pension dues it was made mandatory for all Ministries/ Departments to process pension cases on Bhavishya. Experiences of retirees while working in the government are being preserved in Anubhav which has become a treasure-house of information pertaining to various departments. Sankalp aims to prepare employees for post-retirement life.
28.4 Budget
In the year 2024-25, Department has been allocated Rs 1633.00 lakhs in BE and Rs. 3372.00 lakhs in RE to meet its expenses. For Pensioners’ Portal Scheme, BE for 2024-25 is Rs. 350 lakhs, RE is Rs. 505 lakhs, Actual Expenditure is Rs. 466.66 lakhs for FY 202425 which is $92.41 %$ with respect to RE 202425. For Non Scheme BE for 2024-25 is Rs. 1209.00 lakhs, RE is Rs. 2167.00 lakhs, Actual Expenditure is Rs. 2104.74 lakhs for FY 2024-25 which is $96.99 \%$ with respect to RE 2024-25.
28.5 Important Policy decisions taken by the Department
28.5.1 Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules, 2021
Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare is a nodal Department for
formulation of pension policies/rules/instructions relating to pension and other retirement benefits of Central Government civil employees. The implementation of such rules/ instructions, etc. lies with the concerned administrative Ministry/ Department to whom these rules are applicable.
The pension, gratuity and family pension in respect of the Central Government servants appointed on or before 31st December, 2003 are regulated by the Central Civil Services (Pension) Rules, 2021 (erstwhile CCS(Pension) Rules 1972). The provisions for commutation of pension (not exceeding $40 \%$ ) are contained in the Central Civil Services (Commutation of Pension) Rules, 1981. In the case of Government servants who are boarded out from service on account of a disability or who die due to an injury or disease in the performance of duty, disability pension/extraordinary family pension is sanctioned under the Central Civil Services (Extraordinary Pension) Rules.
The Central Government servants appointed on or after 1st January, 2004 are covered by the National Pension System and their service conditions on Terminal benefits / gratuity are regulated by the Central Civil Services (Implementation of National Pension System) Rules, 2021 and the Central Civil Services (Payment of Gratuity under National Pension System) Rules,
Some important policy improvements made in CCS (Pension) Rules 2021 are as under:
$\checkmark$ The provision for voluntary retirement after twenty years of qualifying service.
$\checkmark$ In cases where the Government servant dies before completing a service of 7 years, family pension shall be payable to the family at enhanced rate of $50 %$ of last pay for first 10 years and thereafter @ $30 \%$ of last pay.
$\checkmark$ A divorced daughter, in whose case a decree of divorce was issued after the death of her parents, will be eligible for family pension if the divorce petition was filed before death of the parents.
$\checkmark$ A child suffering from a disability was earlier eligible for family pension only if his/her income, from sources other than family pension, was less than the minimum family pension (i.e. Rs. 9000/p.m.) and the dearness relief admissible thereon. This was causing hardship to children suffering from a disability. Keeping in view special needs of a child suffering from a disability, the child of a deceased Government servant/pensioner, suffering from a mental or physical disability, shall be eligible for family pension for life, if his/her overall income from sources other than family pension is less than the entitled family pension at ordinary rate and the dearness relief admissible thereon, payable on death of the Government servant/pensioner concerned.
$\checkmark$ Government servant who retires due to bodily or mental infirmity before completing a qualifying service of 10
years would also be eligible for Invalid Pension @ 50\% of last pay, subject to the condition that he was found medically fit before or after appointment to the Government service.
$\checkmark$ Benefit of retrospective notional increase in pay after retirement will be available for pension/ gratuity.
$\checkmark$ A time limit of three months has been fixed for deciding on the question of grant of compassionate allowance, on imposition of penalty of dismissal/removal.
This Department, being the nodal Department for welfare of pensioners, has been continuously endeavoring towards reforming and revising the pension rules and the following major amendments have been brought out in the CCS (Pension) Rules, 2021:
Rule 2 -Applicability of CCS (Pension) Rules 2021
A major decision has been taken as per OM 57/05/2021-P&PW(B) dated 03.03.2023 that in all case where the Government Civil employees has been appointed against a post or vacancy which was advertised/notified for recruitment/appointment, prior to the date of notification for National Pension System i.e. 22.12.2003 and is covered under NPS on joining service on or after 01.01.2004 may be given a one-time option to be covered under CCS (Pension) Rules, 1972/2021.
Rule 8- Power to withhold or withdraw pension
The Rule 8 of the CCS (Pension) Rules, 2021 has been amended towards ease of rules/ procedures by delegating the powers for withholding/ withdrawing pension/ gratuity. The amended notification issued on 07.10.2022.
Rule 50 – Family Pension
As a major step towards empowerment of women employees, this Department vide 1/1(1)/2023-P&PW(E) dated $1^{\text {st }}$ January 2024 has issued instructions under Rule 50 of CCS(Pension) Rules 2021 allowing female Government servants/female pensioners to nominate her child/children for family pension in precedence to her husband in the event of marital discord leading to filing of divorce proceedings in a Court of Law or filing of a case under Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act or Dowry Prohibition Act or Indian Penal Code.
28.5.2 National Pension System (NPS)
On the Good Governance Day, 2022 (25th December, 2022), Hon’ble MoS(PP) released a book on the Central Civil Services (Implementation of National Pension System ) Rules, 2021 published by the Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare. These Rules were earlier notified on 30.03.2021. These Rules inter alia cover the matters relating to registration process and allotment of PRAN, contributions by the employee and the Government, compensation to be paid to
the Government servant in case of delay in registration and credit of contributions to the NPS Account, option for benefits under the CCS(Pension) Rules or NPS Rules in the event of death or disability of Government servant during service, entitlements on superannuation, premature/ voluntary retirement, resignation from service, etc. and the procedure for processing of claims under NPS.
Department has simplified Provisions of Pension Rule and had issued instructions during the Special Campaign 3.0 on Swachhata launched by Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) for disposal of Pending Matters during 2nd October, 2023 to 31st October 2023. Under this campaign, Department of Pension and Pensioners Welfare issued five (5) Notifications/Circulars for ease of rules with respect to NPS matters during the month of October, 2023.
A Committee was constituted by Department of Financial Services vide their O.M. dated 21.10.2016 to suggest measures for streamlining the implementation of the National Pension System under the Chairmanship of Secretary (Pension) with Secretary (Department of Personnel and Training) and Secretary (Department of Financial Services) as members, as per decision of the Cabinet on 29.06.2016.
This Committee submitted its recommendations to Department of Financial Services on 06.03.2018. Thereafter, Department of Financial Services obtained
approval of the Cabinet and forwarded recommendations of the Committee to concerned Departments for action.
Para 8.7.1 of the recommendation of the Committee was as under:
i. “The three-tiered NPS oversight mechanism of the DDO/Head of Office, Joint Secretary (Admin)/ Chief Controller of Accounts and the Financial Advisor set up vide Department of Expenditure’s Office Memorandum No1(2)/EV/2008 dated 3rd February 2009 may be strengthened/streamlined to monitor grievances as well as timely registration and credit of contributions to subscribers’ accounts. Fresh instructions to this effect and for strict compliance of instructions may be issued by Department of Expenditure.”
ii. Accordingly, Department of Expenditure vide their OM No. 1(24)/EV/ 2016 dated 02.07.2019 issued instructions for setting up of NPS oversight mechanism in each Ministry / Department. This OM stipulates, as under:
“since timely credit of deduction made from the salary of Central Government employees towards their contribution to NPS, as also the applicable contribution of the Central Government, to the NPS financial architecture is of paramount importance for availability of due and timely returns thereon towards generation of pension corpus, it has been decided that a Committee in each Ministry/Department shall be constituted as
under to ensure oversight over the NPS contributions crediting: –
(i) Financial Advisor – Head of the Committee
(ii) Joint Secretary (Administration)
(iii) Principal CCA/CCA
(iv) The concerned Head of the office
(v) The concerned DDO
The Committee shall be responsible for the following actions:-
i. Ensuring that the contribution of employees and the Government are credited without delay to the NPS financial architecture both in case of existing employees and employees newly recruited from time to time and the existing system and procedure being followed for the purpose shall be monitored effectively to ensure that no delay in credit of the contributions takes place.
ii. Ensuring that in case any grievance by any employee is received in regard to delay in credit of contribution, either directly from the employee or through PFRDA, the same has been looked into and disposed of in a manner to the satisfaction of the concerned employee.
iii. Any other matter as having a bearing on the issue of crediting/remittance of NPS contributions.
iv. The Committee shall devise its own mechanism as also appropriate checks & balances to ensure that NPS contributions are credited on time in respect of all employees under NPS system.
v. The Committee shall meet at least once in 3 months to review the progress and in case any slippages are noticed, it shall take immediate corrective action. However, the concerned Principal CCA/ CCA shall keep a watch over the progress on a regular basis.
vi. While the above Committee shall be set-up in each Ministry/Department, appropriate mechanism for keeping a watch in respect of attached and subordinate offices under that Ministry/Department shall be put in place by the concerned Financial Advisor, so that the overall oversight in respect of the entire Ministry/Department as a whole is exercised by the Committee as mentioned in para 5 above.
vii. The concerned Financial Advisor shall send a status report every six month to the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare about the result of the monitoring carried out through the above oversight mechanism with concluding remarks whether the
NPS contributions are being credited on time and in case of any slippages, the details of the action taken.”
viii. In pursuance to Department of Expenditure, this Department vide DO letter dated 07.06.2021 and 09.06.2021 requested all Ministries/ Departments to submit six monthly status report and a proforma was also prescribed.
ix. A revised proforma for capturing mode details relating to CCS (Implementation of NPS) Rules, 2021 were also provided vide OM dated 22.06.2023.
x. A review meeting on the status of setting up of National Pension System (NPS) Oversight Mechanism in each Ministry/Department was conducted under the Chairmanship of Secretary (Pension) on 21.02.2024 through Video Conferencing with the Financial Advisor and the representatives of the Ministries/ Departments. Minutes of the meeting were issued on 21.02.2024. As per the decision taken during the meeting, this Department developed an online portal with URL https://pensionersportal.gov.in/N PSfor submission of six-monthly report from the month of October, 2023 to March 2024. This was
communicated to all Ministries/Departments by OM dated 04.06.2024.
xi. Only 39 Ministries/Departments have submitted six monthly reports. Out of which 37 have submitted online report of 52 nodal officers registered on the portal. Two Ministries have submitted report through physical mode. For the last six-monthly report for the period of October, period 2023 to March, 2024, 47 Ministries/Departments had submitted their report. Now, report for the April, 24 to September, 2024 is due for which Ministries / Department have been reminded vide OM dated 14.10.2024 and again on 09.12.2024.
28.5.3 Compendium of Advisories issued
Department of Pension & Pensioners Welfare has issued compendium of Pension related instructions on $25^{\text {th }}$ December, 2024. These instructions are quite helpful in sorting out complicated issues involve in Pension Policy matters such as NPS matters, disciplinary matters, etc.

28.6 Improving Penioners’ Welfare
28.6.1 Digitization of Pension Sanction and Payment Tracking System: Bhavishya
- During the analysis of grievances registered at CPENGRAMS, it is found that around substantial number of grievances are received due to delay in release of first pension/family pension. Therefore, DoPPW took initiative to achieve complete digitalization of the pension payment process from start to finish, wherein the start is online filling of pension forms by the retiree and the finish is to issue of e-PPO which reaches the Digi-locker of the Pensioner and credit of the first pension in pensioner’s account.
- To overcome the problems of delay \& clerical errors in processing the pension cases, duplication as well as financial loss and harassment to the pensioners, the DOPPW introduced, on a pilot basis, a unique innovative centralized pension processing software called ‘Bhavishya’ for all central government Ministries/Departments.
- After a successful pilot, Bhavishya’ was made mandatory for all central civil Ministries and Departments w.e.f 01.01.2017. At present, 99 Ministries/ Departments, 1032 Offices and 9341 DDOs are on Board. The ‘Bhavishya’ software was indigenously made by the Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare and was meant to be a common platform for processing of pension cases
by all civil Ministries/Departments of Government of India.
At a Glance (on 31.03.2025):
| S. No. |
Items | Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | No. Ministries/Departments onboard |
99 |
| 2. | No. Attached/Subordinate Offices on-board |
1032 |
| 3. | No. of DDOs registered | 9341 |
| 4. | No. of cases under process | 28283 |
| 5. | No. of cases processed/PPO issued | 277188 |
This software brought all the stakeholders who were till date decentralized on a single platform. The system laid down a common methodology incorporating all the rules and regulations of CCS Pension Rules, 1972 (now, CCS (Pension) Rules, 2021) and automatic calculation of pension and other retirement dues.
From the pay roll/EIS, the ‘Bhavishya’ software was integrated and would auto fill all the data of the retiring employees and at the beginning of the year provide the necessary MIS to the various departments as well as to the DOPPW the number of employees due to retire in the coming year.
The software has laid down strict timelines for various stages of pension processing across all stakeholders involved. The process starts online 15 months prior to retirement and
the pensioner has to fill up a single form once. The system on its own keeps throwing up alerts to the pensioner as well as to the stakeholder for meeting out the deadlines prescribed for various stages.
Due to the system being digital, there is no duplication of entries and the retiring staff need not leave his office work and run from desk to desk chasing his case. The pension calculation cutting across all Ministries/Departments is accurate since it removes manual intervention. Through this system, any office can directly contact the DOPPW for any clarification, if necessary. It has resulted in saving of huge manpower and time cutting across all Ministries.
Every department through this software can assess in the beginning of the year the number of retirees and this feature is also visible to DOPPW for all retiring central civil pensioners across Government of India. The system is capable of giving real time data of pension processing of central civil retirees up to the stage of first credit of pension in their respective bank’s accounts.
Bhavishya Portal Dashboard
The ‘Bhavishya’ process has also been integrated with the PFMS module of CGA and due to this it has now become possible to
issue electronic PPOs (e-PPO). At present, the Data from Bhavishya is being provided/ transferred to PFMS for 542 PAOs. 209673 ePPOs have been issued till 31.03.2025. The ePPO is transmitted by the concerned Ministry/Department’s PAO to CPAO from where it goes to the Bank. The paying branch can view e-PPO online. Intimation of credit of first Pension& subsequent monthly Pension is done electronically on real time basis and is also communicated to Pensioner via email/SMS alerts. A link has been incorporated in the Bhavishya system to download the e-PPO by the retirees as well as HOO.
DoPPW vide its notification dated 16th July, 2024 released New Single Simplified Pension Application Form 6-A. In this new form, a total 9 Forms/Formats have been merged. This form will be available in Bhavishya/eHRMS to all the Central Government Employees who are going to retire in December 2024 and onwards. This New form and its integration with Bhavishya/e-HRMS was launched on $30^{\text {th }}$ August 2024, at National Media Center, New Delhi, under auspicious presence of Dr Jitendra Singh Hon’ble MoS (PP).
This new form is integrated with Bhavishya/e-HRMS. The retiring officials, who are on e-HRMS, are filling Form 6-A through e-HRMS (only Superannuation cases) and the retiring officials, who are not on e-HRMS, are filling Form 6-A in Bhavishya w.e.f 16.10.2024. As on 31.03.2025, more than 18853 retiring officials have submitted new Form 6-A in Bhavishya.
Integration of Bhavishya with Digi Locker
- Pensioners have to face innumerable hardship at various stages of their retired life due to misplacement of the original copies of their Pension Payment Order (PPO). Therefore, Bhavishya was upgraded to create a permanent record of PPO in DigiLocker of pensioners. This was a technological leap since now the Central Government Pensioners can store their PPOs in their Digi lockers as a permanent record. 7774 retirees have pushed their e-PPOs in DigiLocker till 31.03.2025.
The ‘Bhavishya’ system has also been made available on a Mobile App, thereby making it simples specially for those Para Military Forces who are out in the fields to keep track of their pension cases.
As another step towards ‘Ease of Living’ for pensioners, D/o Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare has introduced the facility to download Electronic Special Seal authority (e-SSA). Now the Retiree as well as the Head of Office (HOO) can download the e-SSA from the Bhavishya system. It will save Pensioners from undue hardship in getting a copy of their SSA at the time of retirement.
Coordination with Defence, Railways, Post and Telecom to automate their Pension processing system on the lines of Bhavishya: As per directives of Parliamentary Standing Committee, DoPPW is regularly pursuing with Defence, Railways, Post and Telecom for getting their pension processing system digitized on the pattern of ‘Bhavishya. As of now, digitization has taken momentum in these
establishments. M/o Defence after introduction of SPARSH Portal, DoT with SAMPANN Portal, Railways with ARPAN software and D/o Posts have made considerable headway in digitization of the pension settlement of their employees. DoPPW is also working towards bringing the Defence, Railways, Post and Telecom on the Department’s Dashboard in order to get regular updates on the number of retiring persons in their respective establishments.
- Real-time monitoring for settlement of family pension claim in CAPF: All the CAPFs viz. BSF, CRPF, CISF, ITBP, Assam Rifles and SSB come under MHA and CCS (Pension) Rules, 1972 (now, CCS (Pension) Rules, 2021) are applicable to them. With a view to curtail the time lag between the date of death in any CAPF and settlement of family pension, a real-time monitoring Dashboard was made functional w.e.f. February 2020 through which the status of delay in family pension can be monitored and reminders sent to MHA to take action on expeditiously starting the family pension.
- Services available on IPP: – At present, the pension portals of State Bank of India (SBI), Canara Bank, Punjab National Bank, Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, Central Bank of India and Union Bank of India have been integrated. The pensioners can now get their pension slip, the status of submission of Life Certificate and Form-16 through the Integrated Pensioners’ Portal (IPP).
– Impact of Bhavishya:
Timely issue of PPO
$\checkmark$ 83% Superannuation PPOs are issued either before retirement or within 30 days.
$\checkmark$ 69\% Family Pension PPOs are issued within 6 months from the date of death.
Introduction of New Single Pension Application Form 6A and its Integration with e-HRMS
DoPPW vide its notification dated 16th July, 2024 released New Single Simplified Pension Application Form 6-A. In this new form, a total 9 Forms/Formats have been merged. This form will be available in Bhavishya/e-HRMS to all the Central Government Employees who are going to retire in December 2024 and onwards. This New form and its integration with Bhavishya/e-HRMS was launched on $30^{\text {th }}$ August 2024, at National Media Center, New Delhi, under auspicious presence of Dr Jitendra Singh Hon’ble MoS (PP).
This new form is integrated with Bhavishya/ e-HRMS. The retiring officials, who are on eHRMS, are filling Form 6-A through eHRMS (only Superannuation cases) and the retiring officials, who are not on e-HRMS, are filling Form 6-A in Bhavishya w.e.f 16.10.2024. As on 31.03.2025, more than 18853 retiring officials have submitted new Form 6-A in Bhavishya.
Integration of Bhavishya with CGHS
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) proposed for integration of CGHS Card application with Bhavishya Portal for the retiring central government employees.
DoPPW immediately agreed to the proposal of MoHFW
The CGHS Application Form duly filled in by the retiree will be sent for approval of $\mathrm{AD} / \mathrm{CMO}$ post which the retiree will be asked to make pre-defined payment for CGHS Card through the Bharatkosh portal. Once the payment has been successfully made by the applicant, CGHS e-Card will be generated immediately and an intimation will be sent to Bhavishya Portal. Subsequently, the card printed or delivered at home by CGHS. Application/APIs has been developed and testing is going on.
28.6.2 CPENGRAMS
CPENGRAMS is an on-line computerized system developed with the objective of speedy redressal and effective monitoring of the pension related grievances for the Central Civil Pensioners. The grievances are either registered directly on the portal or registered by the department on behalf of the complainant after receiving details through email, Post or Integrated Grievance Cell & Call Centre’s Toll free number: 1800-111960 .
In F.Y. 2024-25, the total receipts of the pension grievances is $1,17,812$ with the redressal of $1,14,371$, registering increase of $30 %$ and $31 \%$ in the receipts and redressal respectively, as compared to F.Y. 2023-24.
The redressal rate has kept momentum with the receipts of the grievances owing to the breaking of silos, achieved through active monitoring and coordination with the
stakeholders viz. Ministries / Departments and their Pay and Accounts Offices (PAOs), CPAO and Banks.
Out of 1,14,371 redressal, feedback has been received in 60,215 cases through Feedback Centre of DARPG and availing of facility of grading of redressal, available on CPENGRAMS Portal. To comply with the directions of Hon’ble Prime Minister for sensitive, accessible, and meaningful redressal of grievances, DoPPW issued comprehensive guidelines on 16.10.2024 with emphasis on quality redressal of pensioners’ grievances within 21 days under ‘whole of the Government approach’.
It was ensured that the guidelines are properly followed, thereby resulting in increased satisfaction among pensioners which is evident from the analysis of the feedback of 60,215 redressed cases in F.Y. 2024-25. The percentage of the cases, graded as ‘Excellent’ has increased from $25 \%$ to $33 \%$ while the percentage of cases, graded as ‘Poor’, decreased from $42 \%$ to $35 \%$. This improvement is crucial as the number of receipts of grievances has increased by $30 \%$ as compared to previous F.Y. Re-registration is being done by Feedback Unit after analysis of cases, graded as ‘Poor’, in deserving cases.
Over the last 04 years, steep increase in the defence pensioners’ grievances has been witnessed and around 85,000defence pensioners’ grievances were filed in F.Y. 2024-25, accounting for $72 \%$ of the total grievances received on the portal.
Accordingly, level of interaction with Ministry of Defence was elevated and meetings with Secretary (Defence), Secretary (ESW) and Controller General of Defence Accounts (CGDA) were conducted on
regular intervals, apart from monthly InterMinisterial Review Meetings (IMRMs).
These concerted efforts have contributed towards the motto of DoPPW- ‘Pensioners First’ duly supported by the examination of feedback of 41,784 defence pensioners/family pensioners redressed in F.Y. 2024-25. The $33 %$ complainants have graded their response as ‘Excellent’ as compared to $25 \%$ in last F.Y. Also, corresponding decline in ‘Poor’ feedback from $42 \%$ to $35 \%$ has been noticed.
As a part of above, a month-long Special Campaign, to redress Family Pension grievances, was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MoS (PP) on 1st July, 2024.
A total of 1891 family pension related grievances, pertaining to 46 Ministries/ Departments/Organizations were selected. The campaign was widely publicized through various means such as Akashwani/AIR talk, PIB statements, tweets highlighting 50 Success Stories under #SpecialCampaignFamilyPension.
The Campaign achieved the success rate of $94 \%$ with the redressal of 1769 Family Pension cases, out of the total 1891 family pension cases.
DoPPW is committed towards quality redressal of pensioners’ grievances. Therefore, to achieve the same and to ensure compliance of recommendations of DRPSC in its $127^{\text {th }}$ report, DoPPW, vide OM dated 16.10.2024, has issued comprehensive guidelines for sensitive, accessible and meaningful redressal of Central Government Pensioners’ grievances
on CPENGRAMS Portal requesting Ministries/Departments to redress the Pensioners’ grievances within 21 days under ‘whole of the Government approach’. The stakeholders are regularly encouraged to adhere to the provisions of this OM.
Feedback unit, DoPPW examines the disposed cases and it was noticed that premature closure of the grievances is the primary reason for the ‘Poor’ feedback provided by the complainants. The Feedback unit also re-registered more than 500 deserving cases. This has helped many pensioners got their pensionary dues running in lakhs of rupees after a long period. Some of the examples are as under:
i. Sh. Ramesh Chand, Ex Nb Subedar from Indian Army, got arrear of Disability Element and War Injury Element amounting to Rs. 41.90 Lakhs from year 1996 to year 2023.
ii. Ms. Guljit Kaur, widow of Late Sh. Hardev Singh, Ex Sepoy, Indian Army received OROP arrears of more than Rs. 13 Lakhs after 2 years and her family pension was also revised.
iii. Sh. Satvinder Singh, Ex Naik, Indian Army, got arrears for the period from 01.11.2015 to 30.4.2022 of Rs 13.80 Lakhs after 2 years.
iv. Sh. Harbhajan Singh got War Injury Element arrears of more than Rs. 30 Lakhs after 18 years.
v. Ms. Geetha Bhai, a widow received family pension arrears of Rs. 14 Lakhs which was pending for more than 7 years.
DoPPW accords highest priority to the Super senior pensioners and therefore, special efforts viz. Issue of reminders through the portal and e-mails were done.
Citizen connect was also a major area of thrust in this financial year. This year DoPPW has taken several initiatives to increase penetration of CPENGRAMS among Pensioners. DoPPW has started a daily series of tweets on 05 Success Stories and 02 Testimonials on ‘ X ‘. A total of more than 600 tweets have so far been posted on the DoPPW ‘ $X$ ‘ Handle. A short movie to increase awareness about CPENGRAMS is receiving a good viewership on official YouTube Channel of DoPPW. A total of 70 lakhs SMSs have also been pushed for the purpose containing link of this movie.
Monthly report on CPENGRAMS and Bhavishya was revamped and various additional features viz. comparative analysis of the Ministries/Departments in terms of redressal, pendency and Appeal filed, success stories, testimonials, performance of call centre and presentation in graphical manner were added.
DoPPW, as a part of National Good Governance Week, 2024, organized a National Workshop on Effective Redressal of Pension Grievances on 19.12.2024 in New Delhi.Senior officers from various Ministries & Departments participated in the workshop and benefited from the experiences shared by
the eminent speakers from major stakeholders. Various initiatives undertaken by CPENGRAMS like successful redressal of more than 3.76 lakhs grievances in last 05 years, improved categorization of grievances and Smart Action Taken Report (ATR), humane touch brought in by the inbound Call Centre and outbound Feedback Centre and role of Pensioners’ Welfare Associations in creating awareness about online grievance redressal system, were discussed.

Inauguration of Special Campaign on Redressal of Family Pension Grievances by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble MOS(PP)
100 Days action Plan
As part of 100 days Plan for 2024-25, Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) has implemented several initiatives in 2024 aimed at enhancing the welfare of pensioners, streamlining grievance redressal, and promoting digitization in pension processes. Month long campaign for effective redressal of family pensioners grievances redressed 1737 family pensioners grievances. 54th Pre-Retirement Counselling Workshop was held at Jammu under the chairmanship of Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions to facilitate officials who are about to retire in the superannuation process. Instructions for
enhancement of maximum limit of retirement gratuity and death gratuity for central government employees from Rs. 20 lakhs to Rs. 25 lakhs on reaching the Dearness Allowance rates to 50 percent. 5 Anubhav Awards and 10 Jury Certificates were conferred under Anubhav Awards Scheme 2024.
28.6.3 Pension Adalat
DoPPW’s mandate inter alia includes welfare of Central Government pensioners. Redressal of Pensioners’ grievance is one of the thrust areas in this regard. Keeping in view the mandate, holding of Pension Adalat gives a single platform where the concerned stakeholders, viz., Ministry/ Departments/ Organisation/ CPAO/bank could be brought together for expeditious resolution of long pending grievances to the satisfaction of the petitioner. Pension Adalat provides an additional forum for redressal of pension related grievances obviating the need to approach Court/CAT.
With a view to redress chronic grievances falling within the four walls of extant policy, the system of holding Pension Adalat has been introduced since September, 2017 when first Pension Adalat was held. Continuing this initiative forward, till March, 2025, twelve Pension Adalats have been organized. The success rate of Pension Adalat is more than $70 %$. The last pension Adalat was held in February, 2025. Total of 192 grievances were taken up and 151 grievances were resolved on the spot with a success rate of $79 \%$.
Pension Adalat Flyer

$12^{\text {th }}$ Pension Adalat held in New Delhi
28.6.4 All India Digital Life Certificate Campaign 3.0
- Every year in the month of November a pensioner is required to produce life certificate for further continuation of his pension. In the traditional mode, pensioners could submit life certificate by physically presenting themselves before the pension disbursing authority such as banks or send a certificate issued by a gazetted officer or other designated authorities.
- Due to infirmity or other ailments and old age, this manual system was a cause of extreme discomfort and inconvenience, as pensioners had to wait outside the bank branches in long queues for submission of Life certificate. There was no
mechanism for pensioners to get updated status on recording of their Life Certificate, and it was observed, on the basis of grievances received, that at times, pension was discontinued, due to non -updating of Life Certificate record in the banking system by the concerned staff, even though the pensioner had submitted the same. Keeping in view the concerns of senior pensioners and discomfort faced by them in the manual process, it was felt necessary to streamline the process to make it digital and initiate Door Step Service for submission of Life Certificate.
- In November, 2014 an Aadhar based scheme for online submission of digital life certificate, Jeevan Pramaan, was launched by the Hon’ble Prime Minister with the object to facilitate pensioners to submit life certificate anytime and from anywhere.
- In 2018, DoPPW started a Pilot Programme DLC from home campaign with the assistance of Pensioners’ Associations. The objective of the campaign was to extend support to the aged and infirm pensioners in submission of Life certificate digitally from home. Around 2500 DLC were successfully created by pensioners Associations in 7 cities.
- In October-November 2019, this project was expanded to cover 24 cities i.e. Hyderabad, Ranchi, Bhuvneshwar, Jaipur, Thrissur, Kolkata, Cuttack, Chennai, Guwahati, Madurai, Balasore, Jalandhar, Ahmedabad, Prayagraj, Pune, Dehradun, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Vadodara, Trivandrum, Mysore, Chandigarh, Noida, Delhi. In the year
2019, around 4100 DLCs were collected from such pensioners by the above Pensioners Associations.
- With a view to make Doorstep Services for submission of Life Certificate available to all pensioners across the country, DoPPW roped in India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) under the Department of Posts for Digital Life Certificate. IPPB started Doorstep Service in November, 2020 through its huge network of Postmen & Gramin Dak Sevaks (presently 2,06,200) Thus the major initiative of DoPPW, viz. DLC from Home has reached every nook and corner of the country. This has come as a source of great comfort to Pensioners, especially those residing in rural areas.

- After the coordination with Public Sector Banks Alliance (PSB), the service for collection of Life Certificate has been brought under the umbrella of Doorstep Banking Service. Now pensioners can submit Life Certificate by calling Banking agents at their home. This facility is presently available in 100 cities.
- In order to address the inconvenience faced by senior pensioners in submission of Life Certificate digitally due to non-capturing of their finger bio-metrics, DoPPW issued directions through OMs advising all Pension Disbursing Banks to adopt the Video based Customer Identification Process (V-CIP) as an additional facility for obtaining a Life Certificate from the pensioners, within permissible RBI guidelines. Most of the Banks have adopted VCIP for their pensioners.
- Face Authentication Technology was launched by the Hon’ble Minister of State (PP) on $29^{\text {th }}$ November 2021 with a view to
enhance ease of submission of Digital Life Certificate by pensioners. Through this App a pensioner can submit a Digital Life Certificate from the comfort of home using any Android mobile without attaching any external device. The above technology is a milestone in leveraging technology for the purpose of Life Certificate. As per this facility, the identity of a pensioner is established through face authentication technique on the basis of the live photo captured and submitted online using any Android based smart phone. On being authenticated by the UIDAI server, DLC gets generated. This technology has reduced the dependence of pensioners on external bio-metric and made the process of LC submission more affordable by enabling pensioners to submit their LCs from the comfort of their homes. The Face Authentication Technology has been given wide publicity on social media viz. Youtube, Facebook, Twitter and through print media. - In addition, the Department took steps to facilitate pensioners living abroad for submission of Life Certificate and gave instructions to the Ministry of External Affairs, that all the Indian Embassies/High Commissions/Consulates devise a methodology for endorsing Life Certificates and also to the International Banking Divisions of
Pension Disbursing Banks to facilitate Life Certificate of such Pensioners.
- Keeping in view the difficulties faced by very senior citizens aged 80 years and above, an exclusive window has been provided to enable submission of Life Certificates by them from October $1^{\text {st }}$ onwards. This would help them to avoid the rush at Banks from $1^{\text {st }}$ November onwards, when all pensioners are required to submit their annual life certificates. Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare has issued instructions vide its OM No. 1(2)/2023 P\&PW (H) dated 25.9.2023 regarding facilitation of Digital Life certificate through Face Authentication for Super Senior Pensioners aged 80 years and above from 1st October every year.
- The Department of Pension \& Pensioners’ Welfare, Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions launched a Nation-wide Campaign for promotion of Digital Life Certificate (DLC) for Central Government pensioners during 1st 30th November, 2022. A similar Nation-wide DLC Campaign 2.0 was held from 1st to 30th November, 2023. Nation-wide DLC Campaign 3.0 was held from 1st-30th November, 2024 in 845 cities/districts. The objective of these Nation-wide Campaigns was to promote the use of digital modes for
LC submission with special emphasis on the milestone technology of Face Authentication thereby ensuring comfort and ease of usage. All the registered Pensioners’ Associations, Pension Disbursing Banks and Ministries/Departments of Government of India had been directed to promote the Digital Life Certificate/Face Authentication Technique for giving Life Certificate by organizing special camps for pensioners.
- To promote the campaign, Pension Disbursing Banks joined hands with the Department and provided the Camp venues in different cities. Registered Pensioners’ Associations of the Department played a pivotal role in informing and mobilizing pensioners to visit the camps in different cities. Officials of DoPPW were nominated to monitor the camps and visited various locations for this purpose. During the Nationwide DLC campaign 3.0, camps were held at more than 1984 locations across 845 cities across the country.
- DLC Portal was developed by the Department for monitoring \& providing complete information about the progress of the Campaign. All the Nodal Officers were registered on the Portal to enable them to login and post information about the camps. 1030 Nodal Officers from Banks, Ministry of Defence (SPARSH), Department of
Telecom, UIDAI and Pensioners’ Welfare Associations were registered on the Portal. Regular meetings were held with all the stakeholders to share information about the Campaign and guide them with regard to the techniques to be used for generation of DLCs. In addition, a WhatsApp group was created with Nodal Officers of all stakeholders to post the progress of the camps and any issues being faced.
- The Nation-wide DLC Campaign 3.0, another milestone in the initiatives taken by the Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare towards ensuring Ease of Living of pensioners, was a huge success and was widely covered in Print and Visual Media by PIB and DD News. More than 1.62 crore DLCs were generated of which more than 49.78 lakhs were of Central Government pensioners. More than 52.73 lakhs DLCs were generated using Face Authentication technique of which more than 21.47 lakhs were of Central Government pensioners. An analysis of the age-wise generation of DLCs reveals that more than 43,000 Central Government pensioners above the age of 90 years and more than 4.15 lakhs central government pensioners in the age group $80-90$ years used digital mode for LC submission. During the campaign, representatives from the department, Banks and Pensioners’ Welfare Associations visited
sick/incapacitated/aged pensioners at their homes/hospitals to assist them in DLC generation. With a view to technologically empowering the pensioners, in addition to generating their DLCs, the process was also explained to them for future use. The Digital Empowerment of pensioners featured in Hon’ble PM’s Mann ki Baat and Constitution Day Address.
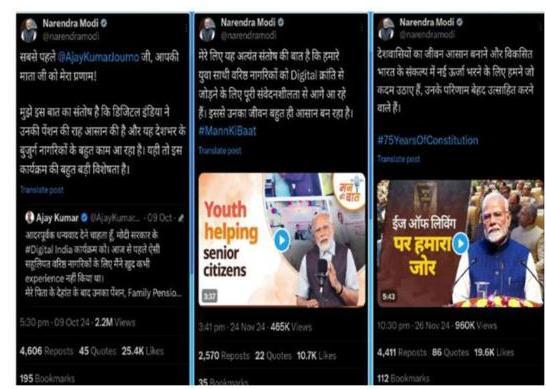
- In order to publicize the Nationwide campaign for promoting DLC this Department sent about 1.20 crore SMSs to Central Government pensioners on their mobile phones. The campaign was widely covered by the newspapers and Doordarshan all over the country. During the campaign period, Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare disseminated 2603tweets from its Twitter account during the period.
Year-wise DLCs generated are as below:
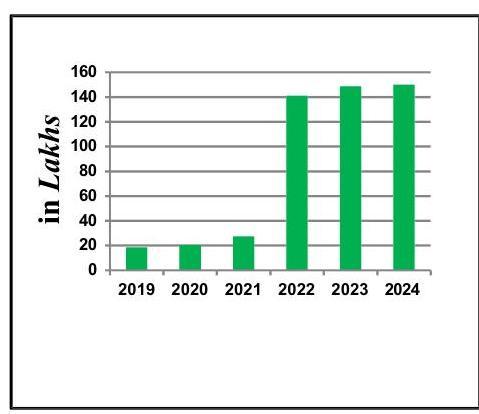
Beside this, other stakeholders also issued tweets. Three videos were uploaded by the Department on its YouTube page (DOPPW_INDIA OFFICIAL) explaining the process of submitting the Life Certificate through Face Authentication Technique in simple language. #DLC Campaign 3.0 created for wider publicity of DLC 3.0 Campaign.
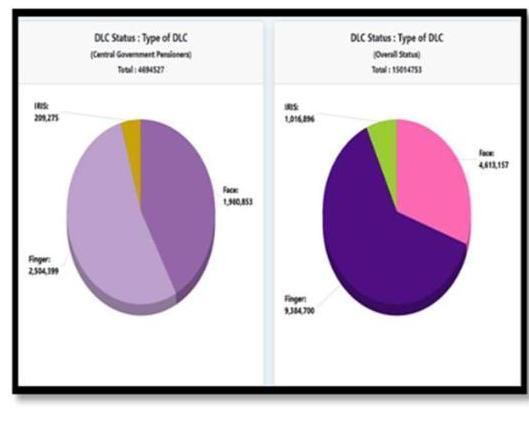
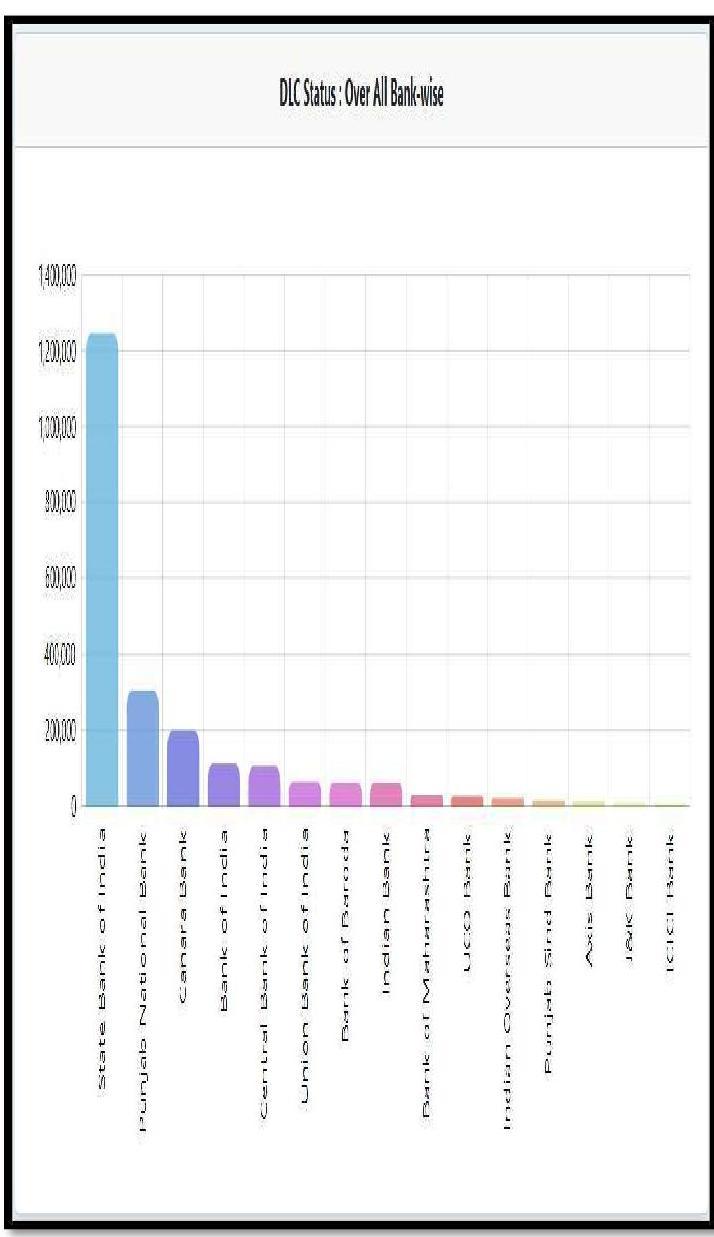
DLC Status: Over All Stake wisk
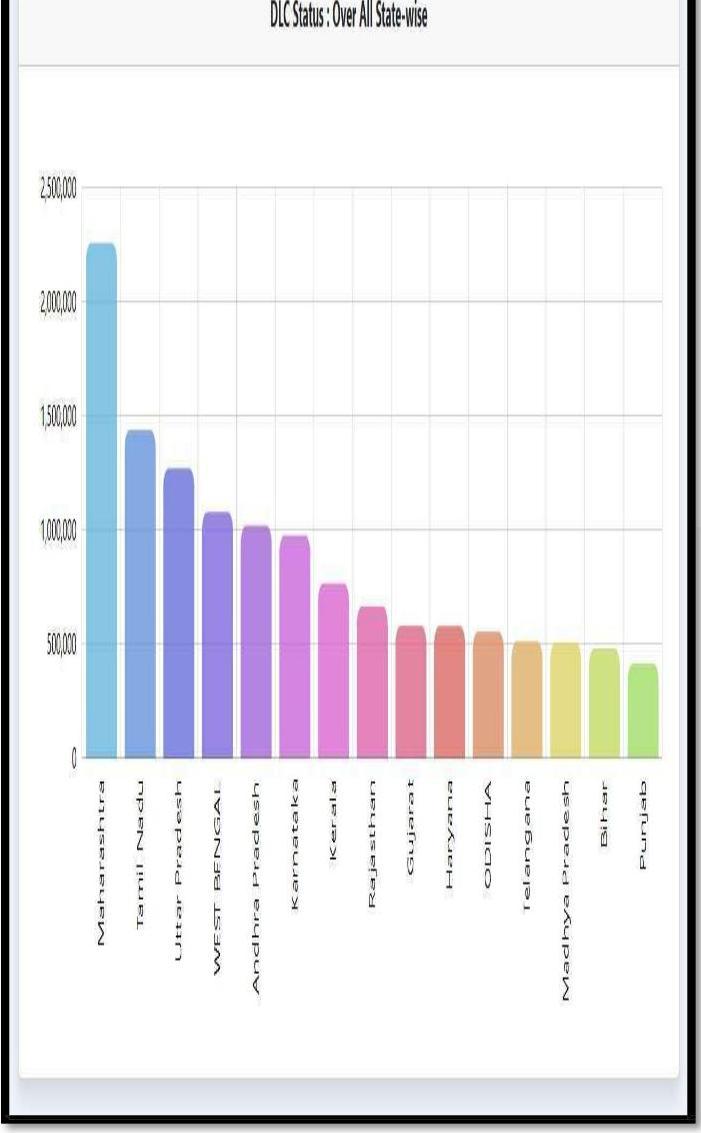

डिजिटल सेवा का लाभ देश के हर पैरालसोलियों को उपलब्ध कराना अस्पताल का उद्देश्य: सीमा
बहुत से देशों के लिए डिजिटल सेवा का लाभ देश के हर पैरालसोलियों को उपलब्ध कराना अस्पताल का उद्देश्य: सीमा




































































































































































































28.6.5 AnubhavAwards
On the directions of the Prime Minister of India, Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) had launched an online platform entitled ‘Anubhav’ in March 2015. It is a means for retiring employees to share their experiences and achievements during their service period through write-ups. This will prove an invaluable tool for helping in future governance related issues.
The Scheme is the watershed moment in the history of Anubhav Portal with many firstsinclusion of employees of Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) and 12 Public Sector Banks (PSBs), introduction of objective marking system and extension of time-limit from 01 year to 03 years after retirement for submitting the write ups. As per the notified scheme, write-ups published from 01.04 .2024 to 31.03 .2025 were to be considered.
To ensure maximum and widespread participation in the scheme, an outreach campaign was conducted by DOPPW from 23.01.2025 to 31.03.2025.
In this series, various initiatives, including conducting of a workshop for the Anubhav Nodal Officers of Ministries/Departments including 12 PSBs and CPSEs on 23.01.2025, operationalization of dedicated cell, release of informative video, sending of e-mails and SMSs to eligible retired officers/officials and regular meeting with the Anubhav Nodal Officers were taken.
These initiatives had a positive impact as the number of write-ups published on Anubhav portal increased steeply from 423 to 1,459 during the outreach campaign period. It includes 124 write-ups from the senior officers from Level-13 and above. Further, due to outreach campaign, number of
Ministries/Departments/Organizations whose employees have submitted their writeups increased remarkably from 17 to 42 , maximum in the history of Anubhav.
The published write-ups will now be evaluated through a 2 -tier process for finalizing the outstanding write-ups for 05 Anubhav Awards and 10 Jury Certificates, to be conferred in the upcoming Annual Anubhav Awards Ceremony.
The list of the awardees is as under:
| Anubhav Awardees-2024 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. |
Name (Ms./Sh.) |
Designation | Organ izatio n |
| 1. | T. Jacob | Secretary | UPSC |
| 2. | Aditi Das Rout | Additional Secretary |
M/o WCD |
| 3. | G Nancharamma |
Technical Officer-D | DRDO |
| 4. | Rajesh Kumar Parida | Deputy Commandant | BSF |
| 5. | Appan Sridhar | Junior Engineer | M/o Railwa ys |
| Jury Certificate Winners-2024 | |||
| S. No. |
Name (Ms./Sh.) |
Designation | Organ izatio n |
| 1. | Sanjeev Sharma |
Chief Commissioner Income Tax | CBDT |
| 2. | Shakuntal a Patnaik |
Deputy Chief Labour Commissioner |
M/o Labour |
| 3. | Sudesh Kumar |
Technical Officer-D | DRDO |
| 4. | Krishna Mohan Shahi |
Assistant Commissioner, Income Tax | CBDT |
| 5. | N. Desingu |
Inspector/ Ministerial |
CISF |
| Rajan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6. | Mrs. G. Swarnalat ha |
Chief Office Superintendent |
M/o Railwa ys |
| 7. | Monirul Islam |
SI | CRPF |
| 8. | Rajendra Singh |
L/Nk | BSF |
| 9. | Surender Singh |
SI | CRPF |
| 10. | Consonti na Lakra |
ASI/NA | CRPF |

Group Photograph with Anubhav Awardees
Workshop on National Anubhav Awards, 2025
Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare, organized a workshop on National Anubhav Awards Scheme, 2025 for the Anubhav Nodal Officers of various Ministries/Departments, including 12 Public Sector Banks and Central Public Sector Enterprises, on 23rd January, 2025, under the chairmanship of Secretary (Pension). An overview of the National Anubhav Awards Scheme, 2025 was discussed along with inclusivity and customized marking system of the Scheme. In the workshop, Nodal Officers benefited from the experiences of the eminent Speakers and discussed best practices on National Anubhav awards
Scheme, 2025. DoPPW urged the Nodal officers to adopt all possible means to encourage the retiring employees for submission of their write-ups on Anubhav portal.
Nationwide “Anubhav Awardees Speak” Webinar Series
The webinar series aims to facilitate experience sharing with relevant stakeholders and concerned Ministries/ Departments/Organizations. The webinar series generally features Anubhav Awardees as speakers to share their experience and to motivate/raise awareness among retiring employees on filling up their own experiences on the Anubhav Portal. It is envisaged that this culture of leaving notes by retirees will become the foundation stone of good governance and administrative reforms in future. The inaugural webinar was held on 22.11.2022.
The series completed its 21st edition in February, 2025 and total 32 speakers from 15 different Ministries/ Departments/ Organizations have participated in the series so far. It has been well received by the audiences and retiring employees join the webinar series from more than 500 locations spread across the country.
28.6.6 Pre-Retirement Counselling (PRC) Delhi & Jammu
$52^{\text {nd }}$ PRC Workshop was conducted at DAIC, Janpath, New Delhi on 20th December, 2023 to empower the retiring employees with crucial insights into various aspects of their transition, including topics like Bhavishya Portal, CGHS Rules, Income Tax Rules, Investments Avenues, etc.

300 Participated at $53^{\text {rd }}$ PRC Workshop held at Ahmedabad on $05^{\text {th }}$ March, 2024 under the forward-thinking initiative ‘Sankalp’ for providing invaluable support to retiring employees, wherein sessions on various topics relevant to them viz Bhavishya Portal, Submission of DLC, Investment Opportunities, CGHS Rules, Income Tax Rules, Investments avenues etc.

In $54^{\text {th }}$ PRC workshop, 300 participated at Jammu under the auspice presence of Honorable MOS(PP) on $19^{\text {th }}$ July, 2024.
In $55^{\text {th }}$ PRC workshop, 1200 retiring participated at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi on $28^{\text {th }}$ August, 2024.
28.6.8 Bankers’ \& Pensioners Awareness
Bankers’ Awareness Program Series
Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare has started a series of Awareness Program for Central Pension Processing Centres and field functionaries handling pension related work in the banks. In these awareness programs, a team of officers from DoPPW take sessions on Pension policy reforms \& digitization regarding disbursement of pension to Central Government pensioners, with the objective of updating the field functionaries of the Banks. Special sessions are organized on Income Tax matters related to pensioners as well as Digital means of submitting the Annual Life Certificates. Representatives from CPAO also attend the program to share the reasons leading to pensioners’ grievances and suggest actions which may be taken by the bank for redressal.
Seven such Awareness Programs have been held so far for filed functionaries of various Banks, viz. State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Canara Bank, Bank of Baroda. The Bankers’ Awareness programme was held on 18-03-2025 at Jaipur.
28.6.7 Pensioners’ Awareness Program:
Department of Pension and Pensioners’ Welfare conducted Pensioners’ Awareness Program at Puducherry on 28th June, 2022. This is the first physical Awareness program post pandemic covering the Southern region
of country. The program was attended by more than 300 pensioners from Chennai and Puducherry in collaboration with Pensioners’ Associations from Chennai and Puducherry. A team of officers from DoP&PW took sessions on Pension policy reforms \& digitization regarding pension/family pension sanction to Central Government pensioners, with the objective of updating the pensioners of the changes made under the “Ease of Living” initiative of the Government. Special sessions were organized on Income Tax matters related to pensioners as well as Digital means of submitting the Annual Life Certificates. The objective of these programs is to spread awareness of the various rules and procedures regarding pension entitlements and processes to Central Government pensioners as well as to update the pensioners about the changes that take place from time to time through various amendments in the policy and procedures. Such programs also serve as a feedback mechanism of pension policy from pensioners. Chief Controller (Pensions), CPAO, MoF also addressed the pensioners providing information about the common grievances faced by pensioners, their modes of redressal as well as new initiatives taken by CPAO to enhance ‘Ease of Living’ of pensioners. A representative from CGHS also addressed the participants and provided information on the queries raised by pensioners.
Similar interactive meetings and Awareness Programs for pensioners were also held at Pune in May, 2023 and at Bengaluru in November, 2023. In addition, online interactive meetings are also held with Pensioners’ Welfare Associations on monthly basis to apprise them of updated rules and take note of their queries,
grievances and suggestions. The Pensioners’ Awareness programme was held on 18-03205 at Jaipur
28.6.8 Social Media Outreach
Providing access to information is an important tool to empower the people, therefore, DoPPW has adopted a policy of spreading awareness amongst the targeted groups on instructions issued time to time and entitlements through workshop and various available medium such as electronic, print and social media. Since Social Media has emerged as a powerful participatory medium of communication in recent times, therefore, DoPPW has adopted a gradual shift towards spreading awareness amongst the targeted groups through social media such as Facebook, Twitter and Documentary films, YouTube etc. The Department has also been creating awareness through SMSs which are sent directly on the Mobile Phone of pensioners. This has resulted in creating greater awareness in the targeted group at minimal costs.
| Number of Tweets on 3483 |
Number of Impressions on Twitter 4,41,842 |
|---|---|
| Number of posts 821 |
Number of reach on Facebook 46,392 |

| S.no | DD/MM/YY | Name of video | No. of Video s |
Views |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | June 27, 2024 | Film on Nationwide DLC Campaign 2.0 | 1 | 591 |
| 3 | August 30, 2024 | Anubhav Award movie, 2024 | 1 | 2730 |
| 4 | Oct 22, 2024 | SOP on DLC using Face Authentication Technique |
2 | 212331 |
| 5. | Oct 29, 2024 | Panel discussion on National DLC Campaign 3.0 |
1 | 3196 |
| 6. | Nov 1, 2024 | Panel discussion with Secretary (Pension), CEO, UIDAI & CGDA DLC Campaign 3.0 on Sansad TV |
1 | 2774 |
| 7 | Nov 10, 2024 | Film on Nationwide Digital Life Certificate Campaign 3.0 |
1 | 644 |
| Total | 7 | $2,22,266$ |
Total no. of Subscribers – 60091. The number of subscribers are increased by 8138 in year 2024-25.
- हंदk संघ क३ राजभाषा होने के कारण फस एवं पAशनभोगी कायाण fवभाग सरकारk क्कर म fहंदk के मेगामी मेयोग को बढ़ावा देने के fलए सfछ्य छप से भूसका fनभा रहा है। पAशन एवं पAशनभोगी कायाण fवभाग का राजभाषा अनुभाग fहंदk अनुवाद का काय[ करने के साथसाथ राजभाषा नी।त तथा राजभाषा अfघfनयम के काया[0वयन संबंधी काय[ देखता है। fवभाग के सभी अनुभाग] म राजभाषा नी।त के काया[0वयन क३ जिंध।त क३ fनगरानी के fलए fवभाग म राजभाषा काया[0वयन सfम।त का गठन fकया गया है। राजभाषा नी।त के काया[0वयन क३ जिंध।त क३ fनगरानी के fलए fवभागा0यद क३ अ0यदता म मेयके fतमाहk म।नयfमत छप से बैठक आयोजिजत क३ जाती है और बैठक म fलए गए fनण[य] पर क३ गई काय[वाहk, fवभाग के सभी अनुभाग] से मेग।त fतमाहk मेग।त lरपोट[ क३ समीद्ा क३ जाती है तथा सरकारk कामकाज म fहंदk के मेयोग को बढ़ाने क३ fदशा म मेयास करने हेतु माग[दश[न fकया जाता है।
- मेयम राजभाषा क३।त[ पुरक्कार : राजभाषा fवभाग, गृह मंह।लय, भारत सरकार दवारा आयोजित आखल भारतीय राजभाषा संक्षेमेलन] म पAशन fवभाग को 300 से कम कर।म[क वाले मंह।लय/ fवभाग क३ |णी म दो बारfवष[ 2023 और वष[ 2024) मेयम राजभाषा क३।त[ पुरक्कार शीश्र मेदान क३ गई। मंह।लय क३ fहंदk सलाहकार सfम।त क३ ।वीं बैठक म माननीय रांयमंहो डॉ. जिजतA3 fसंह जी ने fवभाग क३ सरहना क३।

- हिंदी पद्यवादी का आयोजन :
गृह मंहृ:ालय राजभाषा ।वभाग दवारा समय-समय पर जारः ।कए गए आदेश)/अनुदेश) के ग राजभाषा ।हंदड के मेगामी मेयोग को बढ़ावा देने के ।लए ।दनांक 01.09.2024 से 15.09.2024 तक ।हंदड पद्यवाड़ा मनाया गया िजसम^ पंच मे।तयो।गताय^ आयोजित क३ गई। लगभग 60 अ।धकारय)/कम(चारय) ने उ×साहपूव(क भाग ।लया। ।दनांक 19 ।सतंबर, 2024 को सीएसओआई, चाणा(यपुरः, नई ।दालः ग आयोजित पुरहेकार ।वतरण समारोह गक।म(क, लोक ।शकायत तथा प^शन मंहृःालय क३ ।हंदड सलाहकार स।म।त के गैर-सरकारड सदरुय डॉ अंजनी कुमार ]ीवाहतव को मुद्दिय अ।त।थ के द्रप ग आमं।हृत ।कया गया तथा स।घव प^शन महोदय दवारा मेडल, मेमाणपड और नकद पुरहेकार मेदान ।कए गए। ।वभाग के का।म(क) दवारा स्वर।चत क।वताओं क३ संकलन पिि:हतका “सोपान” का भी ।वमोचन ।कया गया।

- डॉ. जिजत^5 ।संह, माननीय रांयमंह्ी के त×वावधान ग ।वभाग दवारा आयोजित ।व।भUन अ।भयान) जैसे अनुभव पुरहेकार समारोह 2024, रा§ंडयापी ।डिजटल जीवन मेमाणपड अ।भयान 3.0, स्वांछता अ।भयान 3.0, अनुभव अवाड@ स्पीक ]्खला, एकल सरलःकृत पछान आवेदन मेद्रप
6-क और ई-एचआरएमएस के साथ भ।वदृय का ।डिजटल एक३करण, रा§ंडय का मेगालः पर
काय(शालाओं, सेवा।नवृ।a-पूव( परामश(पीआरसी) काय(शालाओं, जस अदालत) का मसाहायक ।नदेशक(रा.भा.) दवारा ।हंदड ग।कया गया। सभी संबंधित हटहै, ।नमंहण-पह, ।मनटवार काय(छम और मेैस ।रलःज द।वभाषी तैयार ।कए गए तथा दूरदश(न, स्थानीय अखबार), ऽवीटर, फैसबुक और युऽयूब के माUयम) से द।वभाषी द्रप ग।चार-।सार ।कया गया।
- स।घव, का क३ अUयदता ग समय-समय पर बहक), प^शनभोगी संघ) तथा ।व।भUन मंहृःालय)/।वभाग) के नोडल अ।धकारय) के साथ क३ गई बैठक) से संबंधित सामरंी, युऽयूब पोहेट और ड द।वभाषी जारः ।कए गए।
वष 2024-25 के दौरान हिंदी: माक्रणणणणकाशन

कामिक, लोक सिकायत तथा पेंशन मंत्रालय भारत सरकार
अगले 100 दिन के लिए कार्य योजना
पेंशन एवं पेंशनभोगी कल्याण विभाग
कामिक, लोक सिकायत तथा पेंशन मंत्रालय भारत सरकार
कामिक, लोक सिकायत तथा पेंशन मंत्रालय भारत सरकार
Annexures
Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances
ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE OF DEPARTMENT OF ADMINISTRATIVE REFORMS AND PUBLIC GRIEVANCES
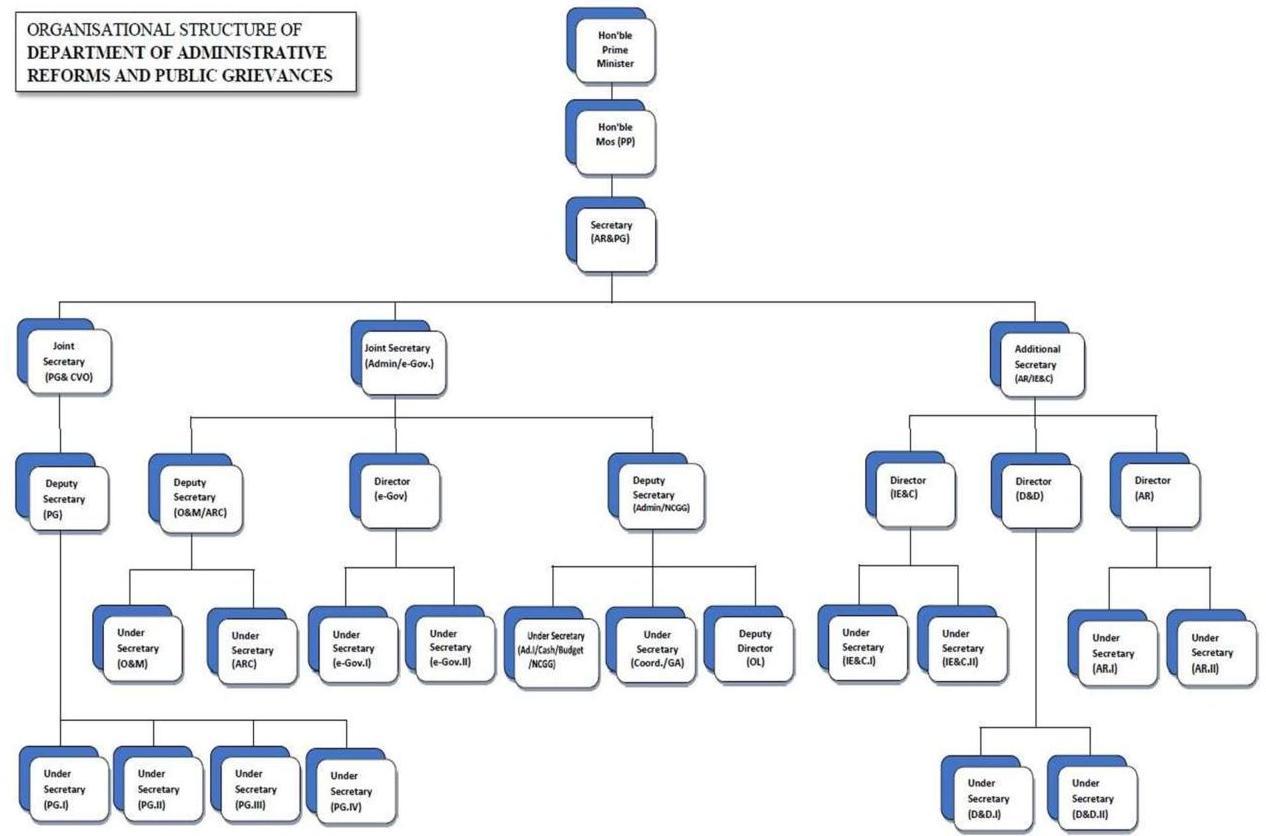
Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances
Incumbency position of Under Secretary and above level officers in D/o ARPG as on 31.01.2025
| Post | Name of Incumbent |
|---|---|
| Secretary | 1. Shri V. Srinivas |
| Additional Secretary | 1. Shri Puneet Yadav |
| Joint Secretary | 1. Ms. Jaya Dubey |
| 2. Smt. Sarita Chauhan | |
| Director | 1. Shri Suvasish Das |
| 2. Shri Rohit Anand | |
| 3. Shri Sardendu Kumar Pandey 4. Shri Tushaba Shinde |
|
| Principal Staff Officer | 1. Shri M.P. Varadhrajan |
| Deputy Secretary | 1. Smt. Sarita Taneja |
| 2. Shri Hari Krishan Bhatt | |
| 3. Shri Parthasarathy Bhaskar Devarakonda | |
| Under Secretary | 1. Shri Udham Singh |
| 2. Shri Rakesh Chandra | |
| 3. Shri R. Rajasekharan | |
| 4. Shri Sunil Kumar Singh | |
| 5. Shri K. Khatminthang | |
| 6. Shri Santosh Kumar | |
| 7. Smt. Anupma Kumari | |
| 8. Shri Kamal Kumar Thakur | |
| 9. Shri Prashant Pandey | |
| 10. Shri Dharam Pal Arora | |
| 11. Smt. Sanjeeta Chatterjee | |
| 12. Shri Lakshmi Chandra | |
| 13. Smt. Vandana Nangia | |
| 14. Shri D.D. Nimje |
| 15. Smt. Preeti Singh Shishodia | |
|---|---|
| 16. Shri Satish Kumar | |
| Deputy Director (OL) | 1. Shri Rakesh Kumar |
| Principal Private Secretary | 1. Shri Sudhir |
| 2. Smt. Ranjana Malik | |
| 3. Smt. Alka Ahuja | |
| 4. Shri D.S. Bisht |
Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women in Workplace
An Internal Complaints Committee has been constituted in the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances for the prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women in the Workplace. It has been constituted with the following:
- Ms. Jaya Dubey, Joint Secretary – Chairperson
- Shri Sanjeev Srivastava, DS – Member
- Ms. Sarita Taneja, DS – Member
- Dr. Sonajharia Minz, YWCA – NGO member
- Smt. Sanjeeta Chatterjee, US – Member Secretary
Women employees are being made aware of the existence of the said Committee from time to time through circulars, display on Notice Boards, and interactions. In this connection, Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances convened a workshop on 09.12.2024 as part of the ‘Sexual Harassment at Workplace Prevention Week’. Shri Rajinder Tuteja, District and Sessions Judge, Dausa, Rajasthan was invited as a lead speaker. He delivered a lecture on “Prevention of Sexual Harassment at Workplace” and elaborated on the provisions of the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition & Redressal) Act, 2013.

Observance of Constitution Day 2024
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) organized a webinar to commemorate Constitution Day (26th Nov’24), marking the adoption of the Constitution of India on November 26, 1949 and to raise awareness about its values and guiding principles. The Secretary, DARPG administered the reading of the Preamble to all officials. The celebration began with introductory remarks by the Secretary (DARPG), followed by a Constitution Day Webinar. The webinar featured two esteemed speakers, Dr. C.K. Mathew, former Chief Secretary, Rajasthan and Shri Apurva Chandra, former Health Secretary who deliberated on the topic “A civil Servant’s Reflection of the Constitution” and “Healthcare for All” respectively. Distinguished Speakers remarked on ongoing Government efforts to uphold the constitutional vision of justice, equality, and dignity for every citizen.
More than 1000 officials of Central Ministries and State Governments including all officials of DARPG, DoPPW and NCGG attended the webinar. In concluding the webinar, participants reaffirmed their dedication to upholding the principles enshrined in the Constitution. This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to promote awareness about the Constitution and its values. The celebration of Constitution Day was also disseminated through PIB Statement and on twitter handle of DARPG.

Observance of Vigilance Awareness Week 2024
The DARPG has observed #Vigilance AwarenessWeek from 28th Oct to 3rd Nov 2024 with the theme: “सWिन ा की संृित से (D) की समृि5”; “Culture of Integrity for Nation’s Prosperity.” Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG, administered the Integrity Pledge to all officials of the Department.

International Women’s Day 2025 commemoration at DARPG
The Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) organized a virtual round-table webinar on March 6, 2025 on the theme “नारी शि4 से िवकिसत भारत” to commemorate the International Women’s Day 2025, celebrating the invaluable contributions of women and highlighting the ongoing efforts towards achieving gender equality and women’s empowerment in India.
2. Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary, DARPG, made the welcome address and emphasized empowering the next generation-young women and adolescent girls-who will be the driving force of transformative change. He stressed that the idea of an empowered India by 2047 cannot be realized without harnessing the full potential of women and in this journey, every individual and every woman matters.

3. Smt. Sumita Dawra, Secretary, MoL&E emphasized the pivotal role of women in Civil Services post-independence, highlighting legislative reforms like maternity and childcare leave that support their dual roles in nation-building and family life. She emphasized the importance of workplace safety, equitable policies, and strong compliance mechanisms to promote gender equity. Smt. Vandita Kaul, Secretary, DoP, highlighted the gender gap in unpaid care work and the empowering role of schemes like Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana. She elaborated women’s contributions in government and shared her personal challenges to inspire more women in Civil Services.
4. During the webinar, IAS officers Ms. Varnali Deka, Harichandana Dasari, Keerthi Jalli, and Tina Dabi shared their administrative efforts towards women’s empowerment. Smt. Snehlata Shrivastava and Smt. Rita Menon also reflected on their experiences as women civil servants. This virtual webinar was attended by more than 250 officers of Government of India and State Governments. The event provided a platform for thoughtful discussion and exchange on critical issues surrounding women’s empowerment in India.
Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances
Welfare of SC, ST, OBC and Persons with Disability (PWD)
As on 31.01.2025, the incumbency position of SC, ST, OBC and Persons with Disability (PwD) in the Group ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ category of officials of Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances is as under:
| Category | Total | SC | ST | OBC | PwBD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group-A | $\mathbf{3 3}$ | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Group-B | $\mathbf{3 2}$ | 5 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| Group-C | $\mathbf{8}$ | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| Total | $\mathbf{7 3}$ | 12 | 3 | 14 | 3 |
The Department has appointed Nodal Officers to look into the complaints/ representations, if any, received from SC, ST & OBC officials and as also to watch their welfare.
Annexure – XIV
Organisational Chart of Department of Pension & Pensioner’s Welfare
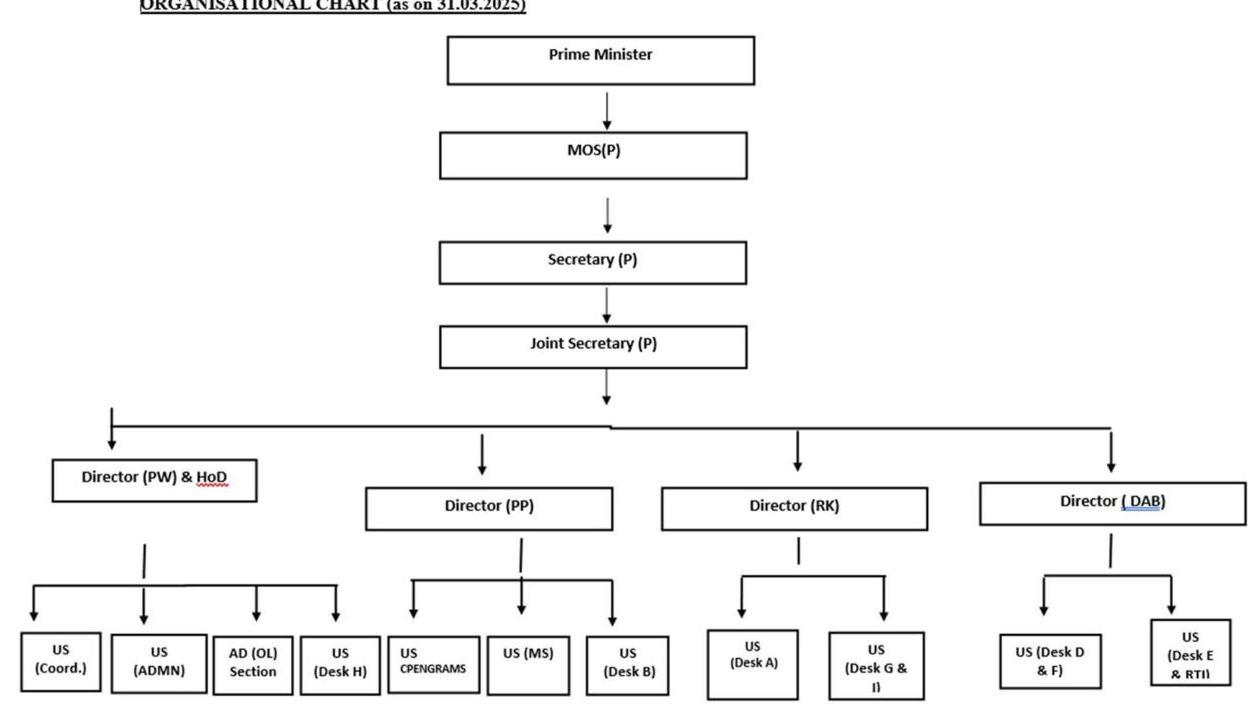
Incumbency position of Officers in D/o Pension & Pensioner’s Welfare as on 31/03/2025
| Post | Name of the incumbent |
|---|---|
| Secretary | Shri V. Srinivas |
| Joint Secretary | Shri Dhrubajyoti Sengupta |
| Director | Shri Pramod Kumar Ms Divya Shri Ravikiran Ubale Shri Rakesh Kumar |
| Under Secretary | Shri S. Chakrabarti Ms. Sonika Khattar Shri Subhash Chander Ms. Meenakshi Shankar Shri Deepak Gupta Shri Dilip Kumar Sahu Ms. Madhu Mankotia Shri Pravesh Kumr Shri Nagender Kumar Md. Ansari |
| Deputy Director (OL) | Ms Manju Gupta |
| Section Officers | Shri Hemant Ms Deborah Umesh Shri Andrew Zomawia Karthak Shri Akhlesh Mann Shri Syed Mohd. Danish Rizvi Ms. Amandeep Kaur Ms. Neelam Meena Shri Ravi Prakash Meena |
.

Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions Government of India
Printed by the Manager, Government of India Press, Minto Road, New Delhi-110002
- Conduct of Cyber Awareness Programme in DoP\&T on 11.12.2024 ↩